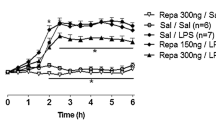
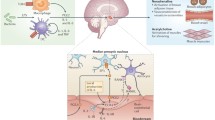
Summary
Two important concepts are presented in this review. First, endotoxin fever, like all fevers, is mediated by a host product, leukocytic pyrogen (LP). The mechanism by which LP production is initiated by endotoxin is discussed and evidence is provided which clearly distinguishes the biological and physical differences between LP and endotoxins. The second concept is that many of the molecular and neurochemical mechanisms by which LP causes fever by its action on the hypothalamic thermoregulatory center are also observed when endotoxins are introduced into the central nervous system. Thus, there may be experimental and clinical situations in which endotoxins can directly affect the hypothalamus and initiate fever. Although this bi-modal effect of endotoxin on the production of fever can occur, the importance of LP in mediating endotoxin and other fevers cannot be overstated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I.L. Bennett Jr andP.B. Beeson,The properties and biologic effects of bacterial pyrogens, Medicine29, 365–400 (1950).
E. Atkins andP. Bodel, Fever. InThe Inflammatory Process pp. 467–514. (Eds.B.W. Zweifach, L. Grant andR.T. McCluskey). Academic Press, New York 1974.
E. Atkins andP. Bodel,Clinical fever: its history, manifestations and pathogenesis, Fedn Proc.38, 57–63 (1979).
R. Elin andS.M. Wolff, Bacterial endotoxins. InCRC Handbook on Microbiology, pp. 215–239. (Eds.A.I. Laskin andH.A. Lechevalier). CRC Press, Cleveland 1973.
C.A. Dinarello andS.M. Wolff,Molecular basis of fever in humans, Am. J. Med.72, 799–819 (1982).
K.E. Cooper andW.I. Cranston,Clearance of radioactive bacterial pyrogen from the circulation, J. Physiol., Lond.166, 41–42P (1963).
J.C. Herion, W.B. Herring, J.G. Palmer andR.I. Walker,Cr 51-labeled endotoxin distribution in granulocytopenic animals., Am. J. Physiol.206, 947–950 (1964).
B. Starzecki, J.L. Reddin, A. Gran andW.W. Spink,Distribution of endotoxin Cr 51 in normal and endotoxin resistant dogs, Am. J. Physiol.213, 1065–1071 (1967).
C.A. Dinarello, P. Bodel andE. Atkins,The role of the liver in the production of fever and in pyrogenic tolerance, Trans. Ass. Am. Physns81, 334–344 (1968).
F. Haeseler, P. Bodel andE. Atkins,Characteristics of pyrogen by isolated rabbit Kupffer cells in vitro, R.E.S.22, 569–581 (1977).
R.K. Root, J.J. Nordlund andS.M. Wolff,Factors affecting the quantitative production and assay of human leukocytic pyrogen, J. Lab. clin. Med.75, 679–693 (1970).
J.J. Nordlund, R.K. Root andS.M. Wolff,Studies on the origin of human leukocytic pyrogen, J. exp. Med.131, 727–743 (1970a).
P. Bodel,Studies on the mechanism of exogenous pyrogen production. I. Investigation of new protein synthesis by stimulated human blood leukocytes, Yale J. Biol. Med.43, 145–163 (1970).
E. Atkins andS.I. Morse,Studies in staphylococcal fever. VI. Responses induced by cell walls and various fractions of staphylococci and their products, Yale J. Biol. Med.39, 297–311 (1967).
K.H. Schleiffer andO. Kandler,Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their toxonomic implications, Bact. Rev.36, 407–426 (1972).
K.H. Schleiffer,Chemical structure of the peptido-glycan, its modifiability and relation to biological activity, Z. Immun Forsch. exp. Ther.149, 104–117 (1975).
J. Rotta,Biologically active components of the cells of Gram-positive bacteria, J. Hyg. Epidem. Microbiol. Immun.18, 353–358 (1974).
A. Adam, R. Ciarbaru, F. Ellouz, J.F. Petit andE. Lederer,Adjuvant activity of monomeric bacterial cell wall peptidoglycans, Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.56, 561–567 (1974).
J. Rotta,Endotoxin-like properties of the peptido-glycan, Z. Immun Forsch. exp. Ther.149, 230–244 (1975).
S. Hamada,Studies on cell walls of group A Streptococcus pyrogens, type 12, Biken's J.14, 214–220 (1979).
R.M. Krause,Immunological activity of the peptido-glycan, Z. ImmunForsch. exp. Ther.149, 136–150 (1975).
W Schachenmayr, B. Heymar andO. Haferkamp,Antibodies to peptidoglycan in sera from populations studies, Z. ImmunForsch. exp. Ther.149, 179–186 (1975).
K. Masek, O. Kadlecova andP. Petrovicky,Pharmacological activity of bacterial peptidoglycan: the effect on temperature and sleep in the rat, Toxicon. suppl.1, 991–1003 (1978).
C.A. Dinarello, R.J. Elin, L. Chedid andS.M. Wolff,The pyrogenicity of synthetic adjuvants, J. infect. Dis.138, 760–767 (1978).
J.F. Cooper, J. Levin andH.N. Wagner Jr,Quantitative comparison of in vitro and in vivo methods for the detection of endotoxin, J. exp. Med.78, 138–148 (1971).
