Summary
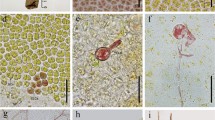
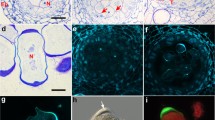
The mitoses and cytokineses leading to the formation of male and female gametes inOedogonium cardiacum are described at the ultrastructural level. Preceeding spermatogenesis, the nucleus and spindle are apically polarized for the first division, abutting the end wall near a ring which is much smaller than that characteristic of vegetative division. Cell division then cuts off a small, discoidal antheridial cell, a process repeated several times for each vegetative cell. The antheridial cell then divides once or twice more, generally transversely and/or longitudinally, but wall rupture and ring expansion play no role in these latter divisions. Fusion of vesicles lead to cross wall formation during the first two divisions, but membrane furrowing through the phycoplast partitions the daughter spermatids at the third and last cytokinesis. Discrete but amorphous bodies inside the poles of spermatogenous spindles are interpreted as Microtubule-Organizing-Centers, responsible for organizing the spindle microtubules.
The nucleus and spindle are also highly polarized for the division that forms an oogonium and its complementary suffultory cell. However, polarization is now strongly basal, and the asymmetric cytokinesis partitions the cell so that most of the cytoplasm moves during expansion into the future oogonium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coss, R. A., and J. D.Pickett-Heaps, 1973: Gametogenesis in the green algaOedogonium cardiacum. II. Spermiogenesis. In preparation.
Fritsch, F. E., 1935: Structure and reproduction of the algae. Vol. I. Cambridge Univ. Press.
Geitler, L., 1961: Über die Polarität der Zellen und Fäden vonOedogonium. Österr. Bot. Z.108, 5–19.
Gussewa, K., 1931: Über die geschlechtliche und ungeschlechtliche Fortpflanzung vonOedogonium capillare Ktz. im Lichte der sie bestimmenden Verhältnisse. Planta12, 293–326.
Hill, G. J. C., andL. Machlis, 1968: An ultrastructural study of vegetative cell division inOedogonium borisianum. J. Phycol.4, 261–271.
—, 1970: Defined media for growth and gamete production by the green algaOedogonium cardiacum. Plant Physiol.46, 224–226.
Hirn, K. E., 1900: Monographie und Ikonographie der Oedogonien. Jb. Wiss.9, 1–35.
Hoffman, L. R., 1961: Studies on the morphology, cytology and reproduction ofOedogonium andOedocladium. Ph. D. Diss., University of Texas, Austin, U.S.A.
—, 1970: Observations on the fine structure ofOedogonium. VI. The striated component of the compound flagellar “roots” ofO. cardiacum. Canad. J. Bot.48, 189–196.
—, 1971: In: Contributions in phycology (B. C. Parker andR. M. Brown, Jr., eds.), pp. 93–106. Lawrence, Kansas: Allen Press.
— andI. Manton, 1963: Observations on the fine structure ofOedogonium. II. The spermatozoid ofO. cardiacum. Amer. J. Bot.50, 455–463.
Locke, M., andN. Krishnan, 1971: Hot alcoholic phosphotungstic acid and uranyl acetate as routine stains for thick and thin sections. J. Cell Biol.50, 550–556.
Manton, I., K. Kowallik, andH. A. von Stosch, 1969 a: Observations on the fine structure and development of the spindle at mitosis and meiosis in a marine centric diatom (Lithodesmium undulatum). I. Preliminary survey of mitosis in spermatogonia. J. Micro.89, 295–320.
— — —, 1969 b: Observations on the fine structure and the development of the spindle at mitosis and meiosis in a marine centric diatom (Lithodesmium undulatum). II. The early meiotic prophases in male gametogenesis. J. Cell Sci.5, 271–298.
— — —, 1970 a: Observations on the fine structure and development of the spindle at mitosis and meiosis in a marine centric diatom (Lithodesmium undulatum). III. The later stages of meiosis I in male gametogenesis. J. Cell Sci.6, 131–157.
— — —, 1970 b: Observations on the fine structure and development of the spindle at mitosis and meiosis in a marine centric diatom (Lithodesmium undulatum). IV. The second meiotic division and conclusion. J. Cell Sci.7, 407–443.
Ohashi, H., 1930: Cytological study ofOedogonium. Bot. Gaz.90, 177–197.
Petry, K., 1968: Entwicklungsgeschichtliche Untersuchungen anChromophyton rosanofii und einigen Chlorophyceen. Österr. Bot. Z.115, 447–481.
Pickett-Heaps, J. D., 1968 a: Ultrastructure and differentiation inChara fibrosa. III. Formation of the antheridium. Aust. J. Biol. Sci.21, 255–274.
—, 1968 b: Ultrastructure and differentiation inChara fibrosa. IV. Spermatogenesis. Aust. J. Biol. Sci.21, 655–690.
—, 1969: The evolution of the mitotic apparatus: An attempt at comparative ultrastructural cytology in dividing plant cells. Cytobios3, 257–280.
—, 1971: Reproduction by zoospores inOedogonium. I. Zoosporogenesis. Protoplasma72, 275–314.
Pickett-Heaps, J. D., 1972 a: Reproduction by zoospores inOedogonium. IV. Cell division in the germling and evidence concerning the possible evolution of the wall rings. Protoplasma74, 195–212.
—, 1972 b: Variation in mitosis and cytokinesis in plant cells: its significance in the phylogeny and evolution of ultrastructural systems. Cytobios5, 59–77.
- 1973: Structure, reproduction and evolution in some green algae. In preparation.
—, andL. C. Fowke, 1970 a: Cell division inOedogonium. II. Nuclear division in O.cardiacum. Aust. J. Biol. Sci.23, 71–92.
—, 1970 b: Cell division inOedogonium. III. Golgi bodies, wall structure and wall formation in O.cardiacum. Aust. J. Biol. Sci.23, 93–113.
Pringsheim, N., 1858: Beiträge zur Morphologie und Systematik der Algen. I. Morphologie der Oedogonien. Jb. Wiss.1, 1–81.
Reynolds, S., 1963: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.17, 208–211.
Spurr, A. R., 1969: A low-viscosity epoxy embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res.26, 31–43.
Tiffany, L. H., 1930: TheOedogoniaceae. Columbus, 188 pp.
Turner, F. R., 1968: An ultrastructural study of plant spermatogenesis: spermatogenesis inNitella. J. Cell Biol.37, 370–393.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coss, R.A., Pickett-Heaps, J.D. Gametogenesis in the green algaOedogonium cardiacum . Protoplasma 78, 21–39 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01281520
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01281520