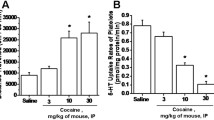
Summary
The human platelet in addition to having serotonin (5-HT) receptors, uptake carriers (receptor) and transmitter storage vesicles, primarily possesses mitochondrial monoamine oxidase (MAO) type B. Similar to the major form of MAO in the human brain, this enzyme actively oxidizes A-B and B substrates (tyramine, dopamine, phenylethylamine) as well as the novel secondary amine anticonvulsant, milacemide and dopaminergic neurotoxin, MPTP. 5-HT oxidation is hardly affected by the platelet enzyme and MAO inhibitors have no net effect on its accumulation. MAO-B is selectively inhibited by 1-deprenyl and thus the platelet enzyme may be useful to monitor the anti-Parkinson activity of such drugs, as related to their ability to inhibit brain MAO-B. The oxidation of the anticonvulsant, milacemide, to glycine in vitro and in vivo by MAO-B, may herald new prospects for the development of inert prodrugs capable of being metabolized to neuroactive substances by MAO-B. The plasma levels of their metabolites may be an index of MAO-B activity found in the platelet and brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashkenazi, R., The structural requirements of phenylethylamines in elicitating the serotonin syndrome, in: Enzymes and Neurotransmitters in Mental Disease, pp. 445–455. Eds E. Usdin, T. L. Sourkes and M. B. H. Youdim. Wiley, Chichester 1980.
Banerjee, D. K., Kelner, K., Offut, L., Pollard, H. B., and Youdim, M. B. H., Selective regulation of MAO-A but not B activity in cultured adrenal medullary endothelial cells by steroids. Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother.87 (1986) 67P.
Banerjee, D. K., Orenberg, R., Youdim, M. B. H., Heldman, E., and Pollard, H. B., Endothelial cells from bovine adrenal medulla develop capillary-like growth patterns in culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA82 (1985) 4702–4706.
Bevan Jones, A. B., Pare, C. M. B., Nicholson Price, K., and Stacey, R. S., Brain amine concentrations after monoamine oxidase inhibitor administration. Br. med. J.i (1972) 17–19.
Birkmayer, W., Riederer, P., Ambrozi, L., and Youdim, M. B. H., Implications of combined treatment with Madopar® and 1-deprenil in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet1 (1977) 439–444.
Braestrup, C., Andersen, H., and Randrup, A., the monoamine oxidase B inhibitor deprenyl potentiates phenylethylamine behavior in rats without inhibition of catecholamine metabolite formation. Eur. J. Pharmac.34 (1975) 181–188.
Cawthon, R. M., Pintar, J. E., Haseltine, F. P., and Breakefield, X. O., Differences in structure of A and B forms of human monoamine oxidase. J. Neurochem.37 (1981) 363–372.
Collins, G. G. S., Sandler, M., Williams, E. D., and Youdim, M. B. H., Multiple forms of human brain mitochondrial monoamine oxidase. Nature, Lond.225 (1970) 817–820.
Curtis, D. R., and Johnston, G. A. R., Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergebn. Physiol. Biol. comp. exp. Pharmac.69 (1974) 97–188.
Da Prada, M., Picotti, G. B., Kettler, R., and Launay, J. M., Serotonin, histamine, catecholamines and octopamine in blood platelets, in: Platelets: Cellular Response Mechanism and Their Biological Significance, pp. 277–288. Eds A. Rotman, F. A. Meyer, C. Gitler and E. Silberberg. Wiley, Chichester 1980.
Davidson, J., Mcleod, M. N., and Blum, R., Acetylation phenotype, platelet monoamine oxidase inhibition and the effectiveness of phenelzine in depression. Am. J. Psychiat.135 (1978) 147–152.
Denney, R. M., and Abell, C. W., The genetics of MAO, in: Monoamine Oxidase and Disease, pp. 243–252. Eds K. F. Tipton, P. Dostert and M. Strolin-Benedetti. Academic Press, London 1984.
Denney, R. M., Thorpe, L., Wesllund, K., Kochersperger, L. M., and Abell, C. W., Visualization of monoamine oxidase A and B in brain and peripheral tissues with monoclonal antibodies specific for the two forms of the enzyme, in: MPTP: A Parkinson Syndrome Producing Neurotoxin, pp. 645–650. Eds S. Markey, N. Castagnoli and I. J. Kopin. Academic Press, New York 1986.
Donelly, C. H., and Murphy, D. L., Monoamine oxidase in man: Enzyme characteristics in platelets, plasma and other human tissues. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmac.12 (1974) 71–85.
