Abstract
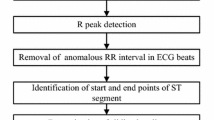
A novel automated system is presented for improved detection of transient ischaemic and heart rate-related ST-segment episodes in ‘real-world’ 24 h ambulatory ECG data. Using a combination of traditional time-domain and Karhunen-Loève transform-based approaches, the detector derives QRS complex and ST-segment morphology feature vectors and, by mimicking human examination of feature-vector time series and their trends, tracks the time-varying ST-segment reference level owing to clinically unimportant, non-ischaemic causes, such as slow drifts, axis shifts and conduction changes. The detector estimates the slowly varying ST-segment level trend, identifies step changes in the time series and subtracts the ST-segment reference level thus obtained from the ST-segment level to obtain the ST-segment deviation time series, which are suitable for detection of ST-segment episodes. The detector was developed using the Long-term ST database containing 24h ambulatory ECG records with human-expert annotated transient ischaemic and heart rate-related ST-segment episodes. The average ST episode detection sensitivity/positive predictivity obtained when using the annotations of the annotation protocol B of the database were 78.9%/80.7%. Evaluation of the detector using the European Society of Cardiology ST-T database as a test database showed average ST episode detection sensitivity/positive predictivity of 81.3%/89.2%, which are better performances, comparable with those of the systems being developed using the European database.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, P., Moody, G. B., andMark, R. G. (1988): ‘Use of the ‘bootstrap’ to assess the robustness of the performance statistics of an arrhythmia detector’,J. Ambulatory Monit.,1, pp. 171–176
ANSI/AAMI EC57:1998. (1998): ‘Testing and reporting performance results of cardiac rhythm and ST-segment measurement algorithms’ (American National Standard Institute/Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, Arlington, VA)
Bezerianos, A., Vladutu, L., andPapadimitriou, S. (2000): ‘Hierarchical state space partitioning with a network self-organising map for the recognition of ST-T segment changes’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,38, pp. 406–415
Bosnjak, A., Bevilacqua, G., Passariello, G., Mora, F., Sanso, B., andCarrault, G. (1995): ‘An approach to intelligent ischaemia monitoring’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,33, pp. 749–756
Daskalov, I. K., Dotsinsky, I. A. andChristov, I. I. (1998): ‘Development in ECG acquisition, preprocessing, parameter measurement, and recording’,IEEE Eng. Med. Biol.,17, pp. 50–58
Efron, B. (1979): ‘Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife’,Ann. Statist.,7, pp. 1–26
Egan, J. P. (1975): ‘Signal detection theory and ROC analysis’ (Academic Press, New York, 1975)
Gallino, A., Chierchia, S., Smith, G., Croom, M., Morgan, M., Marchesi, C., andMaseri, A. (1984): ‘Computer system for analysis of ST segment changes on 24 hour Holter monitor tapes: comparison with other available systems’,J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.,4, pp. 245–252
Garcia, J., Sörnmo, L., Olmos, S., andLaguna, P. (2000): ‘Automatic detection of ST-T complex changes on the ECG using filtered RMS difference series: application to ambulatory ischemia monitoring’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 47, pp. 1195–1201
Jager, F., Jaklič, A., Koren, I, andGyergyek, L. (1989): ‘A real-time personal computer based system for analysis of electrocardiograms’,Comput. Cardiol., pp. 497–500
Jager, F., Moody, G. B., Taddei, A., andMark, R. G. (1991): ‘Performance measures for algorithms to detect transient ischemic ST segment changes’,Comput. Cardiol., pp. 369–372
Jager, F., Moody, G. B., andMark, R. G. (1998a): ‘Detection of transient ST segment episodes during ambulatory ECG monitoring’,Comput. Biomed. Res.,31, pp. 305–322
Jager, F. (1998b): ‘Guidelines for assessing performance of ST analysers’,J. Med. Eng. Technol.,22, pp. 25–30
Jager, F., Taddei, A., Moody, G. B., Emdin, M., Antolič, G., Dorn, R., Smrdel, A., Marchesi, C., andMark, R. G. (2003): ‘Long-term ST database: a reference for the development and evaluation of automated ischaemia detectors and for the study of the dynamics of myocardial ischaemia’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,41, pp. 172–182
Laguna, P., Garcia, J., Roncal, I., Wagner, G., Lander, P., andMark, R. G. (1998): ‘Model-based estimation of cardiovascular repolarization features: ischaemia detection and PTCA monitoring’,J. Med. Eng. Technol.,22, pp. 64–72
Maglaveras, N., Stamkopoulos, T., Pappas, C., andStrintzis, M. G. (1998): ‘An adaptive backpropagation neural network for real-time ischemia episodes detection: development and performance analysis using the European ST-T database’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,45, pp. 805–813
Moody, G. B., andMark, R. G. (1982): ‘Development and evaluation of a 2-lead ECG analysis program’,Comput. Cardiol., pp. 39–44
Papaloukas, C., Fotiadis, D. I., Likas, A., andMichalis, L. K. (2002): ‘An ischemia detection method based on artificial neural networks’,Artif. Intell. Med.,24, pp. 167–178
Presedo, J., Vila, J., Barro, S., Palacios, F., Ruiz, R., Taddei, A., andEmdin, M. (1996): ‘Fuzzy modelling of the expert's knowledge in ECG-based ischaemia detection’,Fuzzy Sets Syst.,77, pp. 63–75
Silipo, R., andMarchesi, C. (1998): ‘Artificial neural networks for automatic ECG analysis’,IEEE Trans. Signal Process.,46, pp. 1417–1425
Stadler, R. W., Lu, S. N., Nelson, S. D., andStylos, L. (2001): ‘A real-time ST segment monitoring algorithm for implantable devices’,J. Electrocardiol.,34, pp. 119–126
Stamkopoulos, T., Diamantaras, K., Maglaveras, N., andStrintzis, M. (1998): ‘ECG analysis using nonlinear PCA neural networks for ischemia detection’,IEEE Trans. Signal Process.,46, pp. 3058–3067
Strintzis, M. G., Stalidis, G., Magnisalis, X., andMaglaveras, N. (1992): ‘Use of neural networks for electrocardiogram (ECG) feature extraction and classification’,Neural Network World,3–4, pp. 313–327
Taddei, A., Distante, G., Emdin, M., Pisani, P., Moody, G. B., Zeelenberg, C., andMarchesi, C. (1992): ‘The European ST-T database: standard for evaluating systems for the analysis of ST-T changes in ambulatory electrocardiography’,Eur. Heart J.,13, pp. 1164–1172
Taddei, A., Costantino, G., Silipo, R. Emdin, M., andMarchesi, C. (1995): ‘A system for the detection of ischemic episodes in ambulatory ECG’,Comput. Cardiol. pp. 705–708
Vila, J., Presedo, J., Delgado, M., Barro, S., Ruiz, R., andPalacios, F. (1997): ‘SUTIL: intelligent ischemia monitoring system’,Int. J. Med. Inform.,47, pp. 193–214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smrdel, A., Jager, F. Automated detection of transient ST-segment episodes in 24h electrocardiograms. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 42, 303–311 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344704
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344704