Abstract
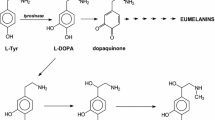
A modification of the tyrosine hydroxylase assay is described in which ascorbate, rather than 2-mercaptoethanol or dihydropteridine reductase with NADPH, is used as the reductant. Enzyme activity is 3–4 times higher with ascorbate than with the other reducing agents. Low blanks are obtained with the ascorbate system provided that catalase is also included. The tissue distribution and kinetic activation of the enzyme have been studied with the ascorbate assay. The results obtained are consistent with the biological and regulatory properties of the enzyme which have been determined with the other reducing systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lerner, P., Hartman, P., Ames, M. M., andLovenberg, W. 1977. The role of reductants in the tyrosine hydroxylase reaction.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 182,164–170.
Shiman, R., Akino, M., andKaufman, S. 1971. Solubilization and partial purification of tyrosine hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla.J. Biol. Chem. 246,1330–1340.
Shiman, R., andKaufman, S. 1970. Tyrosine hydroxylase (bovine adrenal glands). Pages 609–615,in Tabor, H., andTabor, C. W. (eds.), Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 17A, Academic Press, New York.
Nagatsu, T., Levitt, M., andUdenfriend, S. 1964. A rapid and simple radioassay for tyrosine hydroxylase activity.Anal. Biochem. 9,122–126.
Petrack, B., Sheppy, F., andFetzer, V. 1968. Studies on tyrosine hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla.J. Biol. Chem. 243,743–748.
Glowinski, J., andIversen, L. 1966. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]-norepinephrine, [3H]-dopamine and [3H]-DOPA in various regions of the brain.J. Neurochem. 13,655–662.
Cicero, T. J., Sharpe, L. G., Robins, E., andGrote, S. S. 1972. Regional distribution of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain.J. Neurochem. 19,2241–2243.
Lovenberg, W., Bruckwick, E. A., andHanbauer, I. 1975. ATP, cyclic AMP, and magnesium increase the affinity of rat striatal tyrosine hydroxylase for its cofactor.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72,2955–2958.
Nielsen, K. H., Simonsen, V., andLind, K. E. 1969. Dihydropteridine reductase: A method for the measurement of activity, and investigations of the specificity for NADH and NADPH.Eur. J. Biochem. 9,497–502.
Kaufman, S. 1962. Phenylalanine hydroxylase. Pages 809–816,in Colowick, S. P., andKaplan, N. O. (eds.), Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 5, Academic Press, London.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., andRandall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193,265–275.
Brenneman, A. R., andKaufman, S. 1964. The role of tetrahydropteridines in the enzymatic conversion of tyrosine to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 17,177–183.
Lovenberg, W., Walker, M. N., andBaumgarten, H. G. 1976. Clorinated amphetamines: Drugs or toxins.Monogr. Neural Sci. 3,109–114.
Pickel, V. M., Joh, T. H., Field, P. M., Becker, C. G., andReis, D. J. 1975. Cellular localization of tyrosine hydroxylase by immunohistochemistry.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 23,1–8.
Pickel, V. M., Joh, T. H., andReis, D. J. 1975. Ultrastructural localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in noradrenergic neurons of brain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72,659–664.
Fuxe, K., Hökfelt, T., Agnati, L. F., Johansson, O., Goldstein, M., Perez de la Mora, M., Posanni, L., Tapia, T., Teran, L. andPalacios, R. 1978. Mapping out central catecholamine neurons: Immunohistochemical studies on catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes. Pages 67–94,in Lipton, M. A., DiMascio, A., andKilliam, K. F. (eds.), Psychopharmacology: A Generation of Progress, Raven Press, New York.
Lovenberg, W., andBruckwick, E. A. 1975. Mechanisms of receptor mediated regulation of catecholamine synthesis in brain. Pages 149–169,in Usdin, E., andBunney, W. E., Jr. (eds.), Pre- and Postsynaptic Receptors. Marcel Dekker, New York.
Lerner, P., Ames, M. M., andLovenberg, W. 1977. The effect of ethylene glycol bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N′,N′-tetraacetic acid and calcium on tyrosine hydroxylase activity.Mol. Pharmacol. 13,44–49.
Lloyd, T., andKaufman, S. 1974. The stimulation of partially purified bovine caudate tyrosine hydroxylase by phosphatidyl-l-serine.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 59,1262–1269.
Raese, J., Patrick, R. L., andBarchas, J. D. 1976. Phospholipid-induced activation of tyrosine hydroxylase from rat brain striatal synaptosomes.Biochem. Pharmacol. 25,2245–2250.
Harris, J. E., Baldessarini, R. J., Morgenroth, V. H., III, andRoth, R. H. 1975. Activation by cyclic 3′∶5′-adenosine monophosphate of tyrosine hydroxylase in the rat brain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72,789–793.
Lloyd, T., andKaufman, S. 1975. Evidence for the lack of direct phosphorylation of bovine caudate tyrosine hydroxylase following activation by exposure to enzymatic phosphorylating conditions.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 66,907–913.
Zivkovic, B., andGuidotti, A. 1974. Changes of kinetic constant of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase elicited by neuroleptics that impair the function of dopamine receptors.Brain Res. 79,505–509.
Zivkovic, B., Guidotti, A., andCosta, E. 1974. Effects of neuroleptics on striatal tyrosine hydroxylase: Changes in affinity for the pteridine cofactor.Mol. Pharmacol. 10,727–735.
Zivkovic, B., Guidotti, A., Revuelta, A., andCosta, E. 1975. Effect of thioridazine, clozapine and other antipsychotics on the kinetic state of tyrosine hydroxylase and on the turnover rate of dopamine in striatum and nucleus accumbens.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 194,37–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lerner, P., Nosé, P., Ames, M.M. et al. Modification of the tyrosine hydroxylase assay. Neurochem Res 3, 641–651 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00963765
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00963765