Summary
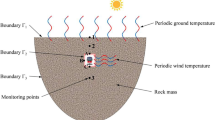
A geothermal and meteorological observation was carried out inside a hot tunnel (named Torigoe tunnel) penetrating through a volcanic zone in northeastern Japan, just after it has been penetrated. Rock wall surface temperature, some thermal properties of rock samples, temperature profile in slender pits drilled into the rock body, temperature of water flowing on the floor and the meteorological elements of air passing through the tunnel are contained in the observation.
Introducing the coefficient of heat transfer determined from the Reynolds analogy for turbulent forced convection in a circular tube, the heat budget of the air-tunnel system is investigated with those observed data. The results show that the net sensible heat of 58.61 kW is drawn out from the tunnel by air passing through it and seems to be overcompensated by the net heat supply of 67.21 kW from the rock wall to air, while for the net latent heat removal of 101.56 kW by air the apparent undercompensation of 80.01 kW is found from the water flowing on the floor. Consideration is carried out on such excess and deficiency of heat supplies.
Zusammenfassung
In einem heißen Tunnel (dem Torigoe-Tunnel), der durch vulkanisches Gebiet im nordöstlichen Japan verläuft, wurden unmittelbar nach Tunneldurchstoß geothermische und meteorologische Untersuchungen durchgeführt. Die Temperatur der Gesteinsoberfläche, spezifische thermische Eigenschaften der Gesteinsproben, das Temperaturprofil von dünnen Bohrkernen, als auch die Temperatur des Wassers am Tunnelgrund und meteorologische Daten der Durchzugsluft werden in dieser Untersuchung berücksichtigt.
Durch Einführung des durch die Reynolds-Analogie determinierten Wärmeaustauschkoeffizienten für turbulente, erzwungene Konvektion in einer kreisförmigen Röhre wird der Wärmehaushalt der Luft im Tunnelsystem unter Heranziehung der angeführten Daten untersucht. Die Resultate zeigen, daß 58.61 kW fühlbare Wärme dem Tunnel durch die Luft entzogen werden, die jedoch durch eine Zufuhr von 67.21 kW von der Felswand an die Luft abgegebener fühlbarer Wärme überkompensiert zu werden scheint, während der dauernden latenten Wärmeabfuhr durch die Luft von 101.56 kW eine Unterkompensierung von 80.01 kW durch das am Tunnelgrund fließende Wasser gegenübersteht. Die Folgen dieses Überschusses bzw. Defizites werden genauer diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budyko, M. I., 1956:Heat Balance of Earth's Surface. Leningrad: Hydrometeorological Press.
Holman, J. P., 1981:Heat Transfer. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Saito, T., Ito, Y., Sekioka, M., 1978: The heat discharge in Shinkurosan waterway tunnel. Studies on the hot dry rock, Kyushu University, 1–16, in Japanese with English abstract.
Sekioka, M., 1980: Unsystematic estimate of heat stored in hot rocks.Journ. Geoth. Resear. Soc. Japan 2, 71–79, in Japanese with English abstract.
Sekioka, M., Yuhara, K., Ito, Y., Saito, T., Goto, H., 1984: A geothermal measurement of the Shizukuishi no. 2 tunnel (a hot tunnel) and consideration on heat budget of fluid passing through the tunnel.Journ. Geoth. Resear. Soc. Japan 6, 279–291, in Japanese with English abstract.
Yuhara, K., 1981: Heat discharge from the Kurobe-Sennindani dry hot rock, Toyama Prefecture, Japan.Bull. Geol. Surv. Japan 32, 227–239, in Japanese with English abstract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 5 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekioka, M., Ito, Y., Ehara, S. et al. Heat budget of air passing through a hot tunnel in northeastern Japan. Theor Appl Climatol 38, 1–7 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00866247
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00866247