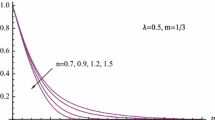
Summary
An exact solution to the problem of lfow past an impulsively started infinite vertical plate in the presence of uniform heat and mass flux at the plate is presented by the Laplace-transform technique. The velocity, the temperature and the concentration profiles are shown graphically. The rate of heat transfer, the skin-friction, and the Sherwood number are also shown on graphs. The effect of different parameters like Grashof number, mass Grashof number, Prandtl number, and Schmidt number are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C′ :
-
species concentration near the plate
- C′ ∞ :
-
species concentration in the fluid far away from the plate
- C :
-
dimensionless concentration
- C p :
-
specific heat at constant pressure
- D :
-
mass diffusion coefficient
- g :
-
acceleration due to gravity
- Gr:
-
thermal Grashof number
- Gc:
-
mass Grashof number
- j″ :
-
mass flux per unit area at the plate
- K :
-
thermal conductivity of the fluid
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- q :
-
heat flux per unit area at the plate
- Sc:
-
Schmidt number
- t′ :
-
time
- t :
-
dimensionless time
- T′ :
-
temperature of the fluid near the plate
- T′ ∞ :
-
temperature of the fluid far away from the plate
- T′ w :
-
temperature of the plate
- u′ :
-
velocity of the fluid in thex′-direction
- u 0 :
-
velocity of the plate
- u :
-
dimensionless velocity
- x′ :
-
coordinate axis along the plate
- y′ :
-
coordinate axis normal to the plate
- y :
-
dimensionless coordinate axis normal to the plate
- β:
-
volumetric coefficient of thermal expansion
- β* :
-
volumetric coefficient of expansion with concentration
- μ:
-
coefficient of viscosity
- ν:
-
kinematic viscosity
- ϱ:
-
density
- τ′:
-
skin-friction
- τ:
-
dimensionless skin-friction
- θ:
-
dimensionless temperature
- er fc :
-
complementary error function
- η:
-
similarity parameter
References
Stokes, G. G.: On the effect of internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums. Cambridge Phil. Trans.IX, 8–106 (1851).
Soundalgekar, V. M.: Free convection effects on the Stokes problem for an infinite vertical plate. ASME J. Heat Transfer99, 499–501 (1977).
Soundalgekar, V. M.: Effects of mass transfer and free convection on the flow past an impulsively started vertical plate. ASME J. Appl. Mech.46, 757–760 (1979).
Das, U. N., Ray, S. N., Soundalgekar, V. M.: Mass transfer effects on flow past an impulsively stated infinite vertical plate with constant mass flux-and exact solution. Heat and Mass Transfer31, 163–167 (1996).
Gebhart, B., Pera, L.: The nature of vertical natural convection flows resulting from the combined buoyancy effects of thermal and mass diffusion. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer14, 2025–2050 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muthucumaraswamy, R., Ganesan, P. & Soundalgekar, V.M. Heat and mass transfer effects on flow past an impulsively started vertical plate. Acta Mechanica 146, 1–8 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01178790
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01178790