Abstract
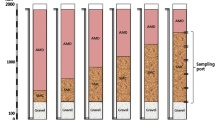
A 19.2 l multiplate anaerobic reactor (MPAR) was used to assess the impact of lime (Ca(OH)2) on the anaerobic treatment of whey permeate effluents. The amount of Ca(OH)2 required to maintain the pH of the whey permeate around 5 ranged between 3.0 and 4.5 kg/m3, which corresponded to concentration varying between 1.62 and 2.43 kg/m3. Soluble chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency exceeded 92% with a methane production rate of 6.7 m3/m3.d. at an organic loading rate (OLR) as high as 20 kg COD/m3.d. Extended operation of the MPAR resulted in the accumulation of significant amounts of calcium precipitates in the sludge bed which reached after three months of operation 0.19, 0.25 and 0.33 kg Ca2+ per kg of suspended solid (SS) in the lower, the middle and the upper compartment of the MPAR, respectively. The volatile suspended solids to suspended solids ratio (VSS/SS) decreased from 0.83 in inoculum to 0.37, 0.22 and 0.08 in the lower, the middle and the upper compartment of the MPAR, respectively. As a result, the soluble COD reduction and the methane production rate decreased to 31% and to 2.3 m3/m3.d. respectively, at OLR of 20 kg COD/m3.d.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barford, J. P.;Cail, R. G.;Callander, I. J.;Floyd, E. J.: Anaerobic digestion of high strength cheese whey utilizing semicontinuous digesters and chemical floculent addition. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 28 (1986) 1601–1607
Yan, S. H.;Hill, C. G.;Amundson, C. H.: Ultrafiltration of whole milk, J. Dairy Science 62 (1979) 23–40
Moddler, H. W.;Emmons, D. B.: Properties of whey protein concentrate prepared under acidic conditions. J. Dairy Science 60 (1977) 177–184
Zellner, G.;Vogel, P.;Kneifel, H.;Winter, J.: Anaerobic digestion of whey and whey permeate with suspended and immobilized complex and a defined consortia. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27 (1987) 306–314
Boening, P. H.;Larsen, V. F.: Anaerobic fluidized bed whey treatment. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 14 (1982) 2539–2556
Switzenbaum, M. S.;Danskin, S. C.: Anaerobic expanded bed treatment of whey. Agricultural Waste 4 (1982) 411–426
Streicher, C.;Milande, N.;Capdeville, B.;Roques, H.: Improvement of the anaerobic digestion of diluted whey in a fluidized bed by nutrient additions. Environ. Technol. 12 (1990) 333–341
De Haast, J.;Britz, T. J.;Novello, J. C.;Verwey, E. W.: Anaerobic digestion of deproteinated cheese whey. J. Dairy Research 52 (1985) 457–467
Schröder, E. W.;De Haast, J.: Anaerobic digestion of deproteinated cheese whey in an upflow sludge blanket reactor. J. Diary Research 56 (1989) 129–139
Hwang, S. H.;Hansen, C. L.: Performance of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating whey permeate. Transactions ASAE 35 (1992) 1665–1671
McCarty, P. L.: Anaerobic waste treatment fundamentals. Part two. Public Works 95 (1964) 123–126
Garcia, J. L.: Taxonomy and ecology of methanogens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 87 (1990) 297–308
Li, A.;Sutton, P. L.: Determination of alkalinity requirements for the anaerobic treatment process. In: Proc. of Proc. of the 38th Industrial waste conference, Purdue Univ., Indiana, pp. 603–613. Ann Arbor Science, Ann Arbor 1984
Ferguson, J. F.;Eis, B. J.;Benjamin, M. M.: Neutralization in anaerobic treatment of an acidic waste. Water Res. 18 (1984) 573–580
Svardal, K.;Kroiss, H.: Neutralization in anaerobic wastewater treatmet. In: Rozzi, A.; Tilche, A. (Eds.): Proc. of In: Poster Paper of 5th Int Symp on Anaerobic Digestion, Bologna, Italy, pp. 335–340. Monduzzi Editore, Bologna, Italy 1988
Rozzi, A.; Limoni, N.; Menegatti, G. B.; Liberti.; Passino, R.: Influenceof Na and Ca alkalinity on UASB treatment of olive mill effluents. Part 1: Preliminary results. Process. Biochem. June (1988) 86–90
Ray, B. T.;Rajan, R. V.: Low-level alkaline solubilization for enhanced anaerobic digestion. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed 62 (1990) 81–87
De Haast, J.;Britz, T. J.;Novello, J. C.: Effect of different neutralizing treatment on the efficiency of an anaerobic digester fed with deproteinated cheese whey. J. Dairy Research 53 (1986) 467–476
Yan, J. Q.;Lo, K. V.;Pinder, K. L.: Instability caused by high strength of cheese whey in a UASB reactor. Biotech. Bioeng. 41 (1992) 700–706
Fox, E. J.;Clanton, C. J.;Goodrich, P. R.;Backus, B. D.;Morris, H. A.: Liming an anaerobic cheese whey digester. Transactions ASAE 35 (1992) 269–274
Hulshoff Pol, L. W.; Webers, H. A. A. M.; Lettinga, G.: The effect of the addition of small amounts of granular sludge to the seed sludge on the start-up of UASB-reactors. In: van den Brink, W. J. (Eds.): Proc. of Proc. of the European Symposium Anaerobic Waste Water Treatment, Den Haag, The Netherlands, pp. 383–392. Noordwijkerhout, Den Haag, The Netherlands 1983
