Abstract
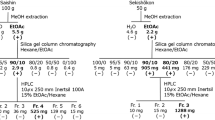
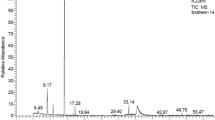
Based on field observations of the effects of the resinous tarweedHemizonia fitchii A. Gray (Asteraceae) on mosquito populations in California, the volatile oil of this plant was investigated for insecticidal activity. Analysis of thé oil by TLC and capillary GC-MS showed the presence of five major constituentś which were identified as the monoterpenoid 1,8-cineole, and the chromenes encecalin, eupatoriochromene (desmethylencecalin), 6-vinyl-7-methoxy-2,2-dimethylchromene, and desmethoxyencecalin. Trace amounts of several volatile fatty acids, alkanes,p-coumarate derivatives, additional chromene derivatives, and numerous mono- and sesquiterpenoids were also detected and identified by GC-MS. Fractionation of the oil by preparative TLC and column chromatography afforded the major chromenes, the identities of which were confirmed by NMR and IR spectral data. The chromenes exhibited weak to moderate toxicity againstCulex pipiens (house mosquito) larvae andOncopeltus fasciatus (large milkweed bug) nymphs. However, no antijuvenile hormone activity was observed for any of the compounds tested against these insect species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthonsen, T. 1969. New chromenes fromEupatorium species.Acta Chem. Scand. 23:3605–3607.
Bjeldanes, L.F., andGeissman, T.A. 1969. Euparinoid constituents ofEncelia californica.Phytochemistry 8:1293–1296.
Bohlmann, F., andGrenz, M. 1970. Neue Isopentenyl-acetophenon-Derivate ausHelianthella uniflora.Chem. Ber. 103:90–96.
Bohlmann, F., andGrenz, M. 1977. Über Inhaltsstoffe der GattungFlourensia.Chem. Ber. 110:295–300.
Bohlmann, F., andJakupovic, J. 1978. Über neue Chromene und andere Inhaltsstoffe vonLagascea rigida.Phytochemistry 17:1677–1678.
Bohlmann, F., Burkhardt, T., andZdero, C. 1973. Naturally Occurring Acetylenes. Academic Press, London.
Bohlmann, F., Jakupovic, J., Ahmed, M., Wallmeyer, M., Robinson, H., andKing, R.M. 1981. Labdane derivatives fromHemizonia species.Phytochemistry 20:2383–2387.
Bohlmann, F., Jakupovic, J., King, R.M., andRobinson, H. 1982. New labdane derivatives fromMadia sativa.Phytochemistry 21:1103–1107.
Bohlmann, F., Tsankova, E., Jakupovic, J., King, R.M., andRobinson, H. 1983. Dimeric chromenes and mixed dimers of a chromene with euparin fromEncelia canescens.Phytochemistry 22:557–560.
Bowers, W.S. 1981. How antijuvenile hormones work.Am. Zool. 21:737–742.
Bowers, W.S. 1982a. Endocrine strategies for insect control.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 31:3–14.
Bowers, W.S. 1982b. Toxicology of the precocenes, pp. 403–427,in J.R. Coates (ed.). Insecticide Mode of Action. Academic Press, New York.
Bowers, W.S., Ohta, T., Cleere, J.S., andMarsella, P.A. 1976. Discovery of insect antijuvenile hormones in plants.Science 193:542–547.
Bowers, W.S., Evans, P.H., Marsella, P.A., Soderlund, D.M., andBettarini, F. 1982. Natural and synthetic allatotoxins: suicide substrates for juvenile hormone biosynthesis.Science 217:647–648.
Brooks, G.T., Pratt, G.E., andJennings, R.C. 1979. The action of precocenes in milkweed bugs (Oncopeltusfasciatus) and locusts (Locusta migratoria).Nature 281:570–573.
Cupp, E.W., Lok, J.B., andBowers, W.S. 1977. The developmental effects of 6,7-dimethoxy-2,2-dimethyl chromene on the preimaginal stages ofAedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae).Entomol. Exp. Appl. 22:23–28.
