Abstract
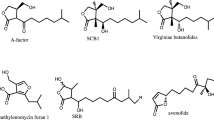
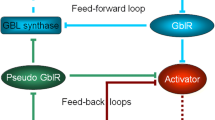
Accumulating data have shown that the metabolites with a γ-butyrolactone ring functions as an autoregulatory factor or a microbial hormone for the expression of various phenotypes not only in a variety ofStreptomyces spp. but also in the distantly related bacteria. A-factor, as a representative of this type of autoregulators, triggers streptomycin biosynthesis and cellular differentiation inStreptomyces griseus. A model for the A-factor regulatory cascade on the basis of recent work is as follows. At an early step in the A-factor regulatory relay, the positive A-factor signal is first received by an A-factor receptor protein that is comparable in every aspect to eukaryotic hormone receptors, and then, via one or more regulatory steps, transmitted to an A-factor-responsive protein that binds to the upstream activation sequence of thestrR gene, a regulatory gene in the streptomycin biosynthetic gene cluster. The StrR protein thus induced appears to activate the other streptomycin biosynthetic genes. This review summarizes the characteristics of A-factor as a microbial hormone and the A-factor regulatory relay leading to streptomycin production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamidis T & Champness W (1992) Genetic analysis ofabsB, aStreptomyces coelicolor locus involved in global antibiotic regulation. J Bacteriol 174: 4622–4628
Adamidis T, Riggle P & Champness W (1990) Mutations in a newStreptomyces coelicolor locus which globally block antibiotic synthesis but not sporulation. J Bacteriol 172: 2962–2969
Anisova LN, Blinova IN, Efremenkova OV, Koz'min YP, Onoprienko VV, Smirnova GM & Khokhlov AS (1984) Development regulators inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Biol Bull Acad Sci USSR 11: 75–84
Beppu T (1992) Secondary metabolites as chemical signals for cellular differentiation. Gene 115: 159–165
Chater KF (1989) Sporulation inStreptomyces. In: Smith I, Slepecky RA & Setlow P (Eds) Regulation of Procaryotic Development: Structural and Functional Analysis of Bacterial Sporulation and Germination. (pp 277–299). American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Chatterjee S, Vijayakumar EKS, Franco CMM, Borde UP, Blumbach J & Ganguli BN (1991) Butalactin: a new butanolide antibiotic fromStreptomyces corchorusii. Tetrahedron Lett 32: 141–144
Distler J, Ebert A, Mansouri K, Pissowotzki K, Stockmann M & Piepersberg W (1987) Gene cluster for streptomycin biosynthesis inStreptomyces griseus: nucleotide sequence of three genes and analysis of transcriptional activity. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 8041–8056
Distler J, Mansouri K, Mayer G, Stockmann M & Piepersberg W (1992) Streptomycin biosynthesis and its regulation in streptomycetes. Gene 115: 105–111
Eberhard A, Burlingame AL, Eberhard C, Kenyon GL, Nealson KH & Oppenheimer NJ (1981) Structural identification of autoinducer ofPhotobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry 20: 2444–2449
Eberhard A, Widrig CA, McBath P & Schineller JB (1986) Analogs of the autoinducer of bioluminescence inVibrio fischeri. Arch Microbiol 146: 35–40
Fernandez-Moreno MA, Martin-Triana AJ, Martinez E, Niemi J, Kieser HM, Hopwood DA & Malpartida F (1992)abaA, a new pleiotropic regulatory locus for antibiotic production inStreptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 174: 2958–2967
Franco CMM, Borde UP, Vijayakumar EKS, Chatterjee S, Blumbach J & Ganguli BN (1991) Butalactin, a new butanolide antibiotic. Taxonomy, fermentation isolation and biological activity. J Antibiot 44: 225–231
Gräfe U, Eritt I, Hänel F, Friedrich W, Roth M, Röder B & Bormann EJ (1986) Factors governing polyketide and glycopeptide productions by streptomycetes. In: Kleinkauf H, van Döhren H, Dornauer H & Nesemann G (Eds) Regulation of Secondary Metabolite Formation. (pp 225–248). VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Weinheim, FRG
Gräfe U, Reinhardt G, Schade W, Eritt I, Freck WF & Radics L (1983) Interspecific inducers of cytodifferentiation and anthracycline biosynthesis fromStreptomyces bikiniensis andS. cyaneofuscatus. Biotechnol Lett 5: 591–596
Gräfe U, Schade W, Eritt I, Freck WF & Radics L (1982) A new inducer of anthracycline biosynthesis fromStreptomyces viridochromogenes. J Antibiot 35: 1722–1723
Hara O & Beppu T (1982a) Mutants blocked in streptomycin production inStreptomyces griseus — the role of A-factor. J Antibiot 35: 349–358
Hara O & Beppu T (1982b) Induction of streptomycin inactivating enzyme by A-factor inStreptomyces griseus. J Antibiot 35: 1208–1215
Hara O, Horinouchi S, Uozumi T & Beppu T (1983) Genetic analysis of A-factor synthesis inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2) andStreptomyces griseus. J Gen Microbiol 129: 2939–2944
Hong S-K, Kito M, Beppu T & Horinouchi S (1991) Phosphorylation of the AfsR product, a global regulatory protein for secondary-metabolite formation inStreptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 173: 2311–2318
Horinouchi S & Beppu T (1990) Autoregulatory factors of secondary metabolism and morphogenesis in actinomycetes. Crit Rev Biotechnol 10: 191–204
Horinouchi S & Beppu T (1992a) Autoregulatory factors and communication in actinomycetes. Annu Rev Microbiol 46: 377–398
