Abstract
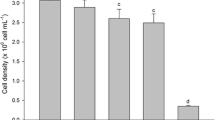
The effect of zinc on cell division, photosynthesis, ultrastructure, respiration, ATP levels, mitochondrial electron-transport chain (ETC)-activity, total thiols and glutathione in the marine diatomNitzschia closterium (Ehrenberg) W. Smith was investigated. Although 65µg Zn 1−1 halved the cell division rate, photosynthesis and respiration were unaffected by zinc concentrations up to 500µg Zn 1−1. Most of the zinc associated with the cells was bound at the cell surface, with only 3 to 4% of this extracellular zinc penetrating the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, zinc exerted its toxicity at a number of sites. Increased ATP production and ETC activity were observed in zinc-treated cells. Zinc also enhanced cellular thiols (SH) and total glutathione, and zinc toxicity was reversible by the addition of thiol compounds such as cysteine. Zinc-thiol binding may be a detoxification mechanism for the cell. It is suggested that increased ATP production may provide the energy required for increased glutathione synthesis at the expense of other energy-requiring processes including cell division. The mechanisms of toxicity of ionic zinc and copper toN. closterium were compared.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Anderson, M. E. (1985). Tissue glutathione. In: Greenwald, R. A. (ed.) CRC handbook of methods for oxygen radical research. CRC Press, Florida, p. 317–323
Bates, S. S., Tessier A., Campbell, P. G. C., Létourneau, M. (1985). Zinc-phosphorus interactions and variation in zinc accumulation during growth ofChlamydomonas variabilis (Chlorophyceae) in batch culture. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 42: 86–94
Chvapil, M. (1973). New aspects in the biological role of zinc: a stabilizer of macromolecules and biological membranes. Life Sciences 13: 1041–1049
Colowick, S. P., Kaplan, N. O. (eds.) (1955). Methods in enzymology. Vol. II. Academic Press, New York
Crespo, S., Sala, R. (1986). Chloride cell mitochondria are target organelles in acute zinc contamination. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 17: 329–331
Davies, A. G. (1973). The kinetics of and a preliminary model for the uptake of radio-zinc byPhaeodactylum tricornutum in culture. In: Radioactive contamination of the marine environment. Proceedings of a symposium, Seattle. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, p. 403–420
Davies, A. G. (1976). An assessment of the basis of mercury tolerance inDunaliella tertiolecta. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 56: 39–57
Davies, A. G. (1978). Pollution studies with marine plankton. Part II. Heavy metals. In: Russell, F. S., Yonge, M. (eds.) Advances in marine biology. Vol 15. Academic Press, London, p. 381–508
Fisher, N. S., Jones, G. J. (1981). Effects of copper and zinc on growth, morphology and metabolism ofAsterionella japonica (Cleve). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 51: 37–56
Gillan, F. T., Fisher, N. S., Johns, R. B. (1983). The effects of copper and zinc on the fatty acids and carotenoids in the marine diatomAsterionella japonica. Botanica mar. 26: 255–257
Grassetti, D. R., Murray, J. F. (1967). Determination of sulfhydryl groups with 2,2′ or 4,4′ dithiodipyridine. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 119: 41–49
Grill, E., Winnacker, E. L., Zenk, M. H. (1985) Phytochelatins: the principal heavy-metal complexing peptides of higher plants. Science, N.Y. 230: 674–676
Grill, E., Winnacker, E. L., Zenk, M. H. (1987). Phytochelatins, a class of heavy-metal-binding peptides from plants, are functionally analogous to metallothioneins. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84: 439–443
Guillard, R. R. L., Ryther, J. H. (1962). Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I.Cyclotella nana andDetonula confervaceae Hustedt (Cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 8: 229–239
Hasle, G. R. (1964).Nitschia andFragilariopsis species studied in the light and electron microscopes. I. Some marine species of the groupsNitzschiella andLanceolatae, Skr. norske Vidensk-Akad. Mat.-naturv. K1(N.S.) 16: 1–48
Holm-Hansen, O., Booth, C. R. (1966). The measurement of adenosine triphosphate in the ocean and its ecological significance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 11: 510–519
Jocelyn, P. C. (1972). Biochemistry of the SH group. Academic Press, New York
Kenner, R. A., Ahmed, S. I. (1975). Measurements of electron transport activities in marine phytoplankton. Mar. Biol. 33: 119–127
Lumsden, B. G., Florence, T. M. (1983). A new algal assay procedure for the determination of the toxicity of copper species in seawater. Envir. Technol. Lett. (U.K.) 4: 271–276
Meister, A. (1981). On the cycles of glutathione in metabolism and transport. In: Estabrook, R. W., Stere, P. (eds.) Current topics in cellular regulation. Vol. 18. Academic Press, New York, p. 21–58
Nath, J., Rebhun, L. I. (1976). Effects of caffeine and other methylxanthines on the development and metabolism of sea urchin eggs. Involvement of NADP+ and glutathione. J. Cell Biol. 68: 440–450
Shigeoka, S., Onishi, T., Nakano, Y, Kitaoka, S. (1987). Characterization and physiological function of glutathione reductase inEuglena gracilis z. Biochem. J. 242: 511–515
Stauber, J. L., Florence, T. M. (1985). The influence of iron on copper toxicity to the marine diatom,Nitzschia closterium (Ehrenberg) W. Smith. Aquat. Toxic. 6: 297–305
Stauber, J. L., Florence, T. M. (1986). Reversibility of copper-thiol binding inNitzschia closterium andChlorella pyrenoidosa. Aquat. Toxic. 8: 223–229
Stauber, J. L., Florence, T. M. (1987). Mechanism of toxicity of ionic copper and copper complexes to algae. Mar. Biol. 94: 511–519
Stauber, J. L., Florence, T. M. (1989). The effect of culture medium on metal toxicity to the marine diatomNitzschia closterium and the freshwater green algaChlorella pyrenoidosa. Wat. Res. 23: 907–911
Tel-Or, E., Huflejt, M., Packer, L. (1985). The role of glutathione and ascorbate in hydroperoxide removal in cyanobacteria. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 132: 533–539
Thomas, P., Woffard, H. W., Neff, J. (1982). Effects of cadmium on glutathione content of mullet (Mugil cephalus) tissues. In: Vernberg, W. B., Calabrese, A., Thurberg, F. P., Vernberg, F. J. (eds.) Physiological mechanisms of marine pollutant toxicity. Academic Press, New York, p. 109–125
Tietze, F. (1969). Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Analyt. Biochem. 27: 502–522
Van den Berg, C. M. G. (1982). Determination of copper complexation with natural organic ligands in seawater by equilibration with MnO2. II. Experimental procedures and application to surface seawater. Mar. Chem. 11: 323–342
Viarengo, A. (1985). Biochemical effects of trace metals. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 16: 153–158
Zhang, M., Florence, T. M. (1987). A novel adsorbent for the determination of the toxic fraction of copper in natural waters. Analytica chim. Acta 197: 137–148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stauber, J.L., Florence, T.M. Mechanism of toxicity of zinc to the marine diatomNitzschia closterium . Mar. Biol. 105, 519–524 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01316323
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01316323