Abstract
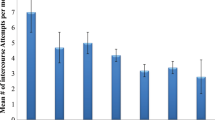
Reports of day-by-day sexual activity for the previous week were collected from a total community sample of over 900 pregnant and nonpregnant Thai women of childbearing age during a fertility survey in 1967–1968. About 13% of the women were pregnant. Examination of the women's intercourse frequencies at various stages of pregnancy revealed a downward trend as pregnancy progressed. However, a difference between the mean frequency for age-matched, nonmenstruating, nonpregnant women and that during any stage of pregnancy was not statistically significant at the p =0.05 level (t test, two-tailed) until the seventh month. Much individual variation existed among the women. Complete abstinence from intercourse during the previous week reached a peak of 72.7% in the ninth month. The increase in abstinence with the progression of pregnancy appeared linear. The importance of these data lies in two methodological facts: they were collected from a total population sample and are therefore unbiased by sample selection; the women were not asked to report their “average” frequencies for some time period in the past. Reports of behavior on each day of only the preceding week were the basis for the conclusion. Although the women are from a different culture, lay and professional advice concerning intercourse during pregnancy is similar to that in the United States. Because intercourse may be discouraged, particularly in the third trimester, it is difficult to attribute the observation of the gradual decline in frequency to a “physiological” reason. This tempting hypothesis, however, is worthy of further study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Falicov, C. J. (1973). Sexual adjustment during first pregnancy and post partum.Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 117: 991–1000.
Kenny, J. A. (1973). Sexuality of pregnant and breastfeeding women.Arch. Sex. Behav. 2: 215–229.
Masters, W. H. and Johnson, V. E. (1966).Human Sexual Response. Little, Brown, Boston, pp. 141–168.
Solberg, D. A., Butler, J., and Wagner, N. N. (1973). Sexual behavior in pregnancy.New Engl. J. Med. 288: 1098–1103.
Udry, J. R., Keovichit, S., Burnight, R., Cowgill, D. O., Morris, N. M., and Yamarat, C. (1971). Pregnancy testing as a fertility measurement technique: A preliminary report on field results.Am. J. Public Health 61: 344–352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research supported by a grant from the Rockefeller Foundation to the Carolina Population Center.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morris, N.M. The frequency of sexual intercourse during pregnancy. Arch Sex Behav 4, 501–507 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01542128
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01542128