Abstract
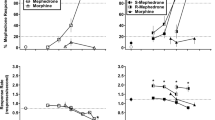
Evidence suggests that stimulants such asd-amphetamine and cocaine act presynaptically by increasing the amount of dopamine (DA) available to stimulate postsynaptic DA receptors. Since two subpopulations of DA receptors (D1 and D2) exist, we investigated the role of both of these receptor subtypes in mediating the internal “state” produced by these stimulants. Two groups of rats (N=8/group) were trained to discriminate intraperitoneal (IP) injections of eitherd-amphetamine (1 mg/kg) or cocaine (10 mg/kg) from saline in a two-lever, water-reinforced, drug discrimination task. After stable performance was established (i.e., more than 85% correct under each training condition), substitution and combination tests were conducted with selective D1 and D2 agonists and antagonists. The D2 agonist quinpirole (0.0313–0.125 mg/kg) mimicked both stimulant cues while the D1 agoinst SKF 38393 (5–20 mg/kg) substituted partially for cocaine but notd-amphetamine. Combination tests with DA antagonists indicated that both the D1 antagonist SCH 23390 (0.0063–0.25 mg/kg) and the D2 antagonist haloperidol (0.125–0.5 mg/kg) attenuated the effects of both stimulants; in addition, the substitution of cocaine (20 mg/kg) ford-amphetamine was blocked by both DA antagonists. The ability of both D1 and D2 antagonists to attenuate the stimulus effects ofd-amphetamine and cocaine raises the possibility that a synergistic (“enabling”) interaction between D1 and D2 receptors may modulate stimulant cues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnt J (1988) The discriminative stimulus properties of the D-1 agonist SKF 38393 and the D-2 agonist (−) NPA are mediated by separate mechanisms. Life Sci 42:565–574
Arnt J, Hyttel J, Perregaard J (1987) Dopamine D1 receptor agonists combined with the selective D2 agonist quinpirole facilitate the expression of oral stereotyped behavior in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 133:137–145
Baldessarini RL (1985) Drugs and the treatment of psychiatric disorders. In: Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Rall TW, Murad F (eds) Goodman and Gilman's The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 7th edn. MacMillan, New York, pp 387–445
Barrett RL, Appel JB (1989) Effects of stimulation and blockade of dopamine receptor subtypes on the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine. Psychopharmacology 99:13–16
Bischoff S, Heinrich M, Sonntag JM, Krauss J (1986) The D-1 dopamine receptor antagonist SCH 23390 also interacts potently with brain serotonin (5-HT2) receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 129:367–370
Braun AR, Barone P, Chase TN (1986) Interaction of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the expression of dopamine agonist induced behaviors. In: Breese GR, Creese I (eds) Neurobiology of central D1 dopamine receptors. Plenum Press, New York, pp 151–166
Christensen AV, Arnt J, Hyttel J, Larsen JJ, Sevendsen O (1984) Pharmacological effects of a specific dopamine D-1 antagonist SCH 23390 in comparison with neuroleptics. Life Sci 34:1529–1540
Clark D, White FJ (1987) D1 dopamine receptor: the search for a function. Synapse 1:347–388
Colpaert FC (1986) Interactions of haloperidol with discriminative responding controlled by 10 mg/kg of cocaine in rats. Drug Dev Res 9:125–131
Colpaert FC, Niemegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1978a) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine andd-amphetamine and antagonism by haloperidol: a comparative study. Neuropharmacology 17:937–942
Colpaert FC, Neimegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1978b) Neuroleptic interference with the cocaine cue: internal stimulus control of behavior and psychosis. Psychopharmacology 58:247–255
Colpaert FC, Neimegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1979) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine: neuropharmacological characteristics as derived from stimulus generalization experiments. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 10:535–546
Cunningham KA (1988) Cocaine: behavioral sensitization and the serotonin syndrome. Soc Neurosci Abstr 14:659
Cunningham KA, Appel JB (1982) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine and phencyclidine: similarities in the mechanism of action. In: Colpaert FC, Slanger JL (eds) Drug discrimination: application in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 181–192
Cunningham KA, Appel JB (1987) Neuropharmacological reassessment of the discriminative stimulus properties ofd-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Psychopharmacology 91:67–93
Cunningham KA, Callahan PM, Appel JB (1985) Dopamine D1 receptor mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties of SKF-38393. Eur J Pharmacol 119:121–125
