Summary
TheTrouton ratio, defined as the ratio of the extensional to the shear viscosity, may reach very high levels in viscoelastic media. Consequently the diagonal components of the deformation rate tensor, often of negligible importance in the analysis of flows ofNewtonian fluids, may be of primary interest here. Several significant phenomena unknown inNewtonian fluid mechanics are seen to have their origin in the tensile normal stresses generated by these extensional deformations of viscoelastic fluid media; they include the separation of particles or bubbles in accelerating flows (the „Uebler” effect), the operability of ductless siphons („Spinnbarkeit“) and, probably, turbulent drag reduction.
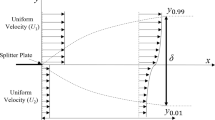
A class of problems which may be treated by neglecting the usual shearing deformation rates and shearing stresses, and considering only the extensional behaviour of the medium, is identified. These problems are characterized by high values of the dimensionless elongation rate, defined as the product of the local extension rate and the natural time of the fluid. As this dimensionless group frequently reaches its highest levels in the primary fluid stream outside a boundary layer this approximation is termed an “Extensional Primary Field” or EPF approximation to focus attention on the primary or “outer” flow, as distinguished from flows in the vicinity of solid surfaces.
The EPF approximation appears to provide a sufficient basis for analysis of several problems: converging flows into an orifice or duet from a larger reservoir, flows through porous solids and elongational flows with free surfaces as in textile fiber-spinning operations and flow in ductless siphons. In several other problems — lubricant squeeze films, turbulent flows under drag reducing conditions and flows about submerged objects — EPF considerations appear to be of importance but may not control the entire problem. The potential importance of EPF considerations in treating fluid mechanically controlled crystallization processes is noted.
Zusammenfassung
Das Trouton-Verhältnis als Verhältnis von Dehnzu Scherviskosität, kann bei viskoelastischen Stoffen sehr hohe Werte erreichen. Das hat zur Folge, daß die bei Newtonschen Flüssigkeiten oft vernachlässigbaren Diagonalgliedern des Schergeschwindigkeitstensors hier sehr bedeutungsvoll werden können. Einige wesentliche bei Newtonschen Flüssigkeiten unbekannte Effekte lassen sich auf diese Normalzugspannung zurückführen. Hierzu gehören die Trennung von Teilchen oder Blasen in beschleunigten Fließvorgängen (Uebler-Effekt) die Spinnbarkeit sowie vermutlich die Turbulenzverminderung.
Es wird eine Klasse von Problemen angesprochen, die bisher nur bei Berücksichtung des Dehnverhaltens behandelt wurden, während der Einfluß von Scherspannung und -geschwindigkeit vernachlässigt wurde. Diese Probleme sind durch hohe Werte der dimensionslosen Deformationsgeschwindigkeit charakterisiert. Die dimensionslose Darstellung wird durch das folgende Produkt definiert: örtliche Dehnungsgeschwindigkeit mal Eigenzeit der Flüssigkeit. Da diese dimensionslose Größe ihren höchsten Wert häufig in einem Primärstrom außerhalb einer Grenzschicht erreicht, wird diese Näherung EPF-Approximation (Extensional Primary Field) genannt, um auf den primären oder „äußeren“ Fluß hinzuweisen, der von Fließerscheinungen in der Nähe fester Oberflächen zu unterscheiden ist.
Die EPF-Näherung scheint eine hinreichende Grundlage für verschiedene Probleme zu bieten wie zum Beispiel für den Ausfluß aus einem Vorratsbehälter in eine Einmündung oder eine Röhre; Fließen durch poröse Festkörper, Fließen bei Dehnerscheinungen mit freier Oberfläche wie z. B. bei Spinnprozessen und Fließen in Siphons. In anderen Fragestellungen sind die EPFLösungen zwar von Einfluß, jedoch nicht entscheidend, wie z. B. bei Schmierfilmen, turbulenten Fließerscheinungen bei Verminderung der inneren Reibung sowie beim Fließen über eingetauchte Körper. Weiterhin wird auf die mögliche Bedeutung von EPF-Betrachtungen bei Kristallisationsprozessen, die aus der flüssigen Phase erfolgen, hingewiesen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appeldoorn, J. K., A. S. L. E. Trans.18, 182 (1965); Trans. A. S. M. E,90 F, 526 (1968).
Astarita, G., Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund.6, 257 (1967).
Astarita, G. andG. Greco, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund.7, 27 (1968).
Astarita, G., G. Marrucci, andD. Acierno, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund.7, 171 (1968).
Bagley, E. B., J. App. Phys.28, 624 (1957); Trans. Soc. Rheol.5, 355 (1961).
Bagley, E. B. andA. M. Birks, J. App. Phys.31, 556 (1960).
Bagley, E. B., A. M. Birks, andG. G. Warren, Film entitled “Polyethylene Flow Studies”, Canadian Industries Ltd., McMasterville (Quebec 1961).
Bakewell, H. P., Ph. D. thesis, Penna. State Univ., Univ. Park, Penna (1966).
Ballman, R. L., Rheol. Acta4, 137 (1965).
Batchelor, G. K., An Introd. to Fluid Dynamics, p. 282–294 Camb. Univ. Press, 1967; Current research (1969).
Blackadder, D. A. andH. M. Schleinitz, Nature200, 778 (1963).
Boles, R. L. andD. C. Bogue, Polymer Sci. Eng. (in press).
