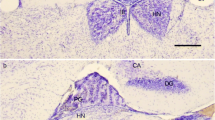
Summary
Pineocytomas have been induced in a high percentage of hamsters inoculated intracerebrally within 24 hours after birth with particular strains of a human papovavirus. Studies on biochemical and ultrastructural characteristics and transformations of such experimentally induced pineal tumors have led to important conclusions and implications: (1) Many of the differentiated pineocytoma cells contained organelles and related structures that are characteristic of hamster pineocytes, and others that are reminiscent of possible phylogenetic precursors, including pineal photoreceptor cells. (2) An inverse relationship was noted between degree of cytological differentiation and level of hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase (HIOMT) activity in the pineocytomas. (3) It is therefore apparent that even when pineal tumor formation leads to great increase in pinealocyte-like cells, their enzymatic capacity for synthesis of melatonin, and possibly of other humoral products, may be only 4 to 7% of that of normal pinealocytes if they are of a relatively less differentiated type.
A number of important and basic questions are accessible and remain to be investigated via experimental pineocytomas, such as: (1) nature and significance of cytological interactions within the pineal; (2) probable occurrences, correlations and transformations of other pineal biosynthetic and hormonal processes; (3) degree and nature of environmental (photic, circadian and circannual factors) and physiologic controls; and (4) kinds of modifications of pineal-related functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelrod, J., Wurtman, R. J., Snyder, S.: Control of hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase activity in the rat pineal gland by environmental lighting. J. Biol. Chem.240, 949–954 (1965).
Bridges, R., Tamarkin, L., Goldman, B.: Effects of photoperiod and melatonin on reproduction in the Syrian hamster. Ann. Biol. anim. Bioch. Biophys.16, 399–408 (1976).
Dalton, A. G., Haguenau, F. (eds. Ultrastructure of animal viruses and bacteriophages. New York: Academic Press. 1973.
Frauchiger, E., O'Hara, P. J., Shortridge, E. H.: Pinealome bei Tieren. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilk.108, 368–372 (1966).
Hoffmann, K.: Testicular involution in short photoperiods inhibited by melatonin. Naturwiss.61, 364–365 (1974).
Kitay, J. I.: Pineal lesions and precocious puberty: A review. J. Clin. Endocrinology and Metabolism14, 622–625 (1954).
Kitay, J. I., Altschule, M. D.: The pineal gland. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. 1954.
Knox, W. E.: Enzyme patterns in fetal, adult and neoplastic rat tissues, p. 232. Basel: S. Karger. 1972.
Kubo, O., Yamasaki, N., Kamijo, Y., Amano, K., Kitamura, K., Demura, R.: Human chorionic gonadotropin produced by ectopic pinealoma in a girl with precocious puberty. J. Neurosurg.47, 101–105 (1977).
Kurumado, K., Mori, W.: Virus-like particles in human pinealoma. Acta Neuropath.35, 273–276 (1979).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265 to 275 (1951).
Luginbühl, H., Fankhauser, R., McGrath, T.: Spontaneous neoplasms of the nervous system in animals. Progr. Neurol. Surg.2, 85–164 (1968).
Marburg, O.: Die Adipositas cerebralis; ein Beitrag zur Pathologie der Zirbeldrüse. Wien. med. Wschr.58, 2618–2622 (1908).
Melnick, J. L.: The papova virus group. In: Viral and Rickettsial Infections of Man (Horsfall, Tamm, eds.), 4th ed., pp. 841–859. Philadelphia: J. B. Lippincott Co. 1965.
Orme, S. K., Wells, S. A., Rabson, A. S., Wurtman, R. J.: In vitro neo-plastic transformation of hamster pineal cells by three oncogenic DNA viruses. Cancer21, 477–482 (1968).
Padgett, B. L., Walker, D. L., ZuRhein, G. M., Eckroade, R. J., Dessel, B. H.: Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. LancetI, 1257–1260 (1971).
Padgett, B. L., Walker, D. L., ZuRhein, G. M., Hodach, A. E., Chou, S. M.: JC Papovavirus in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Infect. Diseases133, 686–690 (1976).