R.J. Elin andS.M. Wolff,Nonspecificity of the Limulus amebocyte lysate test: positive reactions with polynucleotides and proteins, J. infect. Dis.128, 349–351 (1973).
J. Van Noordwijk andY. De Jong,Comparison of the Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) test with the rabbit test: false positives and false negatives. Dev. Biol. Stand.34, 39–43 (1977).
A. Wildfeuer, B. Heymer, D. Spiler, K.H. Schleiffer, E. Vaneh andO. Haferkamp,Use of Limulus assay to compare the biological activity of peptidoglycan and endotoxin, Z. ImmunForsch. exp. Ther.149, 258–264 (1975).
S. Kotani, Y. Watanbe, F. Kinoshita, K. Kato, K. Harada, T. Shiba, S. Kusumoto, Y. Tarumi, L. Ikenaka, S. Okada, S. Kawata andK. Yokogawa,Gelation of the amoebocyte lysate of Tachypleus tridentatus by cell wall digest of several Grampositive bacteria and synthetic peptidoglycan subunits of natural and unnatural configurations, Biken's J.20, 5–10 (1977).
W. Braun,Molecular organization of the rigid layer and the cell wall of Escherichia coli, J. infect. Dis.128 (suppl.), 1–8 (1973).
D.W. Watson andY.B. Kim,Modification of host responses to bacterial endotoxins, J. exp. Med.118, 425–432 (1963).
S.E. Greisman, H.N. Wagner, M. Iio, R.B. Hornick, F.A. Carozza andW.E. Woodward, Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance in man. In:Bacterial Endotoxins, pp. 537–545. (Eds.M. Landy andW. Braun). Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick 1964.
J.H. Mulholland, S.M. Wolff, A. Jackson andM. Landy,Quantitative studies of febrile tolerance and levels of specific antibody evoked by bacterial endotoxin, J. clin. Invest.44, 920–926 (1965).
A. Boivin, I. Mesrobeanu andL. Mesrobeanu,Technique pour la préparation des polysaccharides microbians spécifiques, C. r. Séanc. Soc. Biol.113, 490–492 (1933).
E.T. Rietschel andO. Luederitz,Chemical structure of lipopolysaccharide and endotoxin immunity, Z. ImmunForsch. exp. Ther.149, 201–213 (1975).
O. Luederitz, C. Galanos, V. Lehmann, M. Nurminen, E.T. Rietschel, G. Rosenfelder, M. Simon andO. Westphal,Lipid A: Chemical structure and biological activity, J. infect. Dis.128 (suppl.), 9–21 (1973).
S.M. Wolff, J.H. Mulholland andS.B. Ward,Quantitative aspects of the pyrogenic responses to rabbits to endotoxin, J. clin. Med.65, 268–276 (1965).
S.E. Greisman andR.B. Hornick,Comparative pyrogenic reactivity of rabbit and man to bacterial endotoxin, Proc. soc. Exp. Biol. Med.131, 1154–1158 (1969).
S.M. Wolff,Biological effects of bacterial endotoxins in man, J. infect. Dis.128, (suppl.), 251–256 (1973).
C.A. Dinarello andS.M. Wolff, Exogenous and exogenous pyrogens. InBrain Dysfunction in Infantile Febrile Convulsions, pp. 117–128. (Eds.M.A.B. Brazier andF. Coceani). Raven Press, New York 1976.
R.J. Elin, S.M. Wolff, K.P. McAdam, L. Chedid, F. Audibert, C. Bernard andF. Oberling,Properties of reference Escherichia coli endotoxin and its phthalylated derivative in humans, J. infect. Dis.144, 329–336 (1981).
E. Buskirk, R.H. Thompson, M. Rubenstein andS.M. Wolff,Heat exchange in men and women following intravenous injection of endotoxin, J. appl. Physiol.19, 907–913 (1965).
J.N. Sheagren, S.M. Wolff andN.R. Shulman,Febrile and hematologic responses of rhesus monkeys to bacterial endotoxin. Am. J. Physiol.212, 884–890 (1967).
M. Perlow, C.A. Dinarello andS.M. Wolff,A primate model for the study of human fever, J. infect. Dis.132, 157–164 (1975).
P. Bodel andH. Miller,Pyrogen from mouse macrophages causes fever in mice, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.151, 93–96 (1976).
E. Ribi, R.L. Anacker, K. Kukushi, W.T. Haskin, M. Landy andK.C. Mulner, Relationship of chemical composition to biological activity. InBacterial Endotoxins, pp. 16–28. (Eds.M. Landy andW. Braun). Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick 1964.
A. Nowotny, Chemical detoxification of bacterial endotoxin. InBacterial Endotoxins, pp. 16–28 (Eds.M. Landy andW. Braun). Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick 1964.
M. Niwa, K.C. Milner, E. Ribi andJ.A. Rudbach,Alteration of physical, chemical and biological properties of endotoxin by treatment with mild alkali, J. Bact.97, 1069–1077 (1969).
E. Neter, O. Westphal, O. Luederitz, S.A. Gorzynski andE. Eichenberger,Studies of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides. Effect of heat and chemicals on erythrocyte modifying, antigenic, toxic and pyrogenic properties, J. Immun.76, 377–385 (1956).
