Abstract
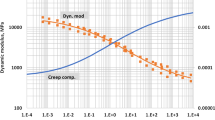
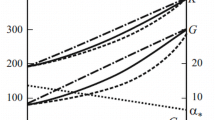
Employing a constitutive equation developed by Farris and Fitzgerald which accounts for the maximum strain ever imposed upon a material as well as a weighted average of the strain history, the family of Pth order Lebesgue norms, the applicability to a sand-asphalt concrete is demonstrated. The inadequacy of linear viscoelasticity theory under repeated or decreasing loadings for these materials is also demonstrated. Practical laboratory determination of the material parameters is described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farris, R. J., “Homogeneous Constitutive Equations for Materials with Permanent Memory,” AFOSR Scientific Report No. 70-1962TR, College of Eng., Univ. of Utah.
Fitzgerald, J. E. and Hufferd, W. L., “Nonlinear Viscoelasticity,” UTEC CE 71-034, Dept. of Civil Eng., Univ. of Utah (Feb. 1971).
Truesdell, C., The Elements of Continuum Mechanics, Springer-Verlag, Inc., New York (1966).
Eringen, A. C., Nonlinear Theory of Continuous Media, McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York (1962).
Taylor, A. E., Introduction to Functional Analysis, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York (1958).
Truesdell, C. andNoll, W., The Nonlinear Field of Mechanics, Encyclopedia of Physics,3,Springer-Verlag, Inc.,Berlin (1965).
Farrts, R. J., “Applications of Nonlinear Viscoelasticity and Cumulative Damage,” 1565-26-a-2, Aerojet Solid Propulsion Company (Oct. 1970).
Lai, J. S. and Findley, W. N., “Stress Relaxation of Nonlinear Viscoelastic Material Under Uniaxial Strain,” Trans. Soc. Rheol.,12 (1968).
Fitzgerald, J. E. andFarris, R. J., “Deficiencies of Viscoelastic Theories as Applied to Solid Propellants,”Bull. of the First Joint Army-Navy-NASA-Air Force Meeting of the Working Group on Mech. Beh., CPIA Pub. No. 160, The Johns Hopkins Univ., MD (May 1970).Also published in Trans. of the Soc. of Rheology (1970).
Volterra, V., Theory of Functionals and Integral and Integro Differential Equations, Dover Publications, Inc., New York (1959).
Green, A. E. and Rivlin, R. S., “The Mechanics of Nonlinear Materials with Memory,” Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal. (1959).
Hermann, L. R., “On a General Theory of Viscoelasticity,” J. Franklin Institute (1965).
Coleman, B. D. and Noll, W., “An Approximation Theorem for Functionals with Applications in Continuum Mechanics,” Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal. (1960).
Fitzgerald, J. E., “Thermomechanical Coupling in Viscoelastic Materials,” Proc. Int. Conf. on Structures, Solid Mech., and Eng. Design in Civil Eng. Mat., Southampton Univ., England (April 21–25, 1969); published by John Wiley and Sons (1972). (Discussion to above).
Fitzgerald, J. E. and Farris, R. J., “Characterization and Analysis Methods for Nonlinear Viscoelastic Materials,” Project THEMIS, publ. UTEC TH70-204 (available through AFOSR) 73–105 (Nov. 1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fitzgerald, J.E., Vakili, J. Nonlinear characterization of sand-asphalt concrete by means of permanent-memory norms. Experimental Mechanics 13, 504–510 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02322338
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02322338