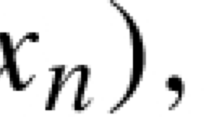Summary
The author applies the method of nondiscrete mathematical induction (see [2–5]) which involves considering the rate of convergence as a function, not as a number, to Newton's process and proves that the rate of convergence is
whered is a positive number depending on the initial data (see Theorem 2.3).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newton, I.: Collected Mathematical Papers. Cambridge University Press 1969
Pták, V.: Deux théorèmes de factorisation. Comptes Rendus Ac. Sci. Paris278, 1091–1094 (1974)
Pták, V.: A theorem of the closed graph type. Manuscripta Math.13, 109–130 (1974)
Pták, V.: A quantitative refinement of the closed graph theorem, Czech. Math. J.99, 503–506 (1974)
Pták, V.: Nondiscrete mathematical induction and iterative existence proofs. Linear Algebra and its Applications (in print)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pták, V. The rate of convergence of Newton's process. Numer. Math. 25, 279–285 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01399416
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01399416