H. Noll andA.I. Braude,Preparation and biological properties of a chemically modified E. coli endotoxin of high immunogenic potency and/or toxicity, J. clin. Invest.40, 1935–1951 (1961).
J.R. Schenck, M.P. Hargie, M.S. Brown, D.S. Evert, A.L. Yoo andF.C. McIntire,The enhancement of antibody formation by E. coli lipopolysaccharide and detoxified derivative, J. Immun.102, 1411–1422 (1969).
L. Chedid, F. Audibert, C. Bona, C. Damais, F. Parant andM. Parant,Biological activities of endotoxins detoxified by alkylation, Infect. Immun.12, 714–721 (1975).
D. Tripoli andA. Nowotny,Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.133, 604–619 (1966).
K. Sveen, T. Hofstad andK.C. Milner,Lethality for mice and chick embryos, pyrogenicity in rabbits and ability to gelate lysate from amoebocytes of Limulus polyphemus by lipopolysaccharides from Bacteroides, Fusobacterium and Veillonella, Acta path. microbiol. scand.85, 388–396 (1977).
R. Hofstad andJ. Kristoffersen,Chemical characteristics of endotoxin from Bacteroides fragilis, J. gen. Microbiol.61, 15–19 (1970).
D.L. Kasper,Chemical and biological characterization of the lipopolysaccharide of Bacteroides fragilis subspecies fragilis, J. infect. Dis.134, 59–66 (1976).
E.T. Rietschel, Y.B. Kim, D.W. Watson, C. Galanos, O. Luederitz andO. Westphal,Pyrogenicity and immunogenicity of Lipid A complexed with bovine serum albumin or human serum albumin, Infect. Immun.8, 173–177 (1973).
C. Galanos, E.T. Rietschel, O. Luederitz, O. Westphal, Y.B. Kim andD.W. Watson,Biological activities of Lipid A complexed with bovine-serum albumin, Eur. J. Biochem.31, 230–239 (1972).
O. Westphal andO. Luederitz,Chemische Erforschung von Lipopolysacchariden gramnegativen Bakterien, Angew. Chem.66, 407–417 (1954).
C.M. Chang andA. Nowotny,Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. Endotoxicity of Lipid A, Immunochemistry12, 19–20 (1975).
S. Konno,Studies on the lipid components of endotoxin. II. Chemical analyses and biological properties of nautral, polar-I and polar-II subfractions, Microbiol. Immunol.22, 287–299 (1978).
S. Konno andM. Yoshioka,Fractionation of lipid components isolated from endotoxin and their chemical and biological properties, Toxicon. Suppl.1, 921–932 (1978).
I.L. Bennett Jr andL.E. Cluff,Bacterial pyrogens, Pharmac. Rev.9, 427–458 (1957).
W.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the cause of fever, New Engl. J. Med.258, 1023–1027 (1958).
E. Atkins Pathogenesis of fever, Physiol. Rev.40, 580–605 (1960).
E. Atkins andE.S. Snell, Fever. InThe Inflammatory Process, pp. 495–525 (Eds.B.W. Zweifach, L. Grant andR.J. McCluskey). Academic Press, New York 1965.
P.B. Beeson,Tolerance to bacterial pyrogens. I. Factors influencing its development, J. exp. Med.86, 29–39 (1947).
P.B. Beeson,Tolerance to bacterial pyrogens. II. Role of the Reticuloendothelial system, J. exp. Med.86, 39–48 (1947).
S.M. Wolff, J.H. Mulholland, S.B. Ward, M. Rubenstein andP.D. Mott,Effect of 6-mercaptopurine on endotoxin tolerance, J. clin. Invest.44, 1402–1409 (1965).
S.M. Wolff, M. Rubenstein, J.H. Mulholland andD.W. Alling,Comparison of hematologic and febrile response to endotoxin in man, Blood26, 190–201 (1965).
E. Atkins andE.S. Snell, A comparison of the biological properties of Gram-negative bacterial endotoxin with leukocyte and tissue pyrogens. InBacterial Endotoxins, pp. 134–148 (Eds.M. Landy andW. Braun). Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick 1964.
S.E. Greisman andW.E. Woodward,Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance. III. The refractory state during continuous intravenous infusions of endotoxin, J. exp. Med.121, 911–933 (1965).
S.E. Greisman, E.J. Young andW.E. Woodward,Mechanisms of tolerance. IV. Specificity of the pyrogenic refractory state during continuous intravenous infusions of endotoxin, J. exp. Med.124, 983–1000 (1966).
F.J. Carey, A.I. Braude andM. Zalesky,Studies with radioactive endotoxin. III. The effect of tolerance on the distribution of radioactivity after intravenous injection of Escherichia coli endotoxin labeled with Cr 51, J. clin. Invest.37, 441–445 (1957).
R.T. Smith, A.I. Braude andF.J. Carey,The distribution of Cr 51-labeled E. coli endotoxin in the generalized Shwartzman reaction, J. clin. Invest.36, 695–699 (1957).
G. Biozzi, B. Benacerraf andB.N. Halpern,The effect of Salmonella typhi and its endotoxin on the phagocytic activity of the reticuloendothelial system in mice, Br. J. exp. Path.36, 226–239 (1955).