Heller, S.R., andMilne, G.W.A. 1978. EPA/NIH Mass Spectral Data Base, Vols. 1–4 (U.S. Dept. of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards, NSRDS-NBS 63). U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
Heller, S.R., andMilne, G.W.A. 1980. EPA/NIH Mass Spectral Data Base, Supplement 1 (U.S. Dept. of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards, NSRDS-NBS 63, Suppl. 1). U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
Hwang, Y.-S., Schultz, G.W., andMulla, M.S. 1983. Structure-activity relationship of fatty acids as mosquito ovipositional repellent. Abstracts of Papers, PEST No. 40, 185th National Meeting of the American Chemical Society, Seattle, Washington, March 1983. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.
Jennings, R.C., andOttridge, A.P. 1979. Synthesis of precocene 1 epoxide (2,2-dimethyl-3,4-epoxy-7-methoxy-2H-l-benzopyran).J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1979:920–921.
Jennings, W., andShibamoto, T. 1980. Qualitative Analysis of Flavor and Fragrance Volatiles by Glass Capillary Gas Chromatography. Academic Press, New York.
Jermy, T., Butt, B.A., McDoNough, L., Dreyer, D.L., andRose, A.F. 1981. Antifeedants for the Colorado potato beetle -I. Antifeeding constituents of some plants from the sagebrush community.Insect Sci. Appl. 1:237–242.
Kubo, I., Klocke, J.A., Matsumoto, T., andKamikawa, T. 1983. Plumbagin as a model for insect ecdysis inhibitory activity, pp. 169–175,in J. Miyamoto (ed.). IUPAC, Pesticide Chemistry: Human Welfare and the Environment, Rational and Biorational Design of Pesticides and Growth Regulators. Pergamon Press, New York.
Maugh, T.H. II. 1982. To attract or repel, that is the question.Science 218:278.
Muller, C.H., andChou, C.-H. 1972. Phytotoxins: An ecological phase of phytochemistry, pp. 201–216,in J.B. Harborne (ed.). Phytochemical Ecology. Academic Press, New York.
Pratt, G.E., Jennings, R.C., Hamnett, A.F., andBrooks, G.T. 1980. Lethal metabolism of precocene-I to a reactive epoxide by locust corpora allata.Nature 284:320–323.
Proksch, P., andRodriguez, E. 1982. High-performance liquid chromatography of chromenes and benzofurans from the genusEncelia (Asteraceae).J. Chromatogr. 240:543–546.
Proksch, P., andRodriguez, E. 1983. Chromenes and benzofurans of the Asteraceae, their chemistry and biological significance.Phytochemistry 22:2335–2348.
Proksch, P., Proksch, M., Towers, G.H.N., andRodriguez, E. 1983. Phototoxic and insecticidal activities of chromenes and benzofurans fromEncelia.J. Nat. Prod. 46:331–334.
Proksch, P., Budzikiewicz, H., Tanowitz, B.D., andSmith, D.M. 1984. Flavonoids from the external leaf resins of fourHemizonia species (Asteraceae).Phytochemistry 23:679–680.
Rodriguez, E. 1983. Cytotoxic and insecticidal chemicals of desert plants, pp. 291–302,in P.A. Hedin (ed.). Plant Resistance to Insects. ACS Symposium Series No. 208, American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.
Scriven, R., andMeloan, C.E. 1984. Determining the active component in 1,3,3-trimethyl-2-oxabicyclo[2,2,2]octane (cineole) that repels the American cockroach,Periplaneta americana.Ohio J. Sci. 84(3):85–88.
Steelink, C., andMarshall, G.P. 1979. Structures, syntheses, and chemotaxonomic significance of some new acetophenone derivatives fromEncelia farinosa Gray.J. Org, Chem. 44:1429–1433.
Swigar, A.A., andSilverstein, R.M. 1981. Monoterpenes. Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc., Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
Verma, M., andMeloan, C.E. 1981. A natural cockroach repellent in bay leaves.Am. Lab. 13(10):64–69.
Wisdom, C., andRodriguez, E. 1982. Quantitative variation of the sesquiterpene lactones and chromenes ofEncelia farinosa.Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 10:43–48.
Wisdom, C.S., Smiley, J.T., andRodriguez, E. 1983. Toxicity and deterrency of sesquiterpene lactones and chromenes to the corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).J. Econ. Entomol. 76:993–998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Part I in the series “Biologically Active Constituents of North American Plants.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klocke, J.A., Balandrin, M.F., Adams, R.P. et al. Insecticidal chromenes from the volatile oil ofHemizonia fitchii . J Chem Ecol 11, 701–712 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988299
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00988299