Abstract
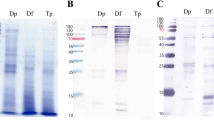
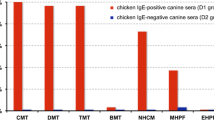
The presence of the enzymatically active allergens equivalent toDer p I (cysteine protease),Der p III (serine protease) and amylase in extracts ofDermatophagoides pteronyssinus, D. farinae andEuroglyphus maynei was determined using appropriate enzymatic techniques. Biochemical equivalents of all three allergens were present in each extract studied. Studies also showed that the mite extracts contained a variety of other biochemically active enzymes including trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase A and B, glucoamylase and lysozyme. Marked differences in the relative concentrations of some of these enzymes in different mite extracts were observed, particularly trypsin and carboxypeptidase A. The enzymes were physicochemically similar to equivalent enzymes from vertebrate and invertebrate sources. Chromatofocusing studies of faecal extracts derived fromD. pteronyssinus andD. farinae showed that several isoforms of each enzyme were present. The data indicated that there were more trypsin isoforms, with pI over a wider range, in extracts prepared fromD. pteronyssinus. Proteases and carbohydrases were also found in extracts prepared from faecally enriched material suggesting that they were endoperitrophic and associated with mite digestion. The data suggest that not only are the group I, III and amylase allergens a consistent feature of most pyroglyphid dust mites but also that other proteases and carbohydrases present in mite faeces are allergenic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, P., 1964. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel filtration. Biochem. J., 91: 222–233.
Baldo, B.A., Ford, S.A. and Tovey, E.R., 1989. Towards a definition of the complete spectrum and rank order of importance of the allergens from the house dust mite,Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. In: Allergy and Molecular Biology, Proceedings of the DPC First International Symposium on Allergy and Molecular Biology. Adv. Biosci., 74: 13–31.
Bowman, C.E. and Childs, M., 1982. Polysaccharidases in astigmatid mites (Arthropoda: Acari). Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 72B: 551–557.
Bowman, C.E. and Lessiter, M.J., 1985. Amylase and esterase polymorphisms in economically important stored product mites (Acari: Astigmata). Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 81B: 353–360.
Brody, A.R., McGrath, J.C. and Wharton, G.W., 1972.Dermatophagoides farinae: The digestive system. J.N.Y. Entomol. Soc., 80: 152–177.
Chua, K.Y., Stewart, G.A., Thomas, W.R., Simpson, R.J., Dilworth, R.J. and Plozza, T.M., 1988. Sequence analysis of cDNA coding for a major house dust mite allergen,Der p I. Homology with cysteine proteases. J. Exp. Med., 167: 175–182.
Chua, K.Y., Doyle, C.R., Simpson, R.J., Turner, K.J., Stewart, G.A. and Thomas, W.R., 1990. Isolation of cDNA coding for the major mite allergenDer p II by IgE plaque immunoassay. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol., 91: 118–123.
Colloff, M.J., Howe, C.W. and Smith, H.V., 1991. IgE binding profiles of atopic sera to house dust mite allergens, using enhanced chemiluminescent immunoblotting. Int. In: Dust Mite Allergens and Asthma. UCB Press, Brussels, pp. 102–106.
Dilworth, R.J., Chua, K.Y. and Thomas, W.R., 1991. Sequence analysis of cDNA coding for a major house dust mite allergen,Der fI. Clin. Exp. Allergy, 21: 25–32.
Erlanger B.F., Kokowsky, N. and Cohen, W., 1961. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 95: 217–278.
Foltmann, B., Szeci, P.B. and Tarasova, N.I., 1985. Detection of proteases by clotting of casein after gel electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem., 146: 353–360.
Hart, B.J., Fain, A. and Hart, D.T., 1990. Differentiation of mite species by using cellulose acetate and equilibrium polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of isoenzymes. Exp. Appl. Acarol., 8: 97–104.
Hartsuck, J.A. and Lipscomb, W.N., 1971. Carboxypeptidase A. In: P.D. Boyer (Editor, The Enzymes, Vol. III. Academic Press, New York, NY, pp. 1–46.
Hearn, M.T.W. and Lyttle, D.T., 1981. Buffer-focusing chromatography using multicomponent electrolyte elution systems. J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Appl., 218: 483–495.
Heymann, P.W., Chapman, M.D., Aalberse, R.C., Fox, J.W. and Platts-Mills, T.A.E., 1989. Antigenic and structural analysis of group II allergens (Der f II andDer p II) from house dust mites (Dermatophagoides spp.). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 83: 1055–1067.
Hughes, T.E., 1950. The physiology of the alimentary canal ofTyroglyphus farinae. Q.J. Microscopical Sci., 91: 45–61.
Hummel, B.C.W., 1959. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin and thrombin. Can. J. Biochem., 37: 1393–1399.
Ino, Y., Ando, T., Haida, M., Nakamura, K., Iwaki, M., Okudaira, H. and Miyamoto, T., 1989 Characterization of the proteases in the crude mite extract. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol., 89: 321–326.
International Workshop Report, 1988. Dust mite allergens and asthma: A worldwide problem. Bull. W.H.O., 66: 769–780.