Cunningham KA, Lakoski JM (1988) Electrophysiological effects of cocaine and procaine on dorsal raphe serotonin neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 148:457–462
Cunningham KA, Lakoski JM (1990) The interactions of cocaine with serotonin dorsal raphe neurons: single unit extracellular recording studies. Neuropsychopharmacology 3:41–50
D'Mello GD, Stolerman IP (1977) Comparison of the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine and amphetamine in rats. Br J Pharmacol 61:415–422
Goudie A, Reid D (1988) Qualitative discrimination between cocaine and amphetamine in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 151:471–474
Gower AJ, Marriott AS (1982) Pharmacological evidence for the subclassification of dopamine receptors in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 77:185–194
Iorio LC, Barnett A, Leitz FH, Houser VP, Korduba CA (1983) SCH 23390, a potential benzazepine antipsychotic with unique interactions on dopaminergic systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:462–468
Jarbe TUC (1978) Cocaine as a discriminative cue in rats: interactions with neuroleptics and other drugs. Psychopharmacology 59:183–187
Jarbe TUC (1984) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine: effects of apomorphine, haloperidol, procaine and other drugs. Neuropharmacology 23:899–907
Kelly E, Nahorski SR (1987) Endogenous dopamine functionally activates D-1 and D-2 receptors in striatum. J Neurochem 49:115–120
Kleven MS, Anthony EW, Goldberg LI, Woolverton WL (1988) Blockade of the discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine in rhesus monkeys with the D1 dopamine antagonist SCH-23390. Psychopharmacology 95:427–429
McKenna ML, Ho BT (1980) The role of dopamine in the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine. Neuropharmacology 19:297–303
McQuade RD, Ford D, Duffy RA, Chipkin RE, Iorio LC, Barnett A (1988) Serotoninergic component of SCH 23390: in vitro and in vivo binding assays. Life Sci 43:1861–1869
Molloy A, Waddington J (1984) Dopaminergic behavior stereospecifically promoted by the D1 agonist R-SK & F 38393 and selectively blocked by the D1 antagonist Sch-23390. Psychopharmacology 82:409–410
Nielsen EB, Jepsen SA (1985) Antagonism of the amphetamine cue by both classical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 111:167–176
Nielsen EB, Randrup K, Andersen PH (1989) Amphetamine discrimination: effects of dopamine receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 160:253–262
Reith MEA, Meisler BE, Sershen H, Lajtha A (1986) Structural requirements for cocaine congeners to interact with dopamine and serotonin uptake sites in mouse brain and to induce stereotyped behavior. Biochem Pharmacol 35:1123–1129
Seeman P (1980) Brain dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 32:229–313
Silverman PB, Schultz KA (1989) Comparison of cocaine and procaine discriminative stimuli. Drug Dev Res 16:427–433
Smith FL, St John C, Yang TFT, Lyness WH (1989) Role of specific receptor subtypes in amphetamine discrimination. Psychopharmacology 97:501–506
Snoddy AM, Tessel RE (1985) Prazosin: effect on psychomotor-stimulant cues and locomotor behavior in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 116:221–228
Stolerman IP, D'Mello DG (1981) Role of training conditions in discrimination of central nervous system stimulants by rats. Psychopharmacology 73:295–303
Stoof JC, Kebabian JW (1984) Two dopamine receptors: biochemistry, physiology and pharmacology. Life Sci 35:2281–2296
Weathersby RT, Appel JB (1986) Dopamine D2 receptor mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties of LY-171555 (quinpirole). Eur J Pharmacol 132:87–91
White FJ, Bednarz LM, Wachtel SR, Hjort S, Brooderson R (1988) Is stimulation of both D1 and D2 receptors necessary for the expression of dopamine-mediated behaviors? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:189–193
Wood DM, Emmett-Oglesby MW (1987) Evidence for D2-receptor involvement in tolerance to the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine. Soc Neurosci Abstr 13:1717
Woolverton WL (1984) Pharmacological analysis of the discriminative stimulus properties ofd-amphetamine in rhesus monkeys. Pharmacologist 26:161
Woolverton WL, Kamien JB, Kleven MS (1987) Blockade of the discriminative stimulus (DS) effects of cocaine andd-amphetamine in rhesus monkeys with the D1 dopamine antagonist SCH-23390. Pharmacologist 29:158
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Callahan, P.M., Appel, J.B. & Cunningham, K.A. Dopamine D1 and D2 mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties ofd-amphetamine and cocaine. Psychopharmacology 103, 50–55 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244073
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244073