Abstract
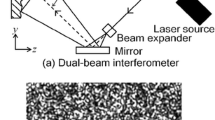
An experimental scheme of digital speckle pattern interferometry using two electromagnetic shutters and a three-frame color image board is presented to measure two in-plane components of incremental displacement field of diffuse objects. The deformation of the entire process from initial elastic deformation to fracture can be observed by using a Magneto Optical (MO) disk that has enough memory to record the image data of the entire process. By this system, some tensile experiments are achieved to investigate the mechanism of plastic deformation. The experimental results show that plastic deformation of tensile deformation is nonuniform. The material deforms in the distribution of domains. In the domains, the main deformation is uniform shear and rotation. At the boundary of the domains, the deformation is very large normal strain. With load, both the range and mode of domains are changing. At the end of plastic deformation, only two domains become dominant, and fracture happens at the boundary of the two domains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sirohi, R.S., “Speckle Methods in Experimental Mechanics,”Speckle Metrology, ed. R.S. Sirohi, Marcel Dekker, New York (1993).
Kienzle, O. andMietzner, K., Atlas Umformter Metallischer Oberflachen, Springer, Berlin (1967).
Yamaguchi, K. andMellor, P.B., ”Thickness and Grain Size Dependence of Limited Strains in Sheet Metal Stretching,”Int. J. Mech. Sci.,18,85–90 (1976).
Lee, C., Chao, Y.J., Sutton, M.A., Peters, W.H., andRanson, W.F., “Determination of Plastic Strains at Notches by Imaging-processing Methods,”Experimental Mechanics,29,214–220 (1989).
Dai, Y.Z., Tay, C.J., andChiang, F.P., “Determination of the Plastic Zone by Laser-speckle Correlation,”Experimental Mechanics,31,348–352 (1991).
Gong, X.L. and Toyooka, S., “Real-time Speckle Interferometry to Observe Plastic Deformation Wave,” Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computer Aided Design of Advanced Materials and Technologies, Tomsk, Russia (1995).
Toyooka, S. andGong, X.L., “Digital Speckle Pattern Interferometry for Observing the Entire Process of Plastic Deformation of a Solid Object,”Jpn. J. Appl. Phys.,34 (12B),L1666-L1668 (1995).
Suprapedi andToyooka, S., “Time-division Observation of Plastic Deformation Process Using Digital Speckle Pattern Interferometry,”Opt. Rev.,4,284–287 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, X.L., Toyooka, S. Investigation on mechanism of plastic deformation by digital speckle pattern interferometry. Experimental Mechanics 39, 25–29 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02329297
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02329297