Donelly, C. H., Richelson, E., and Murphy, D. L., Properties of monoamine oxidase in mouse neuroblastoma NIE-115 cells. Biochem. Pharmac.25 (1976) 1639–1643.
Fowler, C. J., and Strolin-Benedetti, M., The metabolism of dopamine by both forms of monoamine oxidase in the rat brain and its inhibition by cimoxatone. J. Neurochem.40 (1983) 1534–1541.
Fowler, C. J., and Tipton, K. F., Deamination of 5-hydroxytryptamine by both forms of monoamine oxidase in the rat brain. J. Neurochem.38 (1982) 733–736.
Fowler, C. J., O’Carroll, A. M., and Tipton, K. F., Deamination of dopamine by monoamine oxidase A and B in rat and in man, in: Monoamine Oxidase and Disease, pp. 392–393. Eds K. F. Tipton, P. Dostert, and M. Strolin-Benedetti. Academic Press, London 1984.
Fowler, C. J., Tipton, K. F., Mackay, A. V. P., and Youdim, M. B. H., Human platelet monoamine oxidase — A useful enzyme in the study of psychiatric disorders? Neuroscience7 (1982) 1577–1594.
Garrick, N., and Murphy, D. L., Differences in selectivity towards norepinephrine compared to serotonin. Biochem. Pharmac.31 (1982) 4061–4067.
Grahame-Smith, D. G., et al., Human platelet 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors: Binding of [3H]-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Effects of chronic neuroleptic and antidepressant drug administration. Experientia44 (1987) 142–145.
Green, A. R., and Youdim, M. B. H., Effect of monoamine oxidase inhibition by clorgyline deprenyl or tranylcypromine on 5-hydroxytryptamine concentrations in rat brain and hyperactivity following subsequent tryptophan administration. Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother.55 (1975) 415–422.
Green, A. R., Mitchell, B., Tordoff, A., and Youdim, M. B. H., Evidence of dopamine deamination by both type A and type B monoamine oxidase in rat brain in vivo and for the degree of inhibition of enzyme necessary for increased functional activity of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother.60 (1977) 343–348.
Hamon, M., Bourgoin, S., and Youdim, M. B. H., Typtophan hydroxylation in the central nervous system, in: Aromatic Amino Acid Hydroxylases and Mental Diseases, pp. 233–298. Ed. M. B. H. Youdim. Wiley, Chichester 1984.
Heikkila, R. E., Manzio, L., Cabbat, F. S., and Duvoisin, R. C., Protection against the dopaminergic neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl 1,2,3,6-tetra hydropyridine by monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nature311 (1984) 467–469.
Johnston, J. P., Some observations upon a new inhibitor of monoamine oxidase in brain tissue. Biochem. Pharmac.17 (1968) 1285–1297.
Kalir, A., Sabbagh, A., and Youdim, M. B. H., Selective acetylenic ‘suicide’ and reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase type A and B. Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother.73 (1981) 55–64.
Knoll, J., and Magyar, K., Some puzzling pharmacological effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmac.5 (1972) 393–408.
Kochersperger, L. M., Wagnespack, A., Patterson, J. C., Hsieh, C. C. W., Weyler, W., Salach, J. I., and Denney, R. M., Immunological uniqueness of human monoamine oxidase A and B. New evidence from studies with monoclonal antibodies to human monoamine oxidase A. J. Neurosci.5 (1986) 2874–2881.
Kuhn, D., Wolf, W., and Youdim, M. B. H., 5-Hydroxytryptamine release in vivo from a cytoplasmic pool: Studies on the 5-HT behavioural syndrome in reserpinized rats. Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother.84 (1985) 121–129.
Kuhn, D., Wolf, W., and Youdim, M. B. H., Serotonin neurochemistry revisited: A new look at some old axioms. Neurochem. int.8 (1986) 141–154.
Langer, S., and Galzin, A.-M., Studies on the serotonin transporter in platelets. Experientia44 (1987) 127–130.
Larsen, J. K., and Rafaelsen, O. J., Long-term treatment of depression with ISO-carboxazide. Acta psychiat. neurol. scand.62 (1980) 456–463.
Laubscher, A., and Pletscher, A., Shape change and uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine in human blood platelets action of neuropsychiatric drugs. Life Sci.24 (1979) 1833–1840.
Levitt, P., Pintar, J., and Breakefield, X. O., Immunocytochemical demonstration of monoamine oxidase B in brain astrocytes and serotonergic neurons. Proc. natl Acad. Sci. USA79 (1982) 6385–6389.
