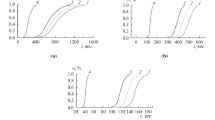
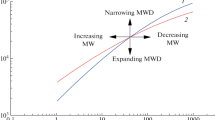
Abstract
A theory of a two-point rheometrical method of determination of the weight-average molecular weightM w of polyamide-6 is presented. The method is based on the measurement of the instantaneous values of zero-shear-rate viscosity of the degrading polymer melt, and a formula is derived which enables the calculation of the initial value ofM w (i.e. at zero-residence-time in molten state) of the investigated sample. The experimental verification of the method proves its applicability. The considerations carried out may be regarded as a first step towards developing a theory of an in-line rheometer for a continuous determination ofM w .
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a T :
-
temperature shift factor
- A :
-
constant, Pa · s · (kg/kmol)−3.4
- b M :
-
molecular weight shift factor
- b M0 :
-
initial molecular weight shift factor
- B :
-
activation energy of viscous flow, kJ/mol
- [c]:
-
concentration of so called active agent
- \(c_{\dot \gamma } \) :
-
shear rate shift factor
- C :
-
frequency factor in Arndt-Arrhenius equation, Pa · s
- C M :
-
Arndt-Arrhenius frequency factor in eq. (8), Pa · s
- d t :
-
residence time shift factor
- D :
-
constant in eq. (29), kg/kmol · (Pa · s)−0.294
- k :
-
degradation reaction rate constant, s−1
- k 1 :
-
polycondensation reaction rate constant, s−1
- k 2 :
-
random chain scission rate constant, s−1
- K :
-
Bueche constant, Pa · s (kg/kmol)
- K T :
-
Bueche constant in eq. (9), Pa · s (kg/kmol)−3.4
- [M]:
-
concentration of active end groups of polymer chains
- M nt :
-
instantaneous number-average molecular weight of the polymer, kg/kmol
- M wt :
-
instantaneous weight-average molecular weight of the polymer, kg/kmol
- M w0 :
-
initial weight-average molecular weight of the polymer, kg/kmol
- M w :
-
weight-average molecular weight of polymer melt, kg/kmol
- (M w0 )solution :
-
M w0 determined using solution method by Matthes, kg/kmol
- (M w0 )melt :
-
M w0 determined using “two-point” rheometrical method, kg/kmol
- M 1 :
-
molecular weight of monomeric segment of the polymer chain, kg/kmol
- m :
-
mass of the unit volume of polymer melt, kg
- n t :
-
instantaneous number of polymer chains in the unit volume of polymer melt
- N :
-
exponent in eq. (1)
- N t :
-
instantaneous total number of joints between monomeric segments within alln t polymer chains
- P nt :
-
instantaneous number-average polymerisation grade of the polymer
- P wt :
-
instantaneous weight-average polymerisation grade of the polymer
- q :
-
ratio, defined by eq. (A-19)
- R :
-
gas constant,R = 8.315 J/mol η K
- s t :
-
ratio, defined by eq. (A-5)
- t :
-
residence time in molten state, s
- t d :
-
limiting residence time in molten state, defined by eq. (35), s
- T :
-
temperature, K
- α :
-
frequency factor in eq. (4), s−1
- β :
-
activation energy of the reaction rate constant, kJ/mol
- \(\dot \gamma \) :
-
shear rate, s−1
- δ :
-
relative error of the melt or solution viscosity determination
- Δ sol :
-
relative error of the solution method by Matthes
- Δ melt :
-
relative error of the two-point rheometrical method
- η t :
-
instantaneous viscosity, Pa · s
- η 0 :
-
zero-shear-rate viscosity, Pa · s
- η 0t :
-
instantaneous zero-shear-rate viscosity, Pa · s
- η 0,0 :
-
initial (at zero-residence time) zero-shear-rate viscosity, Pa · s
- η 01 :
-
instantaneous zero-shear-rate viscosity att =t 1 , Pa · s
- η 02 :
-
instantaneous zero-shear-rate viscosity att = t 2 , Pa · s
- [η]:
-
intrinsic viscosity of the polymer
- ϑ :
-
frequency factor in eq. (35), s
- Λ t :
-
instantaneous rheological time constant in eq. (1), s
- µ :
-
Newtonian viscosity, Pa · s
- ρ :
-
density of the polymer melt, kg/m3
References
Kembłowski, Z., J. Torzecki, Polym. Eng. Sci.23, 425 (1982).
