Abstract
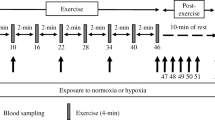
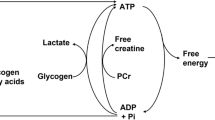
In experiments with graded exercise of 15 men (6 untrained, 3 semitrained, 6 endurance-trained) the trained subjects showed a massive shift to the right of thein vivo O2 dissociation curve (ODC) of femoral venous blood. At a saturation of 20 to 25% (18 mkp/sec)P O 2 was about 9 mm Hg higher for the trained than for the untrained group. The following factors play a role: 1. The 2,3-diphosphoglycerate [2,3-DPG] concentration was increased by 15 to 20% in the trained group which explains about 2 mm Hg of the difference inP O 2. 2. Exercise acidosis in the femoral venous blood depends to a large extent on CO2 in the trained, but on lactic acid in the untrained group. At low saturations the CO2-Bohr effect increases sharply thus having a greater importance in the trained subjects. This factor can explain about 2 mm Hg of the difference. However, influence of chloride and 2,3-DPG on the Bohr effect must be taken into consideration. 3. Since the large ODC-shift to the right of the trained group was not reproducible underin vitro conditions, it is suggested that a rapidly decaying unknown substance accounts for the remaining difference inP O 2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrup, P., Rörth, U., Thorshauge, C.: Dependency on acid-base-status of oxyhemoglobin dissociation and 2,3-diphosphoglycerate level in human erythrocytes. II.In vivo studies. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest.26, 47–52 (1970)
Bärtschi, F., Haab, P., Held, D. R.: Reliability of bloodP CO 2-measurements by the CO2- electrode, the whole-blood (CCO 2)/pH method and the Astrup method. Resp. Physiol.10, 121–131 (1970)
Bauer, C.: Antagonistic influence of CO2 and 2,3-diphosphoglycerate on the Bohr-effect of human haemoglobin. Life Sci.8, 1041–1064 (1969)
Bellingham, A. J., Detter, J. C., Lenfant, C.: Regulatory mechanisms of hemoglobin oxygen affinity in acidosis and alkalosis. J. clin. Invest.10, 100–106 (1971)
Böning, D., Schweigart, U., Tibes, U., Hemmer, B.:In vivo andin vitro investigations on the oxygen dissociation curve of blood of trained and untrained subjects during exercise. Pflügers Arch.332, Suppl. R 78 (1972)
de Bruin, S. H., Rollema, H. S., Janssen, L. H. M., van Os, G. A. J.: The interaction of chloride ions with human hemoglobin. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.58, 210–215 (1974)
Dempsey, J. A., Rodriguez, J., Shahidi, N. T., Reddan, W. G., McDougall, J. D.: Muscular exercise, 2,3-DPG and oxy-hemoglobin affinity. Int. Z. angew. Physiol.30, 34–39 (1971)
Detry, J.-M. R., Rousseau, M., Vandenbroucke, G., Kusumi, F., Brasseur, L. A., Bruce, R. A.: Increased arteriovenous oxygen difference after physical training in coronary heart disease. Circulation44, 109–118 (1971)
Doll, E., Keul, J.: Zum Stoffwechsel des Skelettmuskels. II. Sauerstoffdruck, Kohlensäuredruck, pH, Standardbicarbonat und base excess im venösen Blut der arbeitenden Muskulatur. Untersuchungen an Hochleistungssportlern. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.301, 214–229 (1968)
Duhm, J.: Effects of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate and other organic phosphate compounds on oxygen affinity and intracellular pH of human erythrocytes. Pflügers Arch.326, 341–356 (1971)
Duhm, J., Gerlach, E.: On the mechanisms of the hypoxia-induced increase of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate in erythrocytes. Pflügers Arch.326, 254–269 (1971)
Eaton, J. W., Faulkner, J., Brewer, G. J.: Response of the human red cell to muscular activity. Proc. Soc. exp. Med.132, 886–887 (1969)
Ekblom, B., Åstrand, P.-O., Saltin, B., Steuberg, J., Wallström, B.: Effect of training on circulatory response to exercise. J. appl. Physiol.24, 518–528 (1968)
Faulkner, J., Brewer, G., Eaton, J.: Adaptation of the red blood cell to muscular exercise. In: G. J. Brewer, ed., Red cell metabolism and function. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, Vol. 6, pp. 213–225. New York-London: Plenum Press 1970