Kent, N.A., Hay, D.B., Holland, P.W.H. and Hart, B.J., 1990. The molecular characterisation of house dust mite allergens. Clin. Exp. Allergy, 20 Suppl. 1: 116.
Lake, F.R., Ward, L.D., Simpson, R.J., Thompson, P.J. and Stewart, G.A., 1991. House dust mite derived amylase: Allergenicity and physicochemical characterisation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 87: 1035–1042.
Moritz, B. and Crailsheim, K., 1987. Physiology of protein digestion in the midgut of the honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). J. Insect Physiol., 33: 923–931.
Osserman, E.F. and Lawlor, D.P., 1966, Serum and urinary lysozyme (muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukemia. J. Exp. Med., 124: 921–951.
Peters, W. and Kalnins, M., 1985. Aminopeptidases as immobilised enzymes on the peritrophic membranes of insects. Entomol. Genet., 11: 25–32.
Peterson, G.L., 1983. Determination of total protein. Methods in Enzymology, 91: 95–119.
Simpson, R.J., Nice, E.C., Moritz, R.L. and Stewart, G.A., 1989. Structural studies on the allergenDer p I from the house dust miteDermatophagoides pteronyssinus: similarity with cysteine proteinases. Protein Seq. Data Anal., 2: 17–21.
Stewart, G.A., Butcher, A., Lees, K. and Ackland, J., 1986. Immunochemical and enzymatic analyses of extracts of the house dust miteDermatophagoides pteronyssinus. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 77: 14–24.
Stewart, G.A., Nisbet, A., Thomas, W.R., Chua, K.Y. and Steinkrug, S., 1988. Immunobiology of proteases from the house dust mite. N. Engl. Allergy Proc., 9: 415.
Stewart, G.A., Thompson, P.J. and Simpson, R.J., 1989. Protease antigens from house dust mite. Lancet, 2: 154–155 and correction, Lancet, 2: 462.
Stewart, G.A., Lake, F.R., Bird, C.H. and Thompson, P.J., 1990. Mite allergens as digestive enzymes. In: A. Sehon, D. Kraft and G. Kunkel (Editors), Epitopes of Atopic Allergens, Workshop Proceedings, XIVth Congress of the European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology, Berlin. The UCB Institute of Allergy, Brussels, Belgium, pp. 83–86.
Stewart, G.A., Lake, F.R. and Thompson, P.J., 1991. Faecally derived hydrolytic enzymes fromDermatophagoides pteronyssinus: Physicochemical characterisation of potential allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol., 95: 248–256.
Takahashi, K., Aoki, T., Kohmoto, S., Nishimura, H., Kodera, Y., Matsushima, A. and Inada, Y., 1990. Activation of kallikrein system in human plasma with purified serine protease fromDermatophagoides farinae. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol., 91: 80–85.
Terra, W.R., Ferreira, C. and De Bianchi, A.G., 1979. Distribution of digstive enzymes among the endo- and ectoperitrophic spaces and midgut cells ofRhynchnosciara and its physiological significance. J. Insect Physiol., 25: 487–494.
Terra, W.R., Espinoza-Fuentes, F.P. and Ferreira, C., 1988. Midgut amylase, lysozyme, aminopeptidase and trehalase from larvae and adults ofMusca domestica. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol., 9: 283–297.
Tomarelli, R.M., Charney, J. and Harding, M.L., 1949. The use of azoalbumin as a substrate in the colourimetric determination of peptic and tryptic activity. J. Lab. Clin. Med., 34: 428–433.
Tovey, E.R. and Baldo, B.A., 1987. Comparison by electroblotting of IgE-binding components in extracts of house dust mite bodies and spent mite culture. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 79: 93–102.
Tovey, E.R., Chapman, M.D. and Platts-Mills, T.A.E., 1981. Mite faeces are a major source of house dust allergens. Nature, 289: 592–593.
Trinder, P., 1969. Determination of blood glucose using 4-amino phenazone as oxygen acceptor. J. Clin. Pathol., 22: 246.
Trudinger, M., Chua, K.Y. and Thomas, W.R., 1991. cDNA encoding the major mite allergenDer f II. Clin. Exp. Allergy, 21: 33–37.
Wharton, G.W. and Brody, A.R., 1972. The peritrophic membrane of the miteDermatophagoides farinae: Acariformes. J. Parasitol., 58: 801–804.
Worthington, 1982. Enzymes and Related Biochemicals. Worthington Diagnostic Systems, Freehold, NJ, pp. 28–29.
Yuuki, T., Okumura, Y., Ando, T., Yamakawa, H., Suko, M., Haida, M. and Okudaira, H., 1990. Cloning and sequencing of cDNAs corresponding to major mite allergenDer f II Jpn. J. Allergol., 39: 557–561.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stewart, G.A., Bird, C.H., Krska, K.D. et al. A comparative study of allergenic and potentially allergenic enzymes fromDermatophagoides pteronyssinus, D. farinae andEuroglyphus maynei . Exp Appl Acarol 16, 165–180 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01201499
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01201499