Abstract
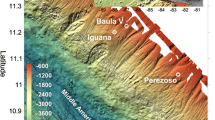
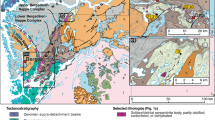
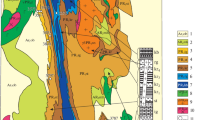
Over 20 occurrences of discontinuous limestone blocks, locally called “calcari aLucina,” were mapped in the Tuscan—Romagna region of the northern Italian Apennines. The limestones, consisting of a variable mixture of authigenic carbonates (calcite, dolomite, and aragonite), sulfides (primarily pyrite), and allogenic silicates, occur in association with turbidite and hemipelagite units that were deposited in foredeep basins during early to late Miocene times. The limestone blocks are interpreted to represent relicts of carbonate buildups formed around methane-rich fluid vents on the basis of their (1) striking petrographic similarities to carbonates from cold vents in the modern oceans; (2) unique chemosynthetic-like fauna, and (3) anomalously negativeδ 13C values (δ 13C = − 16‰ to − 58‰ PDB). The contemporaneous tectonism of the Apennine orogeny is likely to be the primary cause for the expulsion of the methane-rich fluids to the seabed in a manner analogous to the fluid-flow processes occurring at modern accretionary prisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon P (1988) A stable isotope study of magnesites from the Rum Jungle uranium field, Australia: Implications for the origin of strata-bound massive magnesites. Chemical Geology 69:127–145
Aharon P (1994) Geology and biology of modern and ancient submarine hydrocarbon seeps and vents: An introduction. Geo-Marine Letters 14:69–73
Aharon P and Sen Gupta BK (1994) Bathymetric reconstructions of the Miocene-age “calcari aLucina” (northern Apennines, Italy) from oxygen isotopes and benthic Foraminifera. Geo-Marine Letters 14:219–230
Aharon P, Graber ER, and Roberts HH (1992) Dissolved carbon andδ 13C anomalies in the water column caused by hydrocarbon seeps on the northwestern Gulf of Mexico slope. Geo-Marine Letters 12:33–40
Aharon P, Terzi C, Ricci Lucchi F, Vai GB, and Taviani M (1993) Fossil record of hydrocarbon and fluid venting imprinted on the Miocene-ageLucina limestones of the northern Apennines, Italy. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Program with Abstracts, New Orleans, 25–28 April, p 66
Baker PA and Kastner MA (1981) Constraints on the formation of sedimentary dolomite. Science 213:214–216
Beauchamp B, Krouse HR, Harrison JC, Nassichuck WW, and Eliuk LS (1989) Cretaceous cold seep communities and methanederived carbonates in the Canadian Arctic. Science 244:53–56
Berti M, Cuzzani MG, Landuzzi A, Taviani M, Aharon P, and Vai GB (1994) Hydrocarbon-derived imprints in olistostromes of the Early Serravallian Marnoso-arenacea Formation, Romagna Apennines (Italy). Geo-Marine Letters 14:192–200
Boccaletti M, Calamita F, Deiana G, Gelati R, Massari F, Moratti G, and Ricci Lucchi F (1990) Migrating foredeep-thrust belt system in the northern Apennines and southern Alps. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 77:3–14
Boulegue J, Charlou JL, and Jedwab J (1986) Fluids from subduction zones off Japan. EOS, Transactions, American Geophysical Union 67:1204
Brooks JM, Kennicutt MC, Bidigare RR, Wade TL, Powell EN, Denoux GJ, Fay RR, Childress JJ, Fisher CR, Rossman I, and Boland G (1987) Hydrates, oil seepage and chemosynthetic ecosystems on the Gulf of Mexico slope: An update. EOS, Transactions, American Geophysical Union 68:498–499
Buczynski C and Chafetz HS (1991) Habit of bacterially induced precipitates of calcium carbonate and the influence of medium viscosity on mineralogy. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 61:226–233
Campbell KA (1992) Recognition of Mio-Pliocene cold seep setting from the northeast Pacific convergent margin, Washington, USA. Palaios 7:422–433