Markey, S. P., Castagnoli, N. Jr. Trevor, A. J., and Kopin, I. J., (Eds), MPTP: A Neurotoxin Producing a Parkinsonian Syndrome. Academic Press, New York 1986.
Markey, S. P., Johanssen, J. N., Chiueh, C. C., Burns, R. S., and Herkenham, M. A., Interneuronal generation of a pyrimidium ion metabolite may cause drug-induced Parkinsonism. Nature311 (1984) 464–467.
Meldrum, B. S., Drugs acting on amino acid neurotransmitters, in: Myoclonus. Adv. Neurol., vol. 43, pp. 687–706. Eds S. Fahn, C. D. Marsden and M. Van Woert. Raven Press, New York 1986.
Mendlewicz, J., and Youdim, M. B. H., Anti-depressant potentiation of 5-hydroxytryptophan byl-deprenyl a MAO type B-inhibitor. J. neural Transm.48 (1978) 279–286.
Mendlewicz, J., and Youdim, M. B. H., Anti-depressant potentiation of 5-HTP by 1-deprenyl in affective illness. J. affect. Dis.2 (1980) 137–146.
Mendlewicz, J., and Youdim, M. B. H.,l-Deprenil. A selective monoamine oxidase type B inhibitor in the treatment of depression. A double blind evaluation. Br. J. Psychiat.142 (1983) 508–511.
O’Carroll, A. M., Fowler, C. J., Phillips, J. P., Tobia, I., and Tipton, K. F., The deamination of dopamine by human brain monoamine oxidase specificity for the two forms in seven brain regions. Arch. Pharmac.322 (1983) 198–202.
Oreland, L., The activity of human brain and thrombocyte monoamine oxidase (MAO) in relation to various psychiatric disorders, in: Monoamine Oxidase: Structure, Function and Altered Function, pp. 379–387. Eds T. P. Singer, R. W. Von Korff and D. L. Murphy. Academic Press, New York 1979.
Pletscher, A., Platelets as models of monoaminergic neurons, in: Essays in Neurochemistry and Neuropharmacology, vol. 4, pp. 49–101. Eds M. B. H. Youdim, W. Lovenberg, D. F. Sharman and L. Lagnado. Wiley, Chichester 1978.
Pletscher, A., and Laubscher, A., Use and limitation of platelets as models for neurons: Amine release and shape change reaction, in: Platelets: Cellular Response Mechanisms and Their Biological Significance, pp. 267–276. Eds A. Rotman, F. A. Meyer, C. Gitler, and A. Silberberg. Wiley, Chichester 1980.
Pollard, H. B., Ornberg, R., Levine, M., Kellner, K., Morita, K., Levine, R., Forsberg, E., Brocklehurst, K. W., Duong, L., Lelkes, P. I., Heldman, E., and Youdim, M. B. H., Hormone secretion by exocytosis with emphasis on information from chromaffin cell system. Vitams Horm.42 (1986) 109–194.
Raft, D., Davidson, J., Wasik, R., and Mattox, A., Relationship between response to phenelzine and MAO inhibition in a clinical trial of phenelzine amitriptyline and placebo. Neuroendocrinology7 (1981) 122–126.
Reynolds, G. P., Riederer, P., Sandler, M., Jellinger, K., and Seeman, D., Amphetamine and phenylethylamine in post-mortem Parkinson’s brain after (−) deprenyl administration. J. neural Transm.43 (1978) 271–277.
Riederer, P., Youdim, M. B. H., Rausch, W. D., Birkmayer, W., Jellinger, K., and Seemann, D., On the mode of action of 1-deprenyl in human central nervous system. J. neural Transm.43 (1978) 217–226.
Riederer, P., and Youdim, M. B. H., Brain monoamine oxidase activity and monoamine metabolism in Parkinson patients treated with 1-deprenyl. J. Neurochem.46 (1986) 1359–1365.
Roba, J., Milacemide: A novel anti-convulsant, in: New Anticonvulsant Drugs, pp. 179–190. Eds B. S. Meldrum and R. R. Porter, J. Libbey and Co., London 1986.
Salach, J. I., Detmer, K., and Youdim, M. B. H., The reaction of bovine and rat liver monoamine oxidase with (14C)-clorgyline and (14C)-deprenyl. Molec. Pharmac.16 (1979) 234–241.
Salach, J. I., Singer, T. P., Yasunobu, K. T., Minamura, N., and Youdim, M. B. H., Cysteinyl flavin in monoamine oxidase from the central nervous system, in: Monoamine Oxidase and Its Inhibition. Ciba Foundation Symposium 39, New Series, pp. 49–60. Elsevier, Amsterdam 1976.
