Abstract
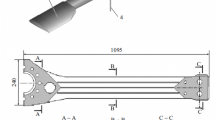
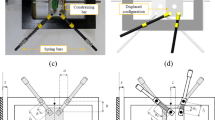
Support excitation of a small spring-mass system, consisting of a massm and two thin wafers in shear, is used as a simple and reliable method to determine the dynamic properties (storage-modulus and complex-modulus loss factor) of elastomeric materials over a fairly broad frequency range. No special equipment or instrumentation is required since ordinary vibration equipment is used. Microminiature accelerometers are used to monitor the support and mass accelerations which eliminates the measurement of small forces and displacements.
The frequency range of interest over which experimental data can be obtained fromone specimen can be varied by the thicknessh of the elastomeric waters and/or the size of the massm. The method discussed has been used to determine the dynamic properties of a wide variety of elastomers with frequencies as high as 6000 Hz. Typical results demonstrating repeatability of the method are shown for a carboxyl-terminated butadiene acrylonitrile (CTBN) specimen over the frequency range of 500–3000 Hz.
The small test setup is easily adaptable for use in small temprature-controlled chambers for temperature/frequency studies of elastomers.
The mathematical model developed for reduction of experimental data is based on the complex shear modulus for the damping model of the elastomer where the spring-mass system is subjected to support excitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
area of wafer specimen bonded to massm
- d * :
-
complex shear distortion
- d o :
-
amplitude of shear distortion
- E :
-
Young's modulus
- E * :
-
complex modulus
- E 1 :
-
storage modulus
- E 2 :
-
loss modulus
- F *o :
-
complex shear force
- F o :
-
amplitude ofF *
- f :
-
excitation frequency, Hz
- f n :
-
natural frequency, Hz
- G * :
-
complex shear modulus
- G :
-
magnitude of shear modulus
- h :
-
thickness of elastomeric water
- j :
-
\(\sqrt { - 1} \)
- K *,k e * :
-
complex stiffness
- m, m o :
-
mass
- t :
-
time, s
- x :
-
displacement of massm
- |X|:
-
amplitude ofx
- y :
-
displacement of support motion
- |Y|:
-
amplitude ofy
- γ*:
-
complex shear strain
- γo :
-
amplitude of shear strain
- δ:
-
loss factor
- μ:
-
Poisson's ratio
- τ*:
-
complex shear stress
- τ0 :
-
amplitude of shear stress
- ϕ, ψ:
-
phase angles
- ω:
-
circular frequency of excitation, rad/s
- ω n :
-
natural circular frequency, rad/s
References
Unger, E.E. and Hatch, D.K., “Your Selection to High-Damping Materials,” Product Engineering, 44–56 (April 1961).
Nolle, A.W., “Methods for Measuring Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Rubberlike Materials,”J. Appl. Phys.,19 (8),753–774 (Aug. 1948).
Smith, G.M., Pao, Y.C. andFickes, J.D., “Determination of a Dynamic Model for Urethane Prosthetic Compounds,”Experimental Mechanics,18 (9),389–395 (Oct. 1978).
The Measurement of the Dynamic Properties of Elastomers and Elastomeric Mounts, ed. B.M. Hillberry, Symposium sponsored by SAE and ASTM, Detroit, MI (Jan. 8–12, 1973).
Ferry, J.D., Fitzgerald, E.R., Grandine, Jr., L.D. andWilliams, M.L., “Temperature Dependence of Dynamic Properties of Elastomers; Relaxation Distributions,”Int. Eng. Chem,44,703–706 (1952).
Thompson, W.T., Theory of Vibration with Applications, 2nd ed. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 13–35 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, G.M., Bierman, R.L. & Zitek, S.J. Determination of dynamic properties of elastomers over broad frequency range. Experimental Mechanics 23, 158–164 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02320404
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02320404