B. Benacerraf, G.J. Thorbecke andD. Jacoby,Effect of zymosan on endotoxin toxicity in mice, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.100, 796–799 (1959).
M.K. Agarwal andL.J. Berry,Effect of Actinomycin-D on RES and development of tolerance to endotoxin in mice, R.E.S.5, 353–367 (1968).
S. Fisher,Localization of radioiodinated endotoxin in organs of mice and rabbits: Effect of Thorotrast, trypan blue, endotoxin and carbon administered intravenously, Nature, Lond.213, 511–512 (1967).
M.I. Arredondo andR.F. Kampschmidt,Effect of endotoxins on phagocytic activity of the RES of the rat, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.112, 78–81 (1963).
A.S. Watnick andA.S. Gordon,Endotoxin influences on carbon clearance and resistance to bacterial infection, R.E.S.1, 170–184 (1964).
G. Lemperle,Effect of RES stimulation on endotoxin shock in mice, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.122, 1012–1015 (1966).
R.A. Tobey, D.F. Peterson, E.C. Anderson andT.T. Puck,Life cycle analysis of mammalian cells. III. The inhibition of division in Chinese hamster cells by puromycin and actinomycin, Biophys. J.6, 567–581 (1966).
L.J. Berry andD.S. Smythe,Some metabolic aspects of injection to bacterial endotoxin, J. Bact.90, 970–977 (1965).
J.G. Howard, D. Rowley andA.C. Wardlaw,Investigations on the mechanism of stimulation of non-specific immunity by bacterial lipopolysaccharides, Immunology1, 181–203 (1958).
E.R. Garieli andH. Holmgren,Studies in the blockade of the reticuloendothelial system, Acta path. microbiol. scand.31, 205–215 (1952).
S.E. Greisman, F.A. Carozza andH. Dixon Hills Jr,Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance. Relationships between tolerance and reticuloendothelial system phagocytic activity in the rabbit, J. exp. Med.117, 663–674 (1963).
H.H. Freedman,Passive transfer of tolerance to the pyrogenicity of bacterial endotoxin, J. exp. Med.111, 453–467 (1960).
H.H. Freedman,Further studies on the passive transfer of tolerance to pyrogenicity of bacterial endotoxin. The febrile and leukopenic responses, J. exp. Med.112, 619–629 (1960).
H.H. Freedman,Reticuloendothelial system and passive transfer of endotoxin tolerance, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.88, 99–115 (1960).
P.B. Beeson,Development of injection to typhoid bacterial pyrogen and its abolition by reticuloendothelial blockade, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.61, 248–251 (1946).
I.L. Bennett Jr andL.E. Cluff,Influence of nitrogen mustard upon reactions to bacterial endotoxin, Shwartzman phenomenon and fever, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.81, 304–308 (1952).
B. Zweifach, B. Benacerraf andL. Thomas,The relationship between the vascular manifestations of shock produced by endotoxin, trauma, and hemorrhage. II. The possible role of the reticulo endothelial system in resistance to each type of shock, J. exp. Med.106, 403–420 (1975).
R.D. Collins andW.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. VI. The interaction of leukocytes and endotoxin in vitro, J. exp. Med.110, 1005–1016 (1959).
S.E. Greisman andR.B. Hornick,Mechanism of endotoxin tolerance with special reference to man, J. infect. Dis.128, 257–268 (1973).
L.E. Cluff,Studies on the effect of bacterial endotoxins on rabbit leukocytes. II. Development of acquired resistance, J. exp. Med.98, 349–358 (1953).
S.H. Rutenberg, A.M. Rutenberg, E.E. Smith andJ. Fine,On the nature of tolerance to endotoxin, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.118, 620–623 (1965).
H.R. Morgan,Resistance to the action of the endotoxins of enteric bacilli in man, J. clin. Invest.27, 706–712 (1948).
H.R. Morgan,Tolerance to the toxic action of somatic antigens of enteric bacteria, J. Immun.59, 129–134 (1948).
R.A. Good,Clinical investigations on patients with agammablobulinemia, J. Lab. clin. Med.44, 803–807 (1954).
R.A. Good andR.L. Carco,A clinical and experimental study of agammaglobulinemia, Lancet75, 245–246 (1955).
A. Boivin andL. Mesrobeanu,Recherches sur les antigénes somatiques et sur les endotoxines des bactéries. IV. Sur l'action anti-endotoxique de l'anticorps, Revue Immunol. Thér. antimicrob.4, 40–56 (1938).
H.R. Morgan,Immunologic properties of an antigenic material isolated from E. typhosa, J. Immun.41, 161–174 (1941).
F.A. Neva andH.R. Morgan,Tolerance to the actions of endotoxins of enteric bacilli in patients convalescent from typhoid and paratyphoid fevers, J. Lab. clin. Med.35, 911–919 (1950).
R.S. Farr, S.L. Clark, Jr, J.E. Proffitt andD.H. Campbell,Some humoral aspects of the development of tolerance to bacterial pyrogens in rabbits, Am. J. Physiol.177, 269–275 (1954).
Y.B. Kim andD.W. Watson,Role of antibody reactions to Gram-negative bacterial endotoxin, Fedn Proc.24, 457 (1965).
Y.B. Kim andD.W. Watson,Modification of host response to bacterial endotoxins. II. Passive transfer of immunity to bacterial endotoxins with fractions containing 19S antibodies, J. exp. Med.121, 751–759 (1965).