Padgett, B. L., Walker, D. L., ZuRhein, G. M., Varakis, J. N.: Differential neurooncogenicity of strains of JC virus, a human polyoma virus, in newborn Syrian hamsters. Cancer Res.37, 718–720 (1977).
Quay, W. B.: Pineal chemistry in cellular and physiological mechanisms. Springfield, Ill.: Charles C Thomas. 1974.
Quay, W. B., Ma, Y.-H., Varakis, J. N., ZuRhein, G. M., Padgett, B. L., Walker, D. L.: Modification of hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase activity in experimental pineocytomas induced in hamsters by a human papovavirus (JC). J. Natl. Cancer Inst.58, 123–127 (1977).
Rabson, S. M., Mendenhall, E. N.: Familial hypertrophy of pineal body, hyperplasia of adrenal cortex and diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Clin. Path.26, 283 (1956).
Reiter, R. J., Blask, D. E., Johnson, L. Y., Rudeen, P. K., Vaughan, M. K., Waring, P. J.: Melatonin inhibition of reproduction in the male hamster: Its dependency on time of day of administration and on an intact and sympathetically innervated pineal gland. Neuroendocrinology22, 107 to 116 (1976).
Reiter, R. J., Rudeen, P. K., Vaughan, M. K.: Restoration of fertility in light-deprived female hamsters by chronic melatonin treatment. J. Comp. Physiol.111, 7–13 (1976).
Reiter, R. J., Vaughan, M. K.: A study of indoles which inhibit pineal antigonadotrophic activity in male hamsters. Endocrine Res. Commun.2, 299–308 (1975).
Reiter, R. J., Vaughan, M. K., Waring, P. J.: Prevention by melatonin of short day induced atrophy of the reproductive systems of male and female hamsters. Acta Endocr.84, 410–418 (1977).
Rubinstein, L. J.: Tumors of the central nervous system. In: Atlas of Tumor Pathology, pp. 269–284. Washington, D. C.: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. 1972.
Russell, D. S.: The pinealoma: its relationship to teratoma. J. Path. Bact.56, 145–150 (1944).
Sokal, R. R., Rohlf, F. J.: Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research, pp. 223–226. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman & Co. 1969.
Turek, F. W., Desjardins, C., Menaker, M.: Melatonin: antigonadal and progonadal effects in male golden hamsters. Science190, 280–282 (1975).
Varakis, J. N., ZuRhein, G. M.: Experimental pineocytoma of the Syrian hamster induced by a human papovavirus (JC). Acta Neuropath.35, 243–264 (1976).
Varakis, J. N., ZuRhein, G. M., Padgett, B. L., Walker, D. L., Quay, W. B., Ma, Y. M.: Experimental pineocytomas: A morphological, virological and biochemical study. J. Neuropath, and Exper. Neurol.35, 355 (1976).
Walker, D. L., Padgett, B. L., ZuRhein, G. M., Albert, A. E., Marsh, R. F.: Human papovavirus (JC): Induction of brain tumors in hamsters. Science181, 674–676 (1973).
Wells, S. A., jr., Wurtman, R. J., Rabson, A. S.: Viral neoplastic transformation of hamster pineal cells in vitro: retention of enzymatic function. Science154, 278–279 (1966).
West, R. J., Lloyd, J. K., Turner, W. M. L.: Familial insulin-resistant diabetes, multiple somatic anomalies, and pineal hyperplasia. Arch. Diseases in Childhood50, 703–708 (1975).
ZuRhein, G. M., Varakis, J. N.: Morphology of brain tumors induced in Syrian hamsters after inoculation with JC virus, a new human papovavirus. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Congress of Neuro-pathology, Budapest, 1974, Vol. 1, pp. 479–481. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation. 1975.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quay, W.B. Experimental and spontaneous pineal tumors: Findings relating to endocrine and oncogenic factors and mechanisms. J. Neural Transmission 48, 9–23 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01670030
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01670030