Childress JJ and Fisher CR (1992) The biology of hydrothermal vent animals: Physiology, biochemistry, and autotrophic symbioses. Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review 30:337–441
Clari P, Gagliardi C, Governa ME, Ricci B, and Zuppi GM (1988) I Calcari di Marmorito: Una testimonianza di processi diagenetici in presenza di metano. Bolletino del Museo Regionale di Scienze Naturali di Torino 6:197–216
Goedert JL and Squires RL (1990) Eocene deep sea communities in localized limestones formed by subduction-related methane seeps, southwestern Washington. Geology 18:1182–1185
Hovland M, Talbot MR, Qvale H, Olaussen S, and Aasberg L (1987) Methane-related carbonate cements in pockmarks of the North Sea. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 57:881–892
Kulm LD and Suess E (1990) Relationship between carbonate deposits and fluid venting: Oregon accretionary prism. Journal of Geophysical Research 95:8899–8915
Kulm LD, Suess E, Moore JC, Carson B, Lewis BT, Ritger SD, Thornburg TM, Embley RW, Rugh WD, Massoth GJ, Langseth MG, Cochrane GR, and Scamman RL (1986) Oregon subduction zone: Venting, fauna and carbonates. Science 231:561–566
MacDonald IR, Boland GS, Baker JS, Brooks JM, Kennicutt MC, and Bidigare RR (1989) Gulf of Mexico hydrocarbon seep communities II: Spatial distribution of seep organisms and hydrocarbons at Bush Hill. Marine Biology 101:235–247
Mattavelli L, Ricchiuto T, Grignani D, and Schoell M (1983) Geochemistry and habitat of natural gases in Po basin, northern Italy. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin 67:2239–2254
Paull CK, Hecker B, Commeau R, Freeman-Lynde RP, Neumann C, Corso WP, Golubic S, Hook JE, Sikes E, and Curray J (1984) Biological communities at the Florida escarpment resemble hydrothermal vent taxa. Science 226:965–967
Ricci Lucchi F (1975) Miocene paleogeography and basin analysis. In: Squires C (Ed.), Geology of Italy. Tripoli: Earth Sciences Society of Libyan Arab Republic, pp 129–236
Ricci Lucchi F and Vai GB (1994) A stratigraphic and tectonofacies framework of the “calcari aLucina” in the Apennine chain, Italy. Geo-Marine Letters 14:210–218
Ritger S, Carson B, and Suess E (1987) Methane-derived authigenic carbonates formed by subduction induced pore-water expulsion along the Oregon—Washington margin. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America 98:147–156
Roberts HH and Aharon P (1994) Hydrocarbon-derived carbonate buildups of the northern Gulf of Mexico continental slope: A review of submersible investigations. Geo-Marine Letters 14:135–148
Roberts HH, Aharon P, Carney R, Larkin JM, and Sassen R (1990) Sea floor responses to hydrocarbon seeps, Louisiana continental slope. Geo-Marine Letters 10:232–243
Sibuet M, Juniper SK, and Pautot G (1988) Cold-seep benthic communities in the Japan subduction zones: Geological control of community development. Journal of Marine Research 46:333–348
Taviani M (1994) The “calcari aLucina” Macrofauna Reconsidered: Deep-sea faunal oases from Miocene-age cold vents in the Romagna Apennines, Italy. Geo-Marine Letters 14:185–191
Terzi C (1992) Applicazioni della geochimica degli isotopi stabili (ossigeno e carbonio): I calcari aLucina dell'Apennino Tosco-Romagnolo. Unpublished PhD dissertation. University of Bologna, 91 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terzi, C., Lucchi, F.R., Vai, G.B. et al. Petrography and stable isotope aspects of cold-vent activity imprinted on Miocene-age “calcari aLucina” from Tuscan and Romagna Apennines, Italy. Geo-Marine Letters 14, 177–184 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01203729
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01203729