Abstract
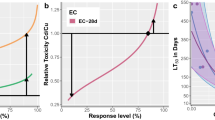
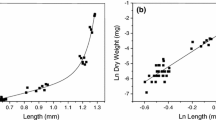
Different life-history stages of the freshwater isopod crustaceanAsellus aquaticus were exposed to a range of cadmium concentrations using a semi-static toxicity testing procedure. Median lethal concentrations (96-hr LC50) ranged from 80 Μg Cd/L for juveniles to >2,000 Μg Cd/L for embryos. Pre-treatment of eggs with cadmium did not increase their tolerance to the metal as juveniles. The responses of each stage are discussed in relation to the use of macroinvertebrate toxicity test data in predicting the hazardous effects of pollutants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adcock JA (1979) Energetics of a population of the isopodAsellus aquaticus. Life history and production. Freshwater Biol 9:343–355
Alekseyev VA, Antipin BN (1976) Toxicological characteristics and symptom complex of acute phenol intoxication in some freshwater crustaceans and molluscs. Gidrobiol Zh Kiev 12:37–44
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1976) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. APHA, Washington, DC
Anderson PD, Spear PA (1980a) Copper pharmacokinetics in fish gills. 1. Kinetics in pumpkinseed sunfishLepomis gibbosus of different body sizes. Water Res 14:1101–1105
— (1980b) Copper pharmacokinetics in fish gills. 2. Body size relationships for accumulation and tolerance. Water Res 14:1107–1111
Aston RJ, Milner AGP (1980) A comparison of populations of the isopodAsellus aquaticus above and below power stations in organically polluted reaches of the River Trent. Freshwater Biol 10:1–14
Beattie JH, Pascoe D (1978) Cadmium uptake by rainbow troutSalmo gairdneri eggs and alevins. J Fish Biol 13:631–637
— (1979) A cadmium-binding protein in rainbow troutSalmo gairdneri. Toxicol Lett 4:241–246
Berglund T (1968) The influence of predation by brown trout onAsellus in a pond. Institute of Freshwater Research, Drotingholm Report No. 48:77–101
Brungs WA, Mount DI (1978) Introduction to a discussion of the use of aquatic toxicity tests for evaluation of the effects of toxic substances. Special Technical Publication 657:15–32, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA
Gauss JD, Woods PE, Winner RW, Skillings JH (1985) Acute toxicity of copper to three life stages ofChironomous tentans as affected by water hardness-alkalinity. Environ Pollut (Series A) 37:149–157
Hellawell JM (1978) Biological Surveillance of Rivers. Water Research Centre, Stevenage and Medmenham, United Kingdom
Holditch DM, Tolba MR (1981) The effect of temperature and water quality on thein vitro development and survival ofA. aquaticus (Crustacea; Isopoda) eggs. Hydrobiologia 78:227–236
Holland DG (1976) The distribution of freshwater malacostraca in the area of the Mersey and Weaver River Authority. Freshwater Biol 6:265–276
Howard AG, Nickless G (1975) Protein binding of cadmium, zinc and copper in limpetsPatella vulgata J Chromatogr 104:457–459
— (1977) Heavy metal complexation in polluted molluscs. I Limpets (Patella vulgata andPatella intermedia). Chembiol Interact 16:107–114
Kito H, Tazawa T, Ose Y, Sato T, Ishikawa T (1982) Protection by metallothionein against cadmium toxicity. Comp Biochem Physiol 73:(1)135–139
Litchfield JT (1949) A method for the rapid graphic solution of time percent effect curves. J Pharmac Exp Ther 97:399–408
Litchfield JT, Wilcoxon FW (1949) A simplified method for evaluating dose-effect experiments. J Pharmac Exp Ther 96:99–113
Maciorowski HD, Clarke RMcV (1977) Advantages and disadvantages of using invertebrates in toxicity testing. In: Aquatic Invertebrate Bioassays. Special Technical Publication 715:36–47 American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA
McCormack JC, Le Cren D (1971) Thirty years of perch investigations in Windermere. Proceedings of the fifth British Coarse Fish Conference, pp 104–108
McKim JM (1976) Evaluation of tests with early life stages of fish for predicting long term toxicity. J Fish Res Board Can 34:1148–1154