Y.B. Kim andD.W. Watson,Role of antibodies in reactions to Gram-negative bacterial endotoxin, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.133, 727–745 (1966).
H.H. Freedman,Passive transfer of protection against lethality of homologous and heterologous endotoxins, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.102, 504–506 (1959).
D.W. Watson andY.B. Kim, Immunological aspects of pyrogenic tolerance. InBacterial Endotoxins, pp. 522–536 (Eds.M. Landy andW. Braun). Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick 1964.
M. Landy, A.G. Johnson, M.E. Webster andJ.F. Sagin,Studies on the O antigen of Salmonella typhosa. II. Immunological properties of the purified antigen, J. Immun.74, 466–473 (1955).
M. Landy,Enhancement of the immunogenicity of typhoid vaccine by retention of the V. antigen, Am. J. Hyg.58, 148–159 (1953).
R. Radvany, N.L. Neale andA. Nowotny,Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. VI. Neutralization of endotoxic O-antigens by homologous O-antibody. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.133, 763–786 (1966).
A. Nowotny, R. Radavany andN. Neale,Neutralization of toxic bacterial O-antigens with O-antibodies while maintaining their stimulus on nonspecific resistance, Life Sci.4, 1107–1110 (1965).
I. Berczi,Endotoxin neutralizing effect of antisera to E. coli endotoxins, Immunitäts. Forsch.132, 303–318 (1967).
S. Ogata andM. Kanamori,Effects of homologous O-antibody on host responeses to lipopolysaccharide from Hersinia enterocolitica: neutralization of its pyrogenicity, Microbiol. Immunol.22, 485–494 (1978).
B. Urbaschek andA. Nowotny,Endotoxin tolerance induced by detoxified endotoxin, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.127, 650–654 (1968).
S.E. Greisman, E.J. Young andF.A. Carozza, Jr.,Immunosuppression and endotoxin tolerance, Clin. Res.14, 332 (1966).
E.J. Young andS.E. Greisman,Transfer of ‘anamnestic’ tolerant responses to endotoxin with spleen cells, Clin. Res.16, 337 (1968).
L. Chedid, M. Parant, F. Boyer andR.C. Skarnes, Nonspecific host responses in tolerance to the lethal effect of endotoxins. InBacterial Endotoxins, pp. 500–516 (Eds.M. Landy andW. Braun). Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick 1964.
D. Rowley,The role of opsonins in non-specific immunity, J. exp. Med.111, 137–149 (1960).
J.G. Michael andF.S. Rosen,Association of ‘natural’ antibodies to Gram-negative bacteria with the gamma-macroglobulins, J. exp. Med.118, 619–628 (1963).
R.F. Kampschmidt, H.F. Upchurch andA. Park,Further studies on carbon clearance after endotoxin in the rat, R.E.S.2, 256–262 (1965).
I.M. Murray,The mechanism of blockade of the reticuloendothelial system, J. exp. Med.117, 139–152 (1963).
H.J. Creech, R.F. Hankwitz Jr andD.R.A. Wharton,Further studies of the immunological properties of polysaccharides from Serratia marcescens. I. The effects of passive and active immunization on the lethal activity of the polysaccharides, Cancer Res.9, 150–159 (1949).
C.A. Stetson, Role of hypersensitivity in reactions to endotoxin. InBacterial Endotoxins, p. 658 (Eds.M. Landy andW. Braun). Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick 1964.
T.G. Kovats,Endotoxin Susceptibility and Hypersensitivity (Monograph). Medical University, Szeged, Szeged, Hungary 1967.
S. Snell andA.I. Braude,Intradermal reactions in man to autologous erythrocytes sensitized with tuberculin or endotoxin, J. Immun.87, 119 (1961).
R.W. Schaedler andR.J. Dubos,The susceptibility of mice to bacterial endotoxins, J. exp. Med.113, 559 (1961).
A.I. Braude andJ. Siemienski,The influence of endotoxin on resistance to infection, Bull. N.Y. Acad. Med.37, 448–462 (1961).
E. Atkins andW.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. I. The presence of transferable pyrogen in the blood stream following the infection of typhoid vaccine, J. exp. Med.101, 519–528 (1955).
E. Atkins andW.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. II. Identification of an exogenous pyrogen in the blood stream following the injection of typhoid vaccine, J. exp. Med.102, 499–516 (1955).
D. Rowley, J.G. Howard andC.R. Jenkins,The fate of 32 P-labeled bacterial lipopolysaccharide in laboratory animals, Lancet270, 366–368 (1956).
W.B. Herring, J.C. Herion, R.T. Walker andJ.G. Palmer,Distribution and clearance of circulating endotoxin, J. clin. Invest.42, 79–87 (1963).
A.I. Braude, F.J. Carey andM. Salesky,Studies with radioactive endotoxin, J. clin. Invest.43, 858–865 (1955).
W.K. Hadley, J. O'Rourke andE. Atkins,Purification and characterization of an endogenous pyrogen, Yale J. Biol. Med.38, 339–353 (1966).
C.A. Dinarello andS.M. Wolff,Mechanisms on the production of fever in humans, Seminars in Inf. Dis.2, 173–192 (1979).