Kembłowski, Z., M. Michniewicz, J. Torzecki, in: G. Astarita, G. Marucci, L. Nicolais (eds.), Rheology, Vol. 3: Applications, p. 175, Plenum Press (New York 1980).
Bartenev, G. M., J. Polym. Sci. A-1,8, 3417 (1970).
Matthes, A., J. Pract. Chem.162, 245 (1943).
Lovett, A. J. et al., J. Polym. Sci., Chem. Ed.11, 2031 (1973).
Conley, R. T., R. A. Guadiana, in: R. T. Conley (ed.), Thermal Stability of Polymers, Vol. 1, Chap. 10, M. Dekker, Inc. (New York 1970).
Eirich, F. R., H. F. Mark, Soc. Chem. Ind. Monograph no. 13 (London) 43 (1961).
Goodings, E. P., ibid., p. 211.
Huczkowski, P., J. Kapko, R. Olesiak, Polymer19, 77 (1978).
Rafler, G. et al., Acta Polymerica31, 633 (1981).
Konomi, T., H. Tani, J. Polym. Sci. A-1,8, 1261 (1970).
Buxbaum, L. H., Angew. Chemie80, 225 (1968).
Abbas, K. B., Polymer21, 936 (1981).
Giori, C., B. T. Hayes, J. Polym. Sci. A-1,8, 335 (1970).
Henblein, G., Zum Ablauf Jonischer Polymerisationsreaktionen, Akademie-Verlag (Berlin 1975).
Heikens, D., J. Polym. Sci.22, 65 (1956).
Reimschuessel, H. K., G. J. Dege, J. Polym. Sci. A-1,8, 3265 (1970).
Reimschuessel, H. K., J. Polym. Sci.41, 457 (1959).
Fukumoto, O., J. Polym. Sci.22, 263 (1956).
Sych, G., Ch. Reichel, Faserforsch. Textiltechn.13, 256 (1962).
Pezzin, G., G. B. Gechele, J. Appl. Polym. Sci.8, 2195 (1964).
Tirrell, M. V. et al., Polym. Eng. Sci.15, 386 (1975).
Tuckett, R. F., Trans. Farad. Soc.41, 351 (1945).
Kardas, J. E. et al., Dokl. ANSSR156, 658 (1964).
Schaefgen, J. R., J. Polym. Sci.41, 133 (1959).
Jellinek, H. H. G., J. Polym. Sci.5, 264 (1950).
Boyd, R. H., in: R. T. Conley (ed.), Thermal Stability of Polymers, Vol. 1, Ch. 3, M. Dekker Inc. (New York 1970).
Tobolsky, A. V., A. M. Kotliar, T. C. P. Lee, ibid., Chap. 4.
Casassa, E. F., J. Polym. Sci.4, 405 (1949).
Engelne, M. V., A. B. Pakšver, Chem. Volokna No. 5, 5 (1973).
Marshall, J., A. Todd, Trans. Farad. Soc.49, 67 (1953).
Tomita, K., Polymer14, 50 (1973).
ibidem17, 221 (1976).
Zamorsky, Z., Faserforsch. Textiltechn.14, 271 (1963).
Malkin, A. Ja. et al., Vysokomol. soedin.A, 23, 1328 (1981).
Laun, H. M., Rheol. Acta18, 478 (1979).
Dietrich, K., S. Tolsdorf, G. Reinisch, Faserforsch. Textiltechn.23, 325 (1972).
Schroth, R., P. Beyer, Faserforsch. Textiltechn.16, 552 (1965).
Dumanskij, I. A., L. V. Khajlenko, L. V. Prokopenko, Koll. Zhurnal25, 646 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kembłowski, Z., Torzecki, J. Determination of the weight-average molecular weight of polyamide-6 on the basis of melt viscosity. Rheol Acta 22, 186–196 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01332371
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01332371