Abstract
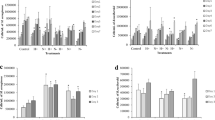
The selective effect of DCMU on photosynthetic activity and growth rate was examined in several marine unicellular algae:Nannochloropsis sp. (Eustigmatohyceae),Dunaliella salina (Chlorophyceae)Isochrysis galbana (Prymnesiophyceae) andChaetoceros sp. (Bacillariophyceae). DCMU at 10−7 M caused an immediate decrease in the photosynthetic rate ofDunaliella andIsochrysis (about 50% inhibition), whereas 10−6 M imposed 80% inhibition in the photosynthetic rate ofChaetoceros. InNannochloropsis the rate was affected only when DCMU concentration exceeded 10−6M. Cellular growth rate of all studied algae was affected by DCMU in a similar manner to photosynthesis. The differential effect of DCMU was further examined in mixed cultures in whichNannochloropsis was cultivated together with an additional species simulating a contamination situation of aNannochloropsis culture. When DCMU was added at concentrations higher than 10−7 M, the growth of the competing algae significantly decreased, whileNannochloropsis maintained a relatively high growth rate. Consequently, after a growth period of 4 to 7 days a clear domination ofNannochloropsis was observed. These results demonstrate that DCMU and probably other herbicides of similar characteristics can be used effectively as a selective tool to suppress contaminating unicellular algae in open ponds in order to maintain a monoculture ofNannochloropsis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubinsky Z, Falkowski PG, Wayman K (1986) Light harvesting and utilization by phytoplankton. Plant Cell Physiol. 27: 1335–1349.
Fahl GM, Kreft L, Altenburger R, Faust M, Boedeker W, Grimme LH (1995) pH dependent sorption, bioconcentration and algal toxicity of sulfonylurea herbicides. Aquat. Toxicol. 31: 175–187.
Galloway R (1988) Media requirements and antibiotic and herbicide sensitivities in lipid-producing microalgae. J. Phycol. 24 (Suppl.): 18.
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I.Cyclotella nana Hustedt andDetonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 8: 229–239.
Kanematsu M, Maeda M, Yoseda K, Yoneda H (1989) Methods to repress the growth ofNannochloropsis-grazing microflagellate. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 55: 1349–1352.
Molander S, Dahl B, Jonsson J, Sjostrom M (1992) Combined effects of Tri-n-butyl Tin (TBT) and Diuron on marine periphyton communities detected as pollution-induced community tolerance. Arch. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 22: 419–427.
Okauchi M (1991) The status of phytoplankton production in Japan. In: Rotifers and Microalgae Culture Systems. Proceedings of a U.S.-Asia workshop. Honolulu, HI, 1991.
Philips EJ, Hansen P, Velardi T (1992) Effect of the herbicide diquat on the growth of microalgae and cyanobacteria. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 49: 750–756.
Seto A, Kumasaka K, Hosaka M, Kojima E, Kashiwakura M, Kato T (1992) Production of eicosapentaenoic acid by a marine microalgae and its commercial utilization for aquaculture. In: Kyle DJ, Ratledge C (eds), Industrial Applications of Single Cell Oils. American Oil Chemists' Society, Champaign, Illinois: 219–234.
Shaish A, Avron M, Ben-Amotz A (1990) Effect of inhibitors on the formation of stereoisomers in the biosynthesis of β-carotene inDunaliella bardawil. Plant Cell Physiol. 31: 689–696.
Sukenik A, Carmeli Y, Berner T (1989) Regulation of fatty acid composition by irradiance level in the eustigmatophyteNannochloropsis sp. J. Phycol. 25: 686–692.
Sukenik A, Takahashi H, Mokady S (1994) Dietary lipids from marine unicellular algae enhance the amount of liver and blood ω fatty acids in rats. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 38: 85–96.
Sukenik A, Zmora O, Carmeli Y (1993) Biochemical quality of marine unicellular algae with special emphasis on lipid composition. II.Nannochloropsis sp. Aquacult. 117: 313–329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonen-Zurgil, Y., Carmeli-Schwartz, Y. & Sukenik, A. Selective effect of the herbicide DCMU on unicellular algae — a potential tool to maintain monoalgal mass culture ofNannochloropsis . J Appl Phycol 8, 415–419 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02178586
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02178586