Abstract
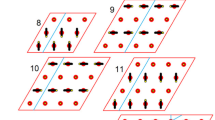
A general description and a historical discussion of trilinear coordinates is given. These coordinates are then used to develop the solution of a simple supported freely vibrating equilaterial triangular plate. The solution gives fundamental frequencies, mode shapes, nodal lines and a general expression for displacements.
An experimental program is described to validate the analytical solution. Nodal lines, mode shapes and displacements are determined by holographic interferometry and compared to theoretical results. Excellent agreement is obtained. A second experimental technique, a fiber-optic device, is used to determine displacements with the results being compared to the displacements obtained by both theoretical and holographic analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A i :
-
points referring to vertices of a triangle
- a i :
-
length of sides of triangle
- C ni :
-
cos\(n\pi \zeta _i \)
- D :
-
flexural rigidity,\(D = {{Eh^3 } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{Eh^3 } {12{\text{ }}(1 - v^2 )}}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {12{\text{ }}(1 - v^2 )}}\)
- E :
-
modulus of elasticity
- H i :
-
altitudes of a triangle,H i =Λ/m i
- i :
-
dummy index, i.e.,i=1,2,3
- l i :
-
cos\(\alpha _i \)
- m i :
-
sin\(\alpha _i \)
- m, n :
-
integers
- R :
-
radius of circumscribed circle
- S ni :
-
sin\(n\pi \zeta _i \)
- w :
-
transverse plate displacements
- (x,y), (x i ,y i ):
-
rectangular cartesian coordinates
- (x 1,x 2,x 3):
-
triaxial coordinates
- \((\alpha _1 ,\alpha _2 ,\alpha _3 )\) :
-
angles referring to the triangle of reference
- β,γ:
-
angle of plate normal to incident and reflected laser beam
- Δ:
-
area of the triangle of reference
- δ:
-
experimental plate displacement
- \(\zeta _i \) :
-
areal coordinates,\(\zeta _i = \eta _i /H_i \)
- \((\eta _1 ,\eta _2 ,\eta _3 )\) :
-
trilinear coordinates
- Λ:
-
2Rm 1 m 2 m 3
- λ:
-
wavelength of laser light
- μ:
-
mass density
- ν:
-
Poisson’s ratio
- ρ:
-
radius of inscribed circle\(\rho = 4R{\text{ sin }}\alpha _1 /2 \cdot \alpha _2 /2 \cdot {\text{sin }}\alpha _3 /2\)
- ω:
-
frequency
References
Whitworth, W. A., Trilinear Coordinates, and Other Methods of Modern Analytical Geometry of Two Dimensions, Deighton, Bell and Co., Cambridge (1866).
Ferrers, N. M., An Elementary Treatise on Trilinear Coordinates, the Method of Reciprocal Polars, and the Theory of Projections, Macmillan and Co., London (1866).
Askwith, E. H., Analytical Geometry of the Conic Sections, A. & C. Black Ltd., London (1918).
Loney, S. L., The Elements of Coordinate Geometry, 2, Trilinear Coordinates, Macmillan and Co., London (1923).
Smith, C., An Elementary Treatise on Conic Sections, Macmillan and Co., London (1919).
Aiken, H., “Trilinear Coordinates,” J. of Appl. Phys.,8 (July 1937).
Mertie, J. B., “Transformation of Trilinear and Quadriplanar Coordinates to and from Cartesian Coordinates,” The American Mineralogist,49 (July 1964).
Argyris, J. H., “Continua and Discontinua,” Matrix Methods in Structural Mechanics, Proc. of the Congress held at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, OH, 11–189 (Oct. 1965).
Bazeley, G. P., Cheung, Y. K., Irons, R. M., Zienkiewicz, O. C., “Triangular Elements in Plate Bendin—Conforming and Nonconforming Solutions,” Matrix Methods in Structural Mechanics, Proc. of the Congress held at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, OH, 547–561 (Oct. 1965).
Williams, R., and Brinson, H. F., “Applications of Trilinear Coordinates to Some Problems in Plane Elasticity,” VPI & SU College of Engineering Report No. VPI-E-72-22 (Oct. 1972).
Leissa, A. W., “Vibration of Plates,”NASA SP-160, U.S. Printing Office, Washington, DC (1969).
Powell, R. L. andStetson, K. A., “Interferometric Vibration Analysis by Wavefront Reconstruction,”J. Opt. Soc. of Amer.,55 (12),1593 (Dec. 1965).
Sampson, R. C., “Holographic-interferometry Applications in Experimental Mechanics,” EXPERIMENTAL MECHANICS,10 (8),313–320 (Aug. 1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, R., Yeow, Y.T. & Brinson, H.F. An analytical and experimental study of vibrating equilateral triangular plates. Experimental Mechanics 15, 339–346 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02318874
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02318874