Abstract
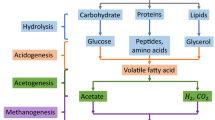
Thermal extraction was used to quantify extracellular polymers (ECP) in granules from anaerobic upflow reactors. The optimal time for extraction was determined as the time needed before the intracellular material gives a significant contribution to the extracted extracellular material due to cell lysis. ECP contents of 41 to 92 mg · g−1 volatile suspended solids of granules were found depending on the type of granular sludge examined. The content of polysaccharides, protein and lipids in the extracted ECP was quantified. Furthermore, the different methyl esters of the lipids were determined and quantified. Lower amounts of polysaccharides and proteins were found in the extracellular material from granules grown on methanogenic and acetogenic substrates compared to granules grown on more complex substrates. In contrast, the lipid content was lower on complex substrates. Changing the feed of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor from a sugar-containing waste-water to a synthetic waste-water containing acetate, propionate and butyrate resulted in a decrease in both the protein and polysaccharide content and an increase in the lipid content of the extracellular material. Furthermore, the amount of protein and polysaccharides in the ECP found under mesophilic conditions was significantly higher than under thermophilic conditions, while the lipid content was lower.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahring BK, Schmidt JE, Winther-Nielsen M, Macario AJL, Conway de Macario E (1993) Effect of medium composition and sludge removal on the production, composition, and architecture of thermophilic (55°C) acetate-utilizing granules from an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2538–2545
American Public Health, Association (1989) Standard methods for the examinatio4a,of water and wastewater, 17th edn. Washington, D.C.
Arneborg N, Salskov-Iversen AS, Mathiasen TE (1993) The effect of growth rate and other growth conditions on the lipid composition ofEscherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:353–357
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Brown MJ, Lester JN (1980) Comparison of bacterial extracellular polymers extraction methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 40:179–185
Bull MA, Steeritt RM, Lester JN (1983) Anaerobic fluidized bed reactors. Biotechnol Lett 5:333–338
Burton K (1956) A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J 62:315–323
Christopherson SW, Glass RL (1969) Preparation of milk fat methylester by alchololysis in an experimental non alcholic solution. J Dairy Sci 52:1289–1290
Costerton JW, Irving RT, Cheng KJ (1981) The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 35:299–324
Dolfing J, Griffioen A, Neerven ARW van, Zevenhuizen LPTM (1985) Chemical and bacteriological composition of granular methanogenic sludge. Can J Microbiol 31:744–750
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Forster CF (1971) Activated sludge surfaces in relation to the sludge volume index. Water Res 5:861–870
Forster CF (1992) Anaerobic upflow sludge blanket reactors: aspects of their microbiology and their chemistry. J Biotechnol 17:221–232
Gehr R, Henry JG (1983) Removal of extracellular material. Water Res 17:1743–1748
Grotenhuis JTC, Smit M, Lammeren AAM van, Status AJM, Zehnder AJB (1991) Localization and quantification of extracellular polymers in methanogenic granular sludge. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:115–119
Guiot SR, Lavoie L, Rocheleau S, MacLeod FA, Costerton JW (1991), Extracellular polymeric substances in anaerobic granules. In: (eds) Sixth international symposium on anaerobic digestion, São Paulo, Brazil, 12–16 May, 1991 (Poster Abstracts). IAWPRC, p 12
Harada H, Endo G, Tohya Y, Momonoi K (1988), High rate performance and its related characteristics of granulated sludges in UASB reactors treating various wastewaters. In: Tilche A, Rozzi A (eds) Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Anaerobic Digestion. Monduzzi editore, Bologna, pp 1011–1020
Kato A, Isaka K, Takahashi H (1971) Floc forming bacteria isolated from activated sludge. J Gen Appl Microbiol 17:439–456
Morgan JW, Forster CF, Evison L (1990) A comparative study of the nature of biopolymers extracted from anaerobic and activated sludges. Water Res 6:743–750
Morgan JW, Evison LM, Forster CF (1991) The internal architecture of anaerobic sludge granules. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 50:211–226
Nester EW, Roberts CE, Lidstrom ME, Pearsall NN, Nester MT (1983) Microbiology, 3rd edn. Holst-Sauders, Japan
Nishikawa S, Kuriyama M (1968) Nucleic acid as a component of mucilage in activated sludge. Water Res 2:811–812
Passore R, Eastwood MA (1986) Human nutrients and diathesis. Churchill Livingstone, London
Robinson RW, Akin DE, Nordstedt RA, Thomas MV, Aldrich HC (1984) Light and electron microscopic examinations of methane-producing biofilms from anaerobic fixed-bed reactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:127–136
Ross WR (1984) The phenomenon of sludge pelletisation in the anaerobic treatment of a maize processing waste. Water SA (Pretoria) 4:197–204
Sam-Soon PALNS, Loewenthal RE, Marais GvR (1987) Hypothesis for pelletisation in the upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor. Water S A (Pretoria) 13:69–80
Sandberg M, Ahring BK (1992) Anaerobic treatment of fish meal process waste-water in a UASB reactor at high pH. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:800–804
Schmidt JE, Ahring BK (1993a) Effects of magnesium on thermophilic acetate-degrading granules in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors. Enzyme Microb Technol 15:304–310
Schmidt JE, Ahring BK (1993b) Effects of hydrogen and formate on the degradation of propionate and butyrate in thermophilic granules from an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:2546–2551
Schmidt JE, Ahring BK (1994) Interspecies electron transfer of H2 and formate during degradation of propionate and butyrate in mesophilic UASB granules. Appl Environ Microbiol
Schmidt JE, Macario AJL, Ahring BK, Conway de Macario E (1992) Effect of magnesium on methanogenic subpopulations in a thermophilic acetate-degrading granular consortium. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:862–868
Shen CF, Kosaric N, Blaszczyk R (1993) The effect of selected heavy metals (Ni, Co and Fe) on anaerobic granules and their extracellular polymeric substance (ECP). Water Res 27:25–33
Wiegant WM (1986) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion for waste and wastewater treatment. Ph.D. thesis, Agricultural University of Wageningen, Wageningen
Zoutberg GR, Mulder R, Teixera de Mattos MJ, Neijssel OM (1988), Aggregate formation in anaerobic gaslift reactors. In: Lettinga G, Zehnder AJB, Grotenhuis JTC, Hulshoff Pol LW (eds) Granular anaerobic sludge; microbiology and technology. Puduc Wageningen, Wageningn, The Netherlands, pp 34–41
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, J.E.E., Ahring, B.K. Extracellular polymers in granular sludge from different upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42, 457–462 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00902757
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00902757