Lettinga, G.;Hulshoff Pol, L. W.; UASB-process design for various types of wastewaters. Wat. Sci. Tech. 24 (1991) 87–107
Verrier, D.: Méthanisation d'effluents agro-alimentaires en réacteurs à cellules fixées. Doct. Thesis, Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Industries Agricoles et Alimentaires, Paris, France 1984
Mahoney, E. M.;Varangu, L. K.;Cairns, W. L.;Kosaric, N.;Murray, R. G. E.: The effect of calcium on microbial aggregation during UASB reactor start-up. Water Sci. Technol. 19 (1987) 249–260
Dubourguier, H. C.;Archer, D. B.;Albagnac, G.;Prensier, G.: Structure and metabolism of methanogenic microbial conglomerates. In: Hall, E. R.; Hobson, P. N. (Eds.): Proc. of 5th Int. Symp. on Anaerobic Digestion, Anaerobic Digestion 1988, Bologna, Italy, pp. 13–23. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK 1988
Hulshoff Pol, L. W.: The phenomena of granulation of anaerobic sludge. Ph.D. Thesis, Agricultural University of Wageningen, The Neterlands 1989
Guiot, S. R.;Gorur, S. S.;Kennedy, K. J.: Nutritional and environmental factors contributing to microbial aggregation during upflow anaerobic sludge bed-filter (UBF) reactor start-up. In: Hall, E. R.; Hobson, P. N. (Eds.): Proc. of 5th Int. Symp. on Anaerobic Digestion, 22–26 May, Bologna, Italy, pp. 47–53. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK 1988
APHA;AWWA;WPCF: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 17th Edition, Public Health Association, Washington D. C. USA. 1989
El-Mamouni, R.;Guiot, S. R.;Rouleau, D.;Mayer, R.;Samson, R.:Comparison of the novel multiplate anaerobic reactor with the upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. In: Wukasch, R. F. (Eds.): Proc. of 46th Industrial Waste Conference, Purdue University, West-Lafayette, IN., USA, pp. 681–687. Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, MI., USA. 1992
Keenan, P. J.;Isa, J.;Switzenbaum, M. S.: Inorganic solids development in a pilot-scale anaerobic reactor treating municipal solid waste landfill leachate. Water. Environ. Res. 65 (1993) 181–188
McCarty, P. L.;McKinney, R. E.: Volatile fatty acid toxicity in anaerobic digestion. J. Wat Pollut. Control Fed. 33 (1961) 223–232
Benefield, L. D.;Randall, C. W.: Biological process design for wastewater treatment. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J. (1980)
Lettinga, G.; de Zeeuw, W. J.; Hulshoff Pol, L. W.; Weigant, W. M.; Rinzema, A.: Anaerobic wastewater treatment based on biomass retention with emphasis on the UASB process. In: Association, C. S. B. (Eds.): Proc. of 4th Int. Symp. on Anaerobic Digestion, Guangzhou, China, pp. 279–301. 1985
Wu, W.;Hu, J.;Gu, X.;Zhao, Y.;Zhang, H.;Gu, G.; Cultivation of anaerobic granular sludge in USAB reactors with aerobic activated sludge as seed. Wat. Res. 21 (1987) 789–799
de Zeeuw, W. J.;Lettinga, G.: Acclimation of digested sewage sludge during start-up of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. In: Proc. In: Proc. 35th Ind. Waste Conf., Purdue Univ, pp. 39–47. Ann Arbor Science, Ann Arbor 1981
Salkinoja-Salonen, M. S.;Nyns, E.-J.;Sutton, P. M.;van den Berg, L.;Wheatley, A. D.: Starting-up of an anaerobic fixed-film reactor. Wat. Sci. Technol. 15 (1983) 305–308
Guiot, S. R.;Rocheleau, S.;Hawari, J. A.;Samson, R.: Induction of granulation by sulphonated-lignin and calcium in upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor. J. Chem. Techn. & Biotechnol. 53 (1992) 45–56
Grotenhuis, J. T. C.: Structure and stability of methanogenic granular sludge. Ph.D. Thesis, Agricultural University of Wageningen, The Netherlands 1992
Jans, A. J. M.: Anaerobic treatment of DMT wastewater. Final report No. O.N. 97135, Dept. Civil Eng., Grontmij n.v., De Bilt, Netherlands 1980
Jördening, H. J.;Pellegrini, A.;Buchholz, K.: Fluidized bed reactors for purification of wastewater with high calcium content. In: Rozzi, A.; (Eds.): Proc. of 5th Int. Symp. Anaerobic Digestion, Bologna, Italy, pp. 289–294. Monduzzi Editors, Bologna, Italy 1988
Guiot, S. R.; Safi, B.; Frigon, J. C.; Mercier, P.; Tremblay, R.; Samson, R.: Performances of a full scale novel multiplate reactor treating cheese whey effluent. In: Proc. of 7th Int. Symp. Anaerobic Digestion, 23–27 Jan., pp. 230–239, Cape Town, South Africa 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors thank Saputo Cheese Ltd. for providing the whey permeate effluents, Alain Corriveau for expert analytical assistance and Hervé Macarie for revising the article. NRC Paper No. 33907
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Mamouni, R., Guiot, S.R., Mercier, P. et al. Liming impact on granules activity of the multiplate anaerobic reactor (MPAR) treating whey permeate. Bioprocess Engineering 12, 47–53 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01112993
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01112993