Abstract
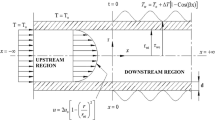
Consideration is given to the influence of viscous dissipation on the thermal entrance region laminar pipe flow heat transfer with convective boundary condition. The Eigenfunction series expansion technique is employed to solve the governing energy equation. The results for axial distributions of dimensionless bulk and wall temperatures, local Nusselt number as well as modified local Nusselt number are presented graphically forNu 0 =0.1, 2, and 100. The complicated variations of conventional local Nusselt number is due to the inappropriate definition of conventional heat transfer coefficient in this problem. A modified local heat transfer coefficient, based on the difference of bulk fluid temperature and wall temperature, is introduced. Its value can clearly indicate the extent and the direction of heat exchange between the fluid in the pipe and the ambient. The effects of outside Nusselt number are also investigated. Significant viscous dissipation effects have been observed for large Br.
Zusammenfassung
Der Einfluß der Zähigkeit auf den thermischen Einlauf wird für laminare Rohrströmung unter gegebenen Bedingungen des Wärmeaustausches mit der Umgebung untersucht. Die Energiegleichung wird mittels Reihenentwicklung der Eigenfunktion gelöst. Die axiale Verteilung der dimensionslosen mittleren Flüssigkeits- und Wandtemperaturen, und der normalen und einer modifizierten örtlichen Nusselt-Zahl werden für äußere Nusselt-ZahlenNu 0 von 0.1, 2 und 100 ermittelt und graphisch dargestellt.Nu 0 ist definiert als das Produkt aus Wärmedurchgangszahl, Rohrradius und der Wärmeleitzahl der Flüssigkeit im Rohr. Die normale örtliche Nusselt-Zahl zeigt einen komplizierten Verlauf. Deswegen wird eine modifizierte ZahlNu e eingeführt, die nicht aus der örtlichen Temperaturdifferenz zwischen Wand und Massenstrom resultiert, sondern aus der Differenz zwischen Einlaufs- und Umgebungstemperatur.Nu e zeigt deutlich die Größe und Richtung des Wärmeaustausches zwischen Flüssigkeit im Rohr und der Umgebung. Beträchtliche Einflüsse der Zähigkeit ergeben sich für große Brinkman-Zahlen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Br :
-
Brinkman number,μu 2 m /k (T e -T 0 )
- C n :
-
expansion coefficients, Eq. (16)
- C p :
-
specific heat
- D n :
-
expansion coefficients, Eq. (18)
- ec :
-
Eckert number,u 2 m /c p (T e -T 0 )
- F n :
-
expansion coefficients, Eq. (19)
- g n :
-
Eigenfunctions, Eq. (14)
- h :
-
local heat transfer coefficient
- h e :
-
modified local heat transfer coefficient
- k :
-
thermal conductivity of the fluid in pipe
- Nu :
-
local Nusselt number,h (2K)/k
- Nu e :
-
modified local Nusselt number,h e (2K)/k
- Nu 0 :
-
outside Nusselt number,UR/k
- Pe :
-
Peclet number,u m (2R)/α.