McLeese DW (1976) Fenitrothion toxicity to the freshwater crayfish. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 16:411–416
Merna JW, Eiselee PJ (1973) The effects of methoxychlor on aquatic biota. US Environmental Protection Agency, Duluth, Minnesota. Ecol Res Series EPA-R3-73-046
Ravera O (1977) Effects of heavy metals cadmium, chromium and lead on a freshwater snailBiomphalaria glabrata (Say) Gastropoda, Prosobranchia. Malacologia 16:231–236
Rehwoldt R, Lasko L, Shaw C, Wirhowski E (1973) The acute toxicity of some heavy metal ions towards benthic organisms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 10:291–294
Sanders HO (1969) Toxicity of pesticides to the crustaceanGammarus lacustris. US Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife. Technical Paper No. 25, US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
— (1972) The toxicities of some insecticides to four species of malacostracan Crustacea. US Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife. Technical Paper No. 66, US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Shazili NAM, Pascoe D (1986) Variable sensitivity of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) eggs and alevins to heavy metals. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 36:468–474
Smith LL, Oseid DM, Adelman IR, Broderius SJ (1976) Effects of hydrogen sulphide on fish and invertebrates. Part 1. Acute and chronic toxicity studies. US Environmental Protection Agency, Duluth, Minnesota, Ecol Res Ser EPA 600/3-76-062(a)
Spear PA, Anderson PD (1975) Fish size as a quantitative function of tolerance to heavy metals. Proceedings of 10th Canadian symposium on water pollution research, Canada, pp 170–178
Steel EA (1961) Some observations on the life history ofAsellus aquaticus (L.) andAsellus meridianus Racovitza (Crustacea; Isopoda). Proc Zool Soc Lond 137:71–87
Stephan CE (1977) Increasing the usefulness of acute toxicity tests. In: Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Assessment. Proceedings of the fifth annual symposium on aquatic toxicology. Special Technical Publication 776:69–81 American Society for Testing and Materials Philadelphia, PA.
Talbot V, Magee RJ (1978) Naturally occurring heavy metalbinding proteins in invertebrates. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 7:73–81
Wier CF, Walter WM (1976) Toxicity of cadmium in the freshwater snailPhysa gyrina (Say). J Environ Qual 5:359–362
Williams KA, Green DWJ, Pascoe D (1984) Toxicity testing with freshwater macroinvertebrates: Methods and application in environmental management. In: Pascoe D, Edwards RW (eds) Freshwater biological monitoring. Advances in Water Pollution Control, Pergamon, London, p 167
— (1985) Studies on the acute toxicity of pollutants to freshwater macroinvertebrates. 1. Cadmium. Arch Hydrobiol 102:(4)461–471
Woodworth J., Pascoe D (1983) Induction of cadmium-binding protein in the three spined stickleback. Aquatic Toxicol 3:141–148
Woodworth J, Evans ASA, Pascoe D (1983) The production of cadmium-binding protein in three species of freshwater fish. Toxicol Lett 15:289–295
Wurtz CB (1962) Zinc effects on freshwater molluscs. Nautilus 76:53–61
Yamamura M, Suzuki KT, Hatakeyama S, Kubota K (1983a) Tolerance to cadmium and cadmium-binding proteins induced in the midge larvaChironomus yoshimatsui (Diptera: Chironomidae). Comp Biochem Physiol C 75:21–24
Yarnamura M, Hatakeyama S, Suzuki KT (1983b) Cadmium uptake and induction of cadmium-binding protein in the waterflea (Moina macrocopa). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 30:298–302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Green, D.W.J., Williams, K.A. & Pascoe, D. The acute and chronic toxicity of cadmium to different life history stages of the freshwater crustaceanAsellus aquaticus (L). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 15, 465–471 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056557
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056557