S.E. Greisman andR.B. Hornick,Demonstration of circulating human endogenous pyrogen, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.139, 690–697 (1972).
P. Bodel andE. Atkins,Human leukocyte pyrogen producing fever in rabbits, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.121, 943–946 (1966).
W.J. Critz,Intracerebroventricular injection of rats: a sensitive assay method for endogenous pyrogen circulating in rats, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.166, 6–11 (1981).
C.A. Dinarello, L. Renfer andS.M. Wolff,Human leukocyte pyrogen: Purification and development of a radioimmunoassay, Proc. Natn. Acad. Sci. USA74, 4624–4627 (1977).
P.B. Beeson,Temperature-elevating effect of a substance obtained from polymorphonuclear leukocytes, J. clin Invest.27, 524 (1948).
E. Atkins, P. Bodel andL. Francis,Release of an endogenous pyrogen in vitro from rabbit mononuclear cells, J. exp. Med.126, 357–386 (1967).
E.S. Snell andE. Atkins,Interactions of gramnegative bacterial endotoxin with rabbit blood in vitro, Am. J. Physiol.212, 1103–1112 (1967).
P. Bodel,Pyrogen release in vitro by lymphoid tissue from patients with Hodgkin's disease, Yale J. Biol. Med.47, 101–112 (1974).
P. Bodel,Studies on the mechanism of endogenous pyrogen production. II. Role of cell products in the regulation of pyrogen release from blood leukocytes, Infect. Immun.10, 451–457 (1974).
P. Bodel andH. Miller,A new sensitive method for detecting human endogenous (leukocyte) pyrogen, Inflamm.3, 103–110 (1978).
P. Bodel,Studies on the mechanism of endogenous pyrogen production. III. Human blood monocytes, J. exp. Med.140, 954–965 (1974).
A.S. Van Meirt andC.T. Can Duin,Further studies on the antipyretic action of polymyxin B in pyrogen-induced fever, Arzneimittel-Forsch.28, 2246–2251 (1978).
I.V. Allen,The cerebral effects of endogenous serum and granulocytic pyrogen, Br. J. exp. Path.46, 25–34 (1965).
C.A. Dinarello, N.P. Goldin andS.M. Wolff,Demonstration and characterization of two distinct human leukocytic pyrogen, J. exp. Med.139, 1369–1381 (1974).
W.I. Cranston, F. Goondale Jr, E.S. Snell andF. Wendt,The role of leukocytes in the initial action of bacterial pyrogens in man, Clin. Sci.15, 219–226 (1956).
J.H. Fessler, K.E. Cooper andW.I. Cranston,Observations on the production of pyrogenic substances by bacteria and human leukocytes, J. exp. Med.113, 1127–1136 (1961).
D.M. Moore, P.A. Murphy, J.P. Chesney andW.B. Wood Jr,Synthesis of endogenous pyrogen by bacteria leukocytes, J. exp. Med.137, 1263–1274 (1973).
L.J. Wright, M.B. Lipsett, G.T. Ross andS. M. Wolff,Effects of dexamethasone and aspirin on the response to endotoxin in man, J. clin. Endocr. Metab.34, 13–17 (1972).
W.G. Clark andH.R. Cumby,Competitive antagonism of leukocytic pyrogen by sodium salicylate and acetaminophen, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.141, 669–672 (1972).
J.R. Vane,Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs, Nature, Lond.231, 232–235 (1971).
P. Bodel, C.F. Reynolds andE. Atkins,The lack of effect of salicylate on pyrogen release from human blood leukocytes in vitro, Yale J. Biol. Med.46, 190–195 (1973).
W.G. Clark andS.G. Moyer,The effects of acetaminophen and sodium salicylate on the release and activity of leukocytic pyrogen in the cat, J. Pharmac. exp. Ther.181, 183–191 (1972).
M. Parant, G. Riveau, F. Parant, C.A. Dinarello, S.M. Wolff andL. Chedid,Effect of indomethacin on increased resistance to bacterial infection and on febrile responses induced by muramyl dipeptide, J. infect. Dis.142, 708–715 (1980).
S.L. Hoo, M.T. Lin, R.D. Wei, C.Y. Chai andS.C. Wand,Effects of sodium acetylsalicylate on the release of pyrogen from leukocytes, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.139, 1155–1158 (1972).
I.L. Bennett Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. V. The fever accompanying pneumococcal infection in the rabbit, Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp.98, 216–235 (1956).
C.A. Rouzer, W.A. Scott, Z.A. Cohn, P. Blackburn andJ.M. Manning.Mouse peritoneal macrophages release leukotriene C in response to a phagocytic stimulus, Proc. Natn. Acad. Sci. USA77, 4928–4932 (1980).
J.I. Kurland andR. Bockman,Prostaglandin E production by human monocytes and mouse peritoneal macrophages, J. exp. Med.147, 952–963 (1978).
W.A. Scott, J.M. Zrike, A.L. Hamill, J. Kempe andZ.A. Cohn,Regulation of arachidonic acid metabolites in macrophages, J. exp. Med.152, 324–335 (1980).
T.A. Cebula, D.F. Hanson, D.M. Moore andP.A. Murphy,Synthesis of four endogenous pyrogens by bacteria macrophages, J. Lab. clin. Med.94, 95–105 (1979).