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number,v/α
- Q w″ :
-
dimensionless wall heat flux, Eq. (27)
- q w ″ :
-
local wall heat flux, Eqs. (20) and (29)
- R :
-
pipe radius
- r:
-
radial coordinate
- T :
-
fluid temperature
- U :
-
outside heat transfer coefficient
- u :
-
axial fluid velocity
- x :
-
axial coordinate
- α :
-
thermal diffusivity of the fluid
- η :
-
dimensionless radial coordinate,r/R
- θ :
-
dimensionless fluid temperature, (T 0 -T)/(T 0 -T e )
- λ n :
-
Eigenvalues, Eq. (14)
- μ :
-
dynamic viscosity of the fluid
- ν :
-
kinematic viscosity of the fluid
- ξ :
-
dimensionless axial coordinate,x/(R Pe)
- ϱ :
-
fluid density
- φ :
-
dimensionless temperature, Eqs. (10) and (13)
- b :
-
bulk
- e :
-
entrance
- m :
-
mean
- 0:
-
ambient
- w :
-
wall
References
Brinkman, H. C.: Heat Effects in Capillary Flow I. Appl. Sci. Res. A 2 (1951) 120
Tyagi, V. P.: Laminar Forced Convection of a Dissipative Fluid in a Channel. J. Heat Transfer. 88 (1966) 161
Ou, J. W.; Cheng, K. C.: Viscous Dissipation Effects on Thermal Entrance Region Heat Transfer in Pipes with Uniform Wall Heat Flux. Appl. Sci. Res. 28 (1973) 289
Ou, J. W., Cheng, K. C.: Viscous Dissipation Effects on Thermal Entrance Heat Transfer in Laminar and Turbulent Pipes Flows with Uniform Wall Temperature. ASME Paper No. 74-HT-50, 1974
Krishnan, K. N.; Sastri, V. M. K.: Numerical Solution of Thermal Entry Length Problem with Variable Viscosities and Viscous Dissipation. Wärme-Stoffübertrag. 11 (1978) 73
Forrest, G.; Wilkinson, W. L.: Laminar Heat Transfer to Power Law Fluids in Tubes with Constant Wall Temperature. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. 51 (1973) 331
Forrest, G.; Wilkinson, W. L.: Laminar Heat Transfer to Power Law Fluids in Tubes with Constant Wall Heat Flux. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. 52 (1974) 10
Winter, H. H.: Temperature Fields in Extruder Dies with Circular Annular, or Silt Cross-Section. Polym. Eng. Sci. 15 (1975) 84
Vlachopoulos, J.; Keung, C. K. J.: Heat Transfer to a Power-Law Fluid Flowing Between Parallel Plates. AIChE J. 18 (1972) 1272
Galili, N.; Takserman-Krozer, R.; Rigbi, Z.: Heat and Pressure Effects in Viscous Flow Through a Pipe I. General Formulation and Basic Solution. Rheol. Acta 14 (1975) 550
Galili, N.; Rigbi, Z.; Takserman-Krozer, R.: Heat and Pressure Effects in Viscous Flow Through a Pipe II. Analytical Solution for Non-Newtonian Flow. Rheol. Acta 14 (1975) 816
Stephan, K.: Wärmetransport in Viskosen nicht-Newtonschen Flüssigkeiten. Chem.-Ing.-Tech. 39 (1967) 243
Cox, H. W.; Macosko, C. W.: Viscous Dissipation in Die Flows. AIChE J. 20 (1974) 785
Griskey, R. G.; Wiehe, I. A.: Heat Transfer to Molten Flowing Polymers. AIChE J. 12 (1966) 308
Forsyth, T. H.; Murphy, N. F.: Experimental Measurement of Temperature Profiles of Molten Flowing Polymers in a Heat Exchanger. Polym. Eng. Sci. 9 (1969) 22
Griskey, R. G.; Choi, M. N.; Siskovic, M.: Heat Transfer to Flowing Thermally Softened Polymers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 13 (1973) 287
Winter, H. H.: Viscous Dissipation in Shear Flows of Molten Polymers. Adv. Heat Transfer 13 (1977) 205
Churchill, R. V.: Operational Mathematics, 2nd Ed. Chap. 9. New York: McGraw-Hill 1958
Hsu, C. J.: Exact Solution to Entry-Region Laminar Heat Transfer with Axial Conduction and the Boundary Condition of the Third Kind. Chem. Eng. Sci. 23 (1968) 457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
In honor of Prof. Dr. U. Grigull to his 70th Birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, T.F., Hawks, K.H. & Leidenfrost, W. Analysis of viscous dissipation effect on thermal entrance heat transfer in laminar pipe flows with convective boundary conditions. Warme- und Stoffubertragung 17, 97–105 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01007225
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01007225