Horinouchi S & Beppu T (1992b) Regulation of secondary metabolism and cell differentiation inStreptomyces: A-factor as a microbial hormone and the AfsR protein as a component of a two-component regulatory system. Gene 115: 167–172
Horinouchi S, Hara O & Beppu T (1984) Unstable genetic determinant of A-factor biosynthesis in streptomycin-producing organisms: cloning and characterization. J Bacteriol 158: 481–487
Horinouchi S, Nishiyama M, Suzuki H, Kumada Y & Beppu T (1985) The clonedStreptomyces bikiniensis A-factor determinant. J Antibiot 38: 636–641
Ishizuka H, Horinouchi S, Kieser HM, Hopwood DA & Beppu T (1992) A putative two-component regulatory system involved in secondary metabolism inStreptomyces spp. J Bacteriol 174: 7585–7594
Khokhlov AS (1982) Low molecular weight microbial bioregulators of secondary metabolism. In: Krumphanzl V, Sikyta B & Vanek Z (Eds) Overproduction of Microbial Products. (pp 97–109). Academic Press, London
Khokhlov AS, Anisova LN, Tovarova II, Kleiner EY, Kovalenko IV, Krasilnikova OI, Kornitskaya EY & Pliner SA (1973) Effect of A-factor on the growth of asporogenous mutants ofStreptomyces griseus, not producing this factor. Z Allg Mikrobiol 13: 647–655
Khokhlov AS, Tovarova II, Borisova LN, Pliner SA, Schevchenko LA, Kornitskaya EY, Ivkina NS & Rapoport IA (1967) A-factor responsible for the biosynthesis of streptomycin by a mutant strain ofActinomyces streptomycini. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 177: 232–235
Kim HS, Nihira T, Tada H, Yanagimoto M & Yamada Y (1989) Identification of binding protein of virginiae butanolide C, an autoregulator in virginiamycin production fromStreptomyces virginiae. J Antibiot 42: 769–778
Kinashi H, Shimaji M & Sakai A (1987) Giant linear plasmids inStreptomyces which code for antibiotic biosynthetic genes. Nature 328: 454–456
Koo H-S, Wu H-M & Crothers KM (1986) DNA bending at adenine thymine tracts. Nature 320: 501–506
Mansouri K, Pissowotzki K, Distler J, Mayer G, Braun C, Ebert A & Piepersberg W (1989) Genetics of streptomycin production. In: Hershberger CL, Queener SW & Hegeman G (Eds) Genetics and Molecular Biology of Industrial Microorganisms. (pp 61–67). American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Miyake K, Horinouchi S, Yoshida M, Chiba N, Mori K, Nogawa N, Morikawa N & Beppu T (1989) Detection and properties of A-factor-binding protein fromStreptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol 171: 7298–7302
Miyake K, Kuzuyama T, Horinouchi S & Beppu T (1990) The A-factor-binding protein ofStreptomyces griseus negatively controls streptomycin production and sporulation. J Bacteriol 172: 3003–3008
Mizuno T (1987) Static bend of DNA helix at the activator recognition site of theompF promoter inEscherichia coli. Gene 54: 57–64
Mori K & Yamane K (1982) Synthesis of optically active forms of A-factor, the inducer of streptomycin biosynthesis in inactive mutants ofStreptomyces griseus. Tetrahedron 38: 2919–2921
Nihira T, Shimizu Y, Kim HS & Yamada Y (1988) Structure activity relationships of virginiae butanolide C, an inducer of virginiamycin production inStreptomyces virginiae. J Antibiot 41: 1828–1837
Ohkishi H, Miyasaka K, Horisaka T, Chou H & Watanabe Y (1988) Strain improvement of a nosiheptide producer,Streptomyces actuosus 40037. In: Fujiwara A (Ed) Proc. 3rd Franco-Japanese Symp. The Impact of Genetics on Industrial Microorganisms. (pp 47–49). Sansei-Do, Tokyo
Retzlaff L, Mayer G, Beyer S, Ahlert J, Verseck S, Distler J & Pierpersberg W (1993) Streptomycin production in streptomycetes: a progress report. In: Baltz RH, Hegeman GD & Skatrud PL (Eds) Industrial Microorganisms: Basic and Applied Molecular Genetics. (pp 183–194). American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Snyder M, Buchman AR & Davis RW (1986) Bent DNA at a yeast autonomously replicating sequence. Nature 324: 87–89
Ueda K, Miyake K, Horinouchi S & Beppu T (1993) A gene cluster involved in aerial mycelium formation inStreptomyces griseus encodes proteins similar to the response regulators of two-component regulatory systems and membrane translocators. J Bacteriol 175: 2006–2016
Vujaklija D, Horinouchi S & Beppu T (1993) Detection of an A-factor-responsive protein that binds to the upstream activation sequence ofstrR, a regulatory gene for streptomycin biosynthesis inStreptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol 175: 2652–2661
Vujaklija D, Ueda K, Hong S-K, Beppu T & Horinouchi S (1991) Identification of an A-factor-dependent promoter in the streptomycin biosynthetic gene cluster ofStreptomyces griseus. Mol Gen Genet 229: 119–128
Yamada Y, Sugamura K, Kondo K, Yanagimoto M & Okada H (1987) The structure of inducing factors for virginiamycin production inStreptomyces virginiae. J Antibiot 40: 496–504
Zhang L, Murphy PJ, Kerr A & Tate ME (1993)Agrobacterium conjugation and gene regulation byN-acyl-L-homoserine lactones. Nature 362: 446–448
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horinouchi, S., Beppu, T. A-factor and streptomycin biosynthesis inStreptomyces griseus . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 64, 177–186 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00873026
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00873026