Strolin-Benedetti, M., Sontag, N., Boucher, T., and Kan, J. P., Aliphatic amines as MAO substrates in the rat. The effect of selective inhibitors on the deamination ofn-pentylamine, in: Function and Regulation of Monoamine Enzymes, pp. 527–538. Eds E. Usdin, N. Weiner and M. B. H. Youdim. Macmillan, London 1981.
Tipton, K. F., Enzymology of monoamine oxidase. Cell Biochem. Funct.4 (1986) 79–87.
Tipton, K. F., Dostert, P., and Strolin-Benedetti, M. (Eds), Monoamine Oxidase and Disease. Academic Press, New York 1984.
Ungar, A., and J. H. Phillips, Regulation of the adrenal medulla. Physiol. Rev.63 (1983) 787–843.
de Varebeke, P. J., Cavalier, R., David-Remacle, M., and Youdim, M. B. H., Conversion of the novel anticonvulsant milacemide to glycine in the brain is mediated by monoamine oxidase B. J. Neurochem. (1987) in press.
Walker, W. H., Kearney, E. B., Seng, R. L., and Singer, J. P., The covalentyl-bound flavin of hepatic monoamine oxidase. 2. Identification and properties of cysteinyl riboflavin. Eur. J. Biochem.24 (1971) 328–331.
Westlund, K., Denney, R., Kochersperger, L., Rose, I. R., and Abell, C., Distinct monoamine oxidase A and B populations in primate brain. Science230 (1985) 181–183.
Wolf, W., Youdim, M. B. H., and Kuhn, D., Does brain 5-HIAA indicate serotonin release or monoamine oxidase activity. Eur. J. Pharmac.109 (1985) 381–387.
Youdim, M. B. H., and Ashkenazi, R., Serotonin in Biological Psychiatry. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmac.34 (1982) 35–60.
Youdim, M. B. H., and Finberg, J. P. M., Monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants, in: Psychopharmacology, pp. 38–57. Eds. D. G. Grahame-Smith, A. Hippius and H. Winoker. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam 1982.
Youdim, M. B. H., and Finberg, J. P. M., Monoamine oxidase inhibitors antidepressants, in: Psychopharmacology, pp. 37–71. Eds D. G. Grahame-Smith, A. Hippius and H. Winoker. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam 1985.
Youdim, M. B. H., and Hefez, A., Platelet function and monoamine oxidase activity in psychiatric disorders, in: Platelets: Cellular Response Mechanisms and their Biological Significance, pp. 289–306. Eds A. Rotman, F. A. Meyer, C. Gitler and A. Silberberg. Wiley, Chichester 1980.
Youdim, M. B. H., Banerjee, D. K., and Pollard, H. B., Isolated chromaffin cells from adrenal medulla contain primarily monoamine oxidase B. Science224 (1984) 619–621.
Youdim, M. B. H., Ben-Harari, R. R., and Bakhle, Y. S., Factors affecting monoamine inactivation in lung, in: Metabolic Aspects of the Lung. Ciba Foundation Symposium, no. 78, pp. 105–128. Eds R. Porter and J. Knight. Elsevier, Amsterdam 1980.
Youdim, M. B. H., Finberg, J. P. M., and Tipton, K. F., Monoamine oxidases, in: Catecholamine II. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Eds U. Trendelenburg and N. Weiner. Springer Verlag, Berlin (1987) in press.
Youdim, M. B. H., Grahame-Smith, D. G., and Woods, H. F., Some properties of human platelet monoamine oxidase in iron-deficiency anaemia. Clin. Sci. molec. Med.50 (1976) 479–486.
Youdim, M. B. H., Collins, G. G. S., Sandler, M., Bevan Jones, A. B., Pare, C. M. B., and Nicholson, W. J., Human brain monoamine oxidase: Multiple forms and selective inhibition. Nature, Lond.236 (1972) 225–228.
Youdim, M. B. H., Woods, H. F., Mitchell, B., Grahame-Smith, D. G., and Callender, S., Human platelet monoamine oxidase activity in iron-deficiency anaemia. Clin. Sci. molec. Med.48 (1975) 287–289.
Youdim, M. B. H., de Varebeke, J. P., Roba, J., Cavalier, R., and Gilbert, P., Formation of glycine form the novel anticonvulsant milacemide is mediated by brain monoamine oxidase B, in: Advances in Epilepsy, Ed. H. Manleis. Raven Press, New York (1987) in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youdim, M.B.H. Platelet monoamine oxidase B: Use and misuse. Experientia 44, 137–141 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01952197
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01952197