Booij, H. C. andA. J. Pennings, Private communication (1969).
Brodnyan, J. G., F. H. Gaskins, andW. Philippoff, Trans. Soc. Rheology1, 109 (1957).
Chan Man Fong, C. F., Rheol. Acta9, 144 (1970).
Christopher, R. K. andS. Middleman, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund.4, 422 (1965).
Clegg, P. L., in: Rheology of Elastomers,P. Mason andN. Wookey, eds. (London 1958).
Cogswell, F. N., Plastic and Polymers36, 109 (1968).
Dauben, D. L. andD. F. Menzie, Trans. Soc. Pet. Eng.,1967, 1065.
Denn, M. M., Chem. Eng. Sci.22, 395 (1967).
Fitzgerald, W. F. andJ. P. Craig, in App. Polymer Symp. — No. 6 — Fiber Drawing and SpinningM. J. Coplan, ed. p.67, Interscience (London-New York 1967).
Gaitonde, N. T. andS. Middleman, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund.6, 147 (1967).
Giesekus, H., Rheol. Acta1, 2 (1958). Also private communication, 1968; Rheol. Acta7, 127 (1968); Rheol. Acta8, 411 (1969).
Ginn, R. F., Ph. D. thesis, Univ. of Delaware, Newark, Delaware (1968).
Ginn, R. F. andA. B. Metzner, Proc. 4th Int. Cong. Rheology, E. H. Lee, ed. Pt. 2, p. 583 (London-New York 1965).
Johansen, F. C., Proc. Roy. Soc.126A, 231 (1930).
Kanel, F. A., Ph. D. thesis, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware (1971).
Kotaka, T., M. Kurata, andM. Tamura, Rheol. Acta2, 179 (1962).
LaNieve, H. L. andD. C. Bogue, J. App. Poly. Sci.12, 353(1968).
Marshall, R. J. andA. B. Metzner, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund.6, 393 (1967).
Metzner, A. B., Amer. Inst. Chem. Eng. J.13, 316 (1967); Trans. A. S. M. E.90F, 531 (1968).
Metzner, A. B., E. L. Carley, andI. K. Park, Modern Plastics37, No. 11, 133 (1960).
Metzner, A. B. andG. Astarita, Amer. Inst. Chem. Eng. J.13, 550 (1967).
Metzner, A. B., E. A. Uebler, andC. F. Chan Man Fong, Amer. Inst. Chem. Eng. J.15, 150 (1969).
Metzner, A. B. andA. P. Metzner, Rheol. Acta9, 174 (1970).
Meyer, W. A., Amer. Inst. Chem. Eng. J.12, 522 (1966).
Mills, R. D., J. Mech. Eng. Sci.10, 133 (1968).
Oliver, D. R., Can. J. Chem. Eng.44, 100 (1966).
Parlato, P., M. Ch. E. thesis, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware (1969).
Patterson, G. K., J. L. Zakin, andJ. M. Rodriguez, Ind. Eng. Chem.61, No. 1, 22 (1969).
Pennings, A. J., In: Crystal Growth, a supplement to J. Phys. and Chem. Solids (London 1967).
Pennings, A. J. andA. M. Kiel, Kolloid Z. u. Z. Polymere205, 160 (1965).
Pickup, T. J. F., Ph. D. thesis, Univ. of Cambridge, Cambridge, England (in prep.) (1968).
Prandtl, L., Proc. 3rd Int. Math. Congr., Heidelberg (1904) or in Coll. Works, II, 575 (1961).
Reynolds, O., Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc.177, 157 (1886) (papers2, 228).
Schlichting, H., Boundary Layer Theory, 6 th ed. (London 1968).
Seyer, F. A. andA. B. Metzner, Can. J. Chem. Eng.45, 121 (1967); Amer. Inst. Chem. Eng. J.15, 426 (1969).
Spriggs, T. W., J. D. Huppler, andR. B. Bird, Trans. Soc. Rheology10, 191 (1966).
Stefan, J., Sitzgber. K. Akad. Wiss. Math. Natur, Wien69, pt. 2, 713 (1874).
Tanner, R. I., Trans. A. S. L. E.8, 179 (1965); Trans. Soc. Rheology12, 155 (1968).
Tordella, J. P., Trans. Soc. Rheology1, 203 (1957).
Townsend, A. A., The Structure of Turbulent Shear Flow (Cambridge Univ. Press 1966).
Truesdell, C. andW. Noll, Hdbh. der Physik III/3, 472 (Berlin-Heidelberg-Göttingen, 1965).
Uebler, E. A., Ph. D. thesis, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware (1966).
Vrentas, J. S., J. L. Duda, andK. G. Bargeron, Amer. Inst. Chem. Eng. J.12, 837 (1966).
Wells, C. S. andJ. G. Spangler, Phys. Fluids10, 1890 (1967).
White, J. L., Amer. Inst. Chem. Eng. J.12, 1019 (1966).
Zidan, M. Z. A., Dissertation, Tech. Univ. Hannover (Hannover, Germany 1968), Rheol. Acta8, 89 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Vorgetragen auf der Jahrestagung der Deutschen Rheologen in Bad Münster a. Stein vom 28.–30. Mai 1969.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metzner, A.B. Extensional primary field approximations for viscoelastic media. Rheol Acta 10, 434–445 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01993723
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01993723