Abstract
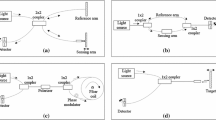
A micro-interferometric technique for measuring out-of-plane thermal displacements on a scale commensurate with the dimensions of the fiber/matrix unit cell is described. A scanning micro-interferometer is used to image surface displacements of samples containing a single-pitch-based carbon fiber embedded in an epoxy matrix. The interferometer design gives the necessary resolution to detect small changes in thermal displacements in the fiber/matrix interface region. The samples were heated electrically through the fiber to create radially symmetric temperature and displacement fields. Repeatable displacement measurements were obtained on a radial line across the interface region with an accuracy of ±25 Å. A sharp expansion of the matrix surrounding the fiber was observed with each heating. Overall, the experiments demonstrate the utility of micro-interferometry for measuring submicron displacements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox, B.N., Morris, W.L. and James, M.R., “High Sensitivity, High Spatial Resolution Strain Measurements in Composites and Alloys,” Proc. Nondestr. Test. and Eval. of Advanced Mat. and Comp. Conf., 25–39 (1986).
Morris, W.L. and Cox, B.N., “Thermal Fatigue of Unidirectional Graphite Composites,” Proc. 6th Int. Conf. on Comp. Mat., ed. F.L. Matthews, N.C.R. Buskell, J.M. Hodgkinson, and J. Morton,4,344–352 (1987).
Morris, W.L., Inman, R.V. andCox, B.N., “Microscope Deformation in a Heated Unidirectional Graphite-epoxy Composite,”J. Mat. Sci., 24:199–204 (1989).
James, M.R., Morris, W.L. andCox, B.N., “A High Accuracy Automated Strain Field Mapper,”Experimental Mechanics,20 (1),60–67 (March1990).
Scott, W.R., Huber, S. andRyan, M., “An Image Scanning Heterodyne Microinterferometer,”Rev. of Progress in Quantitative Nondestr. Eval., Plenum Press, New York,7B,1065–1073 (1988).
Scott, W.R., Ryan, M.J., Granata, D.M. and Sottos, N.R., “Nondestructive Evaluation and Characterization of Composite Materials Microinterferometry,” 1st Navy Independent Research/Independent Exploratory Development Symp., CPIA Publication 492,1,481–491 (1988).
Huber, S., Scott, W.R. andSands, R., “Detection and Analysis of Waves Propagating in Boron/Aluninum Composite Materials,”Rev. Progress in Quantitative Nondest. Eval., Plenum Press, New York,6B,1065–1073 (1987).
Ryan, M.J., Scott, W.R. andSottos, N.R., “Scanning Heterodyne Micro-interferometry for High Resolution Contour Mapping, Rev. of Progress in Quantitative Nondest. Eval., Plenum Press, New York (1990).
Carslaw, H.C. andJaeger, J.C., Conduction of Heat in Solids, Oxford Science Publications, New York (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sottos, N.R., Scott, W.R. & McCullough, R.L. Micro-interferometry for measurement of thermal displacements at fiber/matrix interfaces. Experimental Mechanics 31, 98–103 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02327559
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02327559