Abstract
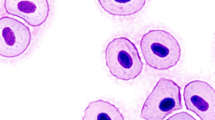
Erythrocyte micronuclei (MN) frequencies of 280 winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus) from Chesapeake Bay to the southern Scotian Shelf including Long Island Sound were measured. The MN data were combined with data previously reported for 224 flounder and the combined data sets were analyzed. Incidences of MN were elevated sixfold in flounder from the New York Bight Apex as compared to frequencies for fish from the inshore Gulf of Maine and Block Island Sound, and twice those found in Georges Bank and Long Island Sound flounder. Inshore New Jersey fish had higher MN frequencies than those from inshore Gulf of Maine and Block Island Sound. The occurrence of MN in flounder from inshore Virginia was higher than in flounder from inshore Gulf of Maine and Block Island Sound. The large subset of stations from Long Island Sound indicated higher frequencies of MN in flounder from Hempstead and Shoreham as compared to most other sites in the Sound.
There was no significant difference in the frequency of MN between males and females, but males had significantly more MN than sexually immature flounder. Flounder over the entire sampling area had increased levels of MN during the fall months of the year. This is probably influenced by the maternal cycle of gonadal maturation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bigelow HB, Schroeder WC (1953) Fishes of the Gulf of Maine. Fish Bull, Fish and Wildlife Service Vol. 53. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Boehm P (1983) Chemical contaminants in northeast United States marine sediments. NOAA Tech Rept NOS 99. 82 pp
Boller K, Schmid W (1970) Chemische mutagenese beim sauger. Das knochenmark des chinesischen hamsters alsin vivo-test-system. Hamatologische befunde nach behandlung mit trenimon. Humangenetik 11:35–54
Brunetti R, Majone F, Gola I, Beltrame C (1988) The micronucleus test: Examples of application to marine ecology. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 44:65–68
Carmody DJ, Pearce JB, Yasso WE (1973) Trace metals in sediments of the New York Bight. Mar Pollut Bull 4:132–135
Danila DJ, Kennish MJ (1981) Tagging study of winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus) in Barnegat Bay, New Jersey. In: The Ocean—An International Workplace. Oceans 81 Conference Record—Boston, MA, Sept. 16–18, 1981, Vol. 2, pp 759–764
Danila DJ (1987) Monitoring the marine environment of Long Island Sound at Millstone Nuclear Power Station: Summary of studies prior to Unit 3 operation. Northeast Utilities Environmental Lab, April 1987
Das RK, Nanda NK (1986) Induction of micronuclei in peripheral erythrocytes of fishHeteropneustes fossilis by mitomycin C and paper mill effluent. Mut Res 175:67–71
Greig RA, Reid RN, Wenzloff DR (1977) Trace metal concentrations in sediments from Long Island Sound. Mar Pollut Bull 8:183–188
Greig RA, Schurman S, Pereira J, Naples P (1983) Metals and PCB concentrations in sediments from Long Island Sound. Bull Environ Contain Toxicol 31:257–262
Hooftman RN (1981) The induction of chromosome aberrations inNotobranchius rachowi (Pisces:Cyprinodontidae) after treatment with ethylmethanesulphonate or benzo(a)pyrene. Mut Res 91:347–352
Hooftman RN, de Raat WK (1982) Induction of nuclear anomalies (micronuclei) in the peripheral blood erythrocytes of the eastern mudminnowUmbra pygmaea by ethyl methanesulphonate. Mut Res 104:147–152
Hooftman RN, Vink GJ (1981) Cytogenetic effects on the eastern mudminnow,Umbra pygmaea, exposed to ethylmethanesulphonate, benzo(a)pyrene and river water. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 5:261–269
Hose JE, Hannah JB, Puffer HW, Landolt ML (1984) Histologic and skeletal abnormalities in benzo(a)pyrene-treated rainbow trout alevins. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 13(6):675–684
Hose JE, Cross JN, Smith SG, Diehl D (1987) Elevated circulating erythrocyte micronuclei in fishes from a contaminated site off southern California. Mar Environ Res 22:167–176
Hughes JB, Nelson DA, Perry DM, Miller JE, Sennefelder GR, Pereira JJ (1986) Reproductive success of the winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus) in Long Island Sound. ICES C.M. 1986/E:10, M.E.Q., Demers Fish Ctte
Jaylet A, Zoll C (1990) Tests for detection of genotoxins in freshwater. Rev Aquat Sci 2(2):151–166
Johnson LL, Casillas E, Collier TK, Varanasi U (1988) Contaminant effects on ovarian development in English sole (Parophrys vetulus) from Puget Sound, Washington. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:2133–2146
Longwell AC, Perry D, Hughes JB, Hebert A (1983) Frequencies of micronuclei in mature and immature erythrocytes of fish as an estimate of chromosome mutation rates—results of field surveys on windowpane flounder, winter flounder, and Atlantic mackerel. ICES, C.M. 1983/E:55, M.E.Q., Demers and Pelag Fish Cttes
MacGregor JT, Wehr CM, Gould DH (1980) Clastogen-induced micronuclei in peripheral blood erythrocytes: The basis of an improved micronucleus test. Environ Mutagen 2(4):509–514
MacLeod WD Jr, Ramos LS, Friedman AJ, Burrows DG, Prohaska PG, Fisher DL, Brown DW (1981) Analyses of residual chlorinated hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons and related compounds in selected sources, sinks, and biota of New York Bight. NOAA Tech Memo OMPA-6
Metcalfe CD (1988) Induction of micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities in the erythrocytes of mudminnows (Umbra limi) and brown bullheads (Ictalurus nebulosus). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 40:489–495
National Research Council (Ocean Sciences Board) (1985) Oil in the Sea—Inputs, Fates, and Effects. Nat Acad Press, Washington, DC
Schmid W (1976) The micronucleus test for cytogenetic analysis. In: Hollaender A (ed) Chemical mutagens: Principles and methods for their detection. Vol. 6, Plenum Press, New York, pp 31–53
Sindermann CJ, Esser SC, Gould E, McCain BB, McHugh JL, Morgan RP, Murchelano RA, Sherwood MJ, Spitzer PR (1982) Effects of pollutants on fishes. In: Mayer G (ed) Ecological stress and the New York Bight: Science and management. Estuarine Research Federation, Columbia, SC, pp 23–38
Valdes EA (1987) New York Bight winter flounder move surprisingly long distances: In: NEFC monthly highlights, National Marine Fisheries Service, Northeast Fisheries Center, Woods Hole, MA, November, 1987
von Westernhagen H, Rosenthal H, Dethlefsen V, Ernst W, Harms U, Hansen PD (1981) Bioaccumulating substances and reproductive success in Baltic flounder (Platichthys flesus). Aquat Toxicol 1:85–99
Warren L (1977) The ecology ofCapitella capitella in British waters. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 57:151–159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hughes, J.B., Hebert, A.T. Erythrocyte micronuclei in winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus): Results of field surveys during 1980–1988 from Virginia to Nova Scotia and in Long Island Sound. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 20, 474–479 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065835
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065835