Garby, L., Robert, U., Zaar, B.: Proton- and carbaminolinked oxygen affinity of normal human blood. Acta physiol. scand.84, 482–492 (1972)
Grimby, G., Häggendal, E., Saltin, B.: Local Xenon clearance from the quadriceps muscle during exercise in man. J. appl. Physiol.22, 305–310 (1967)
Hasart, E., Roth, W., Jagemann, K., Pansold, B.: 2,3-Diphosphoglyceratkonzentration in Erythrocyten und körperliche Belastung. Med. Sport13, 112–118 (1973)
Kjellberg, S. R., Rudhe, M., Sjöstrand, T.: Increase of the amount of hemoglobin and blood volume in connection to physical training. Acta physiol. scand.19, 146–151 (1950)
Koller, S.: Statistische Auswertung der Versuchsergebnisse. In: Handb. Physiol. Pathol. Chem. Anal., K. Lang, E. Lehnartz, eds., Vol. 2, pp. 931–1036. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1955
Krimsky, I.: D-glycerate-2,3-diphosphat. In: H. U. Bergmeyer, Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, 2. Aufl., Vol. II, pp. 1397–1399. Weinheim (Bergstr.): Verlag Chemie 1970
Lichtman, M. A., Miller, D., Cohen, J., Waterhouse, C.: Reduced red cell glycolysis, 2,3-diphosphoglycerate and adenosine triphosphate concentration, and increased hemoglobinoxygen affinity caused by hypophosphatemia. Ann. intern. Med.74, 562–568 (1971)
Meier, U., Böning, D., Rubinstein, H. J.: Oxygenation dependent variations of the Bohrcoefficient related to whole blood and erythrocyte pH. Pflügers Arch.349, 203–213 (1974)
Severinghaus, J. W.: Blood gas calculator. J. appl. Physiol.21, 1108–1116 (1966)
Shappell, S. D., Murray, J. A., Bellingham, A. J., Woodson, R. D., Detter, J. C., Lenfant, C.: Adaptation to exercise: role of hemoglobin affinity for oxygen and 2,3-diphosphoglycerate. J. appl. Physiol.30, 827–837 (1971)
Shappell, S. D., Murray, J. A., Nasser, M. G., Wills, R. E., Torrance, J. D., Lenfant, C. J.: Acute change in hemoglobin affinity for oxygen during angina pectoris. New Engl. J. Med.282, 1219–1224 (1970)
Siggaard-Andersen, O.: The acid-base-status of the blood, 2nd ed. Copenhagen: Munksgaard 1964
Siggaard-Andersen, O.: Oxygen-linked hydrogen ion binding of human hemoglobin. Effects of carbon dioxide and 2,3-diphosphoglycerate. I. Studies on erythrolysate. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest.27, 351–360 (1971)
Sproule, B. J., Archer, R. K.: Changes in intravascular temperature during heavy exercise. J. appl. Physiol.14, 983–984 (1959)
Sproule, B. J., Mitchell, J. H., Miller, W. F.: Cardiopulmonary physiological responses to heavy exercise in patients with anemia. J. clin. Invest.39, 378–388 (1960)
Tibes, U., Hemmer, B., Schweigart, U., Böning, D., Fotescu, D.: Exercise acidosis as cause of electrolyte changes in femoral venous blood of trained and untrained man. Pflügers Arch.347, 145–158 (1974)
Varnauskas, E., Bergmann, H., Houk, P., Bjoerntop, P.: Haemodynamic effects of physical training in coronary patients. Lancet1966 II, 8–12
Varnauskas, E., Bjoerntop, P., Fahlen, M., Prerovsky, I., Sternberg, J.: Effects of physical training on exercise blood flow and enzymatic activity in skeletal muscle. Cardiovasc. Res.4, 418–422 (1970)
Waldeck, F., Zander, R.: Lageveränderungen der Sauerstoffbindungskurve in Abhängigkeit von den intraerythrocytären Kationen- und Hämoglobinkonzentrationen. Klin. Wschr.47, 1068–1078 (1969)
Wyndham, C. H., Strydom, N. B.: Körperliche Arbeit bei hoher Temperatur. In: W. Hollmann, ed., Zentrale Themen der Sportmedizin, pp. 131–150. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft BO 360/2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Böning, D., Schweigart, U., Tibes, U. et al. Influences of exercise and endurance training on the oxygen dissociation curve of blood underin vivo andin vitro conditions. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 34, 1–10 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999910
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999910