P. Bodel,Colchicine stimulation of pyrogen production by human blood monocytes, J. exp. Med.143, 1015–1056 (1976).
P. Bodel andJ.W. Hollingsworth,Pyrogen release from human synovial exudate cells, Br. J. exp. Path.49, 11–19 (1968).
E. Atkins, P.W. Askenase, L. Francis andH.A. Bernheim,Release of an endogenous pyrogen from guinea pig leukocytes: the role of T lymphocytes and correlation with suppression (desensitization) of delayed hypersensitivity, J. Immun.125, 2069–2075 (1980).
D.F. Hanson, P.A. Murphy andB.E. Windle,Failure of bacteria neutrophils to secrete endogenous pyrogen when stimulated with staphylococci, J. exp. Med.151, 1360–1371 (1980).
R.G. Petersdorf andI.L. Bennett Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. IV. The effect of heat on endogenous and exogenous pyrogen in the serum of dogs, Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp.100, 197–208 (1957).
S. Kanoh, H. Kawasaki, M. Yoshida, A. Nishio andK. Mochida,Some factors influencing the production of leukocytic pyrogen from polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro, Jap. J. Pharmac.17, 125–132 (1967).
G.W. Gander andF. Goodale,Chemical properties of leukocytic pyrogen. I. Partial purification of rabbit leukocytic pyrogen, Exp. Mol. Path.1, 417–426 (1962).
C.A. Dinarello andH.A. Bernheim,Ability of human leukocytic pyrogen to stimulate brain prostaglandin synthesis in vitro, J. Neurochem.373, 702–708 (1981).
G.W. Rafter, R.D. Collins andW.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. VI. Preliminary chemical characterization of leukocytic pyrogen, J. exp. Med.111, 831–840 (1960).
M.S. Kozak, H.H. Hahn, W.J. Lennarz andW.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. XVI. Purification and further chemical characterization of granulocytic pyrogen, J. exp. Med.127, 341–357 (1968).
H.K. Kaiser andW.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. IX. The production of endogenous pyrogen by polymorphonuclear leukocytes, J. exp. Med.115, 27–36 (1962).
H.K. Kaiser andW.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. X. The effect of certain enzyme inhibitors on the production and activity of leukocytic pyrogen, J. exp. Med.115, 37–47 (1962).
C.A. Dinarello andS.M. Wolff,Partial purification of human leukocytic pyrogen, Inflamm.2, 179–189 (1977).
G.W. Rafter, S.F. Cheuk, D.W. Kraus andW.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. XIV. Further observations on the chemistry of leukocytic pyrogen, J. exp. Med.123, 433–444 (1966).
P. Bodel, A. Wechsler andA. Atkins,Comparison of endogenous pyrogens from human and rabbit leukocytes utilizing Sephadex filtration, Yale J. Biol. Med.41, 376–387 (1969).
C. Rosendorff andJ.J. Mooney,Central nervous system sites of action of a purified leukocytic pyrogen, Am. J. Physiol.220, 597–603 (1971).
P.A. Murphy, T.A. Cebula, J. Levin andB.E. Windle,Rabbit macrophages secrete two biochemically and immunologically distinct endogenous pyrogens, Infect. Immun.34, 177–183 (1981).
P.A. Murphy, J. Chesney andW.B. Wood Jr,Further purification of rabbit leukocytic pyrogen, J. Lab. clin. Med.83, 310–322 (1974).
P.A. Murphy, P.L. Simon andW.F. Willoughby,Endogenous pyrogens made by rabbit peritoneal exudate cells are identical with lymphocyte activating factors made by rabbit alveolar macrophages, J. Immun.124, 2498–1503 (1980).
P.A. Murphy, T.A. Cebula andB.E. Windle,Heterogeneity of rabbit endogenous pyrogens is not attributable to glycosated variants of a single polypeptide chain, Infect. Immun.34, 184–191 (1981).
C.A. Dinarello, L. Renfer andS.M. Wolff,The production of antibody against human leukocytic pyrogen, J. clin. Invest.60 465–472 (1977).
P. Bodel, P. Ralph, K. Wong andJ.C. Long,Endogenous pyrogen production by Hodgkin's disease and human histiocytic lymphoma cell lines in vitro, J. clin. Invest.65, 514–518 (1980).
M.K. King andW.B. Wood Jr,Studies on the pathogenesis of fever. IV. The site of action of leukocytic and circulating endogenous pyrogen, J. exp. Med.107, 291–303 (1958).
D. Lorber, M. Tenebaum, S. Thurston, G.W. Gander andF. Goodale,The fate of circulating pyrogen in the rabbit, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.137, 896–901 (1971).
Y. Townsend andW.I. Cranston,Sites of clearance of leukocytic pyrogen in the rabbit, Clin. Sci.56, 265–268 (1979).
C.A. Dinarello, P. Weiner andS.M. Wolff,Radiolabeling and disposition in rabbits of purified human leukocytic pyrogen, Clin. Res.26, 522A (1978).
R.D. Adler, M. Rawlins andW.I. Cranston,The effect of salicylate on pyrogen-induced fever in man, Clin. Sci.37, 91–97 (1969).
K.E. Cooper, W.I. Cranston andA.J. Honour,Obervations on the site and mode of action of pyrogens in the rabbit brain, J. Physiol.191, 325–337 (1967).
