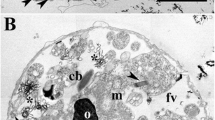
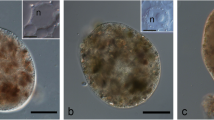
Summary
Generation of movement in benthic diatoms is thought to be intimately associated with secretion at the raphe, a slit in the silica cell wall. The presence and distribution of extracellular substances and their source was investigated cytochemically by transmission electron microscopy. Extracellular material, possibly-acid mucopolysaccharide, was observed consistently within the entire length of the raphe of both valves and also as a sheath enveloping the silica frustule. Such quantities of extracellular material are absent in conventionally fixed motile diatoms. Numerous cytoplasmic vesicles, with fibrillar contents, distributed peripherally but concentrated along the raphe and at the cell poles, react strongly with a polysaccharide specific stain; their distribution in the cell and polysaccharide content suggest these may be the source of raphe and sheath material. Results support the most recent theories on the mechanism of locomotion in outline only; the details cannot be clarified. Localization procedures using alcian blue and silver staining of peroxidised sections are discussed briefly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behnke, O., Zelander, T., 1970: Preservation of intercellular substances by the cationic dye alcian blue in preparative procedures for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res.31, 424–438.
Chamberlain, A. H. L., 1976: Algal settlement and secretion of adhesive materials. Proc. 3rd Int. Biodegradation Symp. (Sharpley, J. M., Kaplan, A. M., eds.), pp. 417–432. Barking (UK): Applied Science Publishers Ltd.
Coombs, J., Volcani, B. E., 1968: Studies on the biochemistry and fine structure of silica-shell formation in diatoms. Chemical changes in the wall ofNavicula pelliculosa during its formation. Planta82, 280–292.
Cox, E. J., 1981: Mucilage tube morphology of three tube-dwelling diatoms and its diagnostic value. J. Phycol.17, 72–80.
Drews, G., Nultsch, W., 1962: Spezielle Bewegungsmechanismen von Einzellern. In: Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology (Ruhland, W., ed.),17, pp. 876–919. Berlin: Springer.
Drum, R. W., 1969: Light and electron microscope observations on the tube-dwelling diatomAmphipleura rutilans (Trentepohl) Cleve. J. Phycol.5, 21–26.
—,Pankratz, H. S., 1964: Pyrenoids, raphes and other fine structures of diatoms. Amer. J. Bot.51, 405–418.
—,Hopkins, J. T., 1966: Diatom locomotion: an explanation. Protoplasma62, 1–33.
—,Pankratz, H. S., Stoermer, E. F., 1966: Diatomeenschalen im elektronenmikroskopischen Bild (Helmcke, J. G., Krieger, W., eds.), Teil VI. Lehr: Cramer.
Edgar, L. A., 1979: Diatom locomotion. Bristol: Ph. D. Thesis.
—, 1980: Fine structure ofCaloneis amphisbaena (Bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol.16, 62–72.
Francisco, A. De, Roth, L. E., 1977: The marine diatomStriatella unipunctata. I. Cytoplasmic fine structure with emphasis on the Golgi apparatus. Cytobiologie14, 191–206.
Harper, M. A., 1977: Movements. In: The Biology of Diatoms (Werner, D., ed.), pp. 224–249. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
—,Harper, J. T., 1967: Measurements of diatom adhesion and their relationship with movement. Brit. Phycol. Bull.3, 195–207.
Hopkins, J. T., 1967: The diatom trail. J. Queckett micr. Cl.30, 209–217.
—,Drum, R. W., 1966: Diatom motility: an explanation and a problem. Brit. Phycol. Bull.3, 63–67.
Hufford, T. L., Collins, G. B., 1972: The stalk of the diatomCymbella cistula: SEM observations. J. Phycol.8, 208–210.
Huntsman, S. A., Sloneka, J. M., 1971: An exocellular polysaccharide from the diatomGomphonema olivaceum. J. Phycol.7, 261–264.
Lauterborn, R., 1896: Untersuchungen über Bau, Kernteilung und Bewegung der Diatome. Leipzig: Engelmann.
Lewin, J. C., 1955: The capsule of the diatomNavicula pelliculosa. J. gen. Microbiol.13, 162–169.
Lewis, P. R.,Knight, D. P., 1977: Staining methods for sectioned material. In: Practical Methods in Electron Microscopy (Glauert, A. M., ed.) 5(1), pp. 77–135.
Marinozzi, V., 1961: Silver impregnation methods of ultrathin sections for electron microscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.9, 121–133.
Mollenhauer, H. H., 1964: Plastic embedding mixtures for use in electron microscopy. Stain Technology39, 11.
Parker, B. C., Diboll, A. G., 1966: Alcian stains for histochemical localization of acid and sulphated polysaccharides in algae. Phycologia6, 37–46.
Pickett-Heaps, J. D., Tippit, D. H., Andreozzi, J. A., 1978: Cell division in the pennate diatomPinnularia. I. Early stages in mitosis. Biol. Cellulaire33, 71–78.
— — —, 1979: Cell division in the pennate diatomPinnularia, III. The valve and associated cytoplasmic organelles. Biol. Cellulaire35, 195–198.
Reimann, B. E. P., Lewin, J. C., Volcani, B. E., 1965: Studies on the biochemistry and fine structure of silica shell formation in diatoms. I. The structure of the cell wall ofCylindrotheca fusiformis Reimann andLewin. J. Cell Biol.24, 39–55.
— — —, 1966: Studies on the biochemistry and fine structure of silica shell formation in diatoms. II. The structure of the cell wall ofNavicula pelliculosa (Breb) Hilse. J. Phycol.2, 74–84.
Ross, R., Cox, E. J., Karayeva, N. I., Mann, D. G., Paddock, T. B. B., Simonsen, R., Sims, P. A., 1979: An amended terminology for the siliceous components of the diatom cell. Nova Hedwigia Beih.64, 513–533.
Schenk, E., 1981: Note from the Biological Stain Commission. A newly certified dye-Alcian Blue 8 GX. Stain Technol.56, 129–131.
Schofield, B. H., Williams, B. R., Doty, S. B., 1975: Alcian blue staining of cartilage for electron microscopy. Application of the critical electrolyte concentration principle. Histochem. J.7, 139–149.
Scott, J. E., Dorling, J., 1969: Periodate oxidation of acid polysaccharides. III. A PAS method for chondroitin sulphates and other glycosamino-glycuronans. Histochemie19, 295–307.
Thiéry, J.-P., 1967: Mise en évidence des polysaccharides sur coupes fines en microscopie électronique. J. Microscopie6, 987–1018.
—, 1969: Role de l'appareil de Golgi dans la synthèse des mucopolysaccharides, étude cytochimique. I. Mise en évidence de mucopolysaccharides dans les vésicules de transition entier, l'ergastoplasme et l'appareil de Golgi. J. Microscopie8, 689–708.
Tippit, D. H., Pickett-Heaps, J. D., 1977: Mitosis in the pennate diatomSurirella ovalis. J. Cell Biol.73, 705–727.
Trainor, F. R., 1978: Introductory Phycology. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edgar, L.A., Pickett-Heaps, J.D. Ultrastructural localization of polysaccharides in the motile diatomNavicula cuspidata . Protoplasma 113, 10–22 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01283035
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01283035