W.L. Veale andK.E. Cooper,Comparison of sites of action of prostaglandin E1 and leukocytic pyrogen in brain, Proc. Symp. Temp. Regul. Drug Act. Paris 218–226 (1975).
J.M. Lipton, C.A. Dinarello andJ.I. Kennedy,Fever produced in the squirrel monkey by human leukocytic pyrogen, Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.160, 426–428 (1979).
Y. Sakata, A. Moromota, Y. Takase andN. Murakami,Direct effects of endogenous pyrogen on medullary temperature-responsive neurons in rabbits, Jap. J. Physiol.31, 247–257 (1981).
C.M. Blatteis andK.A. Smith,Hypothalamic sensitivity to leukocytic pyrogen of adult and newborn pigs, J. Physiol.296, 177–192 (1979).
E.P. Schoener andS.C. Wang,Leukocytic pyrogen and sodium acetylsalicylate on hypothalamic neurons in the cat, Am. J. Physiol.229, 185–190 (1975).
J.M. Lipton andG.P. Trzcinka,Persistence of febrile response to pyrogens after PO/AH lesions in squirrel monkeys, Am. J. Physiol.231, 1638–1648 (1976).
Y. Sekata,Effects of pyrogen on the medullary temperature-responsive neuron of rabbits, Jap. J. Physiol.29, 585–596 (1979).
T. Nakayama andJ.D. Hardy,unit responses in the rabbits brain stem to changes in brain and cutaneous temperature, J. appl. Physiol.27, 848–857 (1969).
W. Feldberg, K.P. Gupta, A.S. Milton andS. Wendlandt,Effect of pyrogen and antipyretics on prostaglandin activity in cisternal c.s.f. of unanesthetized cats, J. Physiol. Lond.234, 279–303 (1973).
W. Feldberg andK.P. Gupta,Pyrogen fever and prostaglandin-like activity in cerebrospinal fluid, J. Physiol., Lond.228, 41–53 (1973).
P.N. Saxena, M.M. Beg, K.C. Singhal andM. Ahmad,Prostaglandin-like activity in the cerebrospinal fluid of febrile patients, Indian J. med. Res.70, 495–498 (1979).
L.S. Wolff andO.A. Mamer,Measurement of prostaglandin F2A levels in human cerebrospinal fluid in normal and pathological conditions, Prostaglandins9, 183–192 (1975).
A.S. Milton andS. Wendlandt,Effects on body temperature of prostaglandins of the A, E and F series on injection into the III ventricle of unanesthetized cats and rabbits, J. Physiol., Lond.218, 325–336 (1971).
A.S. Milton, Prostaglandins and fever. InBrain Dysfunction in Infantile Febrile Convulsions, pp. 129–410 (Eds.M.A.B. Brazier andF. Coceani). Raven Press, New York 1976.
W.E. Brenner, J.R. Dingfelder, L.G. Staurovsky, T. Kumarasamy andD.A. Grimes,Intramuscular administration of 15-(S)-15-methylprostaglandin E2-methyl ester for induction of abortion, Am. J. Obstet. Gynec.120, 833–836 (1974).
J.T. Stitt andJ.D. Hardy,Evidence that prostaglandin E1 may be a mediator in pyrogenic fever in rabbits, Biometerorology5, 112 (1972).
J.T. Stitt andJ.D. Hardy,Microelectrophoresis of PGE1 onto units in the rabbit hypothalamus, Am. J. Physiol.229, 240–245 (1975).
H.A. Bernheim, T.M. Gilbert andJ.T. Stitt,Prostaglandin E levels in third ventricular cerebrospinal fluid of rabbits during fever and changes in body temperature, J. Physiol., Lond.301, 69–78 (1980).
C.A. Harvey, A.S. Milton andD.W. Straughan,Prostaglandin E levels in cerebrospinal fluid of rabbits and the effects of bacterial pyrogen and antipyretic drugs, J. Physiol., Lond.248, 26–27 (1975).
W.K. Philipp-Dormston andR. Siegert,Prostaglandins of the E and F series in rabbit cerebrospinal fluid during fever induced by Newcastle disease virus, E. or coli-endotoxin, or endogenous pyrogen, Med. Microbiol. Immunol.159, 279–284 (1974).
J.A. Splawinski, Z. Gorka, E. Zacny andB. Wojtaszek,Hyperthermic effects of arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha in rats, Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.374, 15–21 (1978).
W.G. Clark andH.R. Cumby,Antagonism by antipyretics of the hyperthermic effect of a prostaglandin precursor, sodium arachidonate, in the cat, J. Physiol., Lond.257, 581–595 (1976).
A.S. Milton,Prostaglandin E, and endotoxin fever, and the effects of aspirin, indomethacin and 4-acetamidophenol, Adv. Biosci.9, 495–500 (1972).
P.K. Dey, W. Feldberg K.P. Gupta, A.S. Milton andS. Wendlandt,Further studies on the role of prostaglandin in fever, J. Physiol., Lond.241, 629–646 (1974).
R.C. Skarnes, S.K. Brown, S.S. Hull andJ.A. McCracken,Role of prostaglandin E in the biphasic fever response to endotoxin, J. exp. Med.154, 1212–1224 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinarello, C.A. Molecular mechanisms in endotoxin fever. Agents and Actions 13, 470–486 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02176419
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02176419