Summary
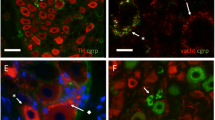
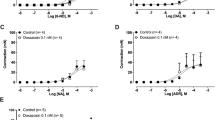
Vasa deferentia of rats chronically treated with high doses of guanethidine sulphate (30 or 60 mg/Kg/day i.p.) were examined using electron microscopic, fluorescence histochemical and pharmacological techniques. Counts of the axon population in segments of the proximal (urethral) end of the vas deferens showed a reduction to approximately 55% and 35% in the number of axon profiles after treatment for one week with the two dose levels respectively. In the same period only a few cell bodies in the hypogastric ganglion (from which most of the adrenergic innervation of the vas deferens arises) reached the stage of terminal degeneration. Although many axons showed some abnormalities, the number of axons observed in terminal stages of degeneration in treated tissue did not exceed, at any stage examined, the very small numbers observed in control tissue. Organ bath studies showed that the contractile response to transmural stimulation was lost fastest at the distal (epididymal) end of the treated vas deferens. These results have led to the conclusion that, in contrast to the degeneration of adrenergic axons produced by surgery or 6-hydroxydopamine, the sympathectomy produced by guanethidinein vivo involves theretraction of adrenergic axons prior to complete degeneration of the cell bodies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akert, K., Cuénod, M., Moor, H.: Further observations on the enlargement of synaptic vesicles in degenerating optic nerve terminals of the avian tectum. Brain Res.25, 255–263 (1971)
Berl, S., Puszkin, S.: Actin-like properties of colchicine binding protein isolated from brain. Nature (Lond.)225, 558–559 (1970)
Botár, J.: The autonomic nervous system. Budapest: Akadémiai Kiado 1966
Bowler, K., Duncan, C. J.: Actomyosin-like protein from crayfish nerve: a possible molecular explanation of permeability changes during excitation. Nature (Lond.)211, 642–643 (1966)
Burnstock, G., Evans, B., Gannon, B. J., Heath, J. W., James, V.: A new method of destroying adrenergic nerves in adult animals using guanethidine. Brit. J. Pharmacol.43, 295–301 (1971a)
Burnstock, G., Gannon, B. J., Malmfors, T., Rogers, D. C.: Changes in the physiology and fine structure of the taenia of the guinea-pig caecum following transplantation into the anterior eye chamber. J. Physiol. (Lond.)219, 139–154 (1971b)
Burton, P. R., Kirkland, W. L.: Actin detected in mouse neuroblastoma cells by binding of heavy meromyosin. Nature (Lond.) New Biol.239, 244–246 (1972)
Cajal, S. Ramon Y.: Degeneration and regeneration of the nervous system, vol. I. (R.M. May, translator and editor). New York: Hafner 1959
Chang, C.-M., Goldman, R. D.: The localisation of actin-like fibres in cultured neuroblastoma cells as revealed by heavy meromyosin binding. J. Cell Biol.57, 867–874 (1973)
Clementi, F.: Modifications ultrastructurelles provoquées par quelques médicaments sur les terminaisons nerveuses adrénergiques et sur la médullaire surrénale. Experientia (Basel)21, 171–176 (1965)
Cuénod, M., Sandri, C., Akert, K.: Enlarged synaptic vesicles as an early sign of secondary degeneration in the optic nerve terminals of the pigeon. J. Cell Sci.6, 605–613 (1970)
Cuénod, M., Sandri, C., Akert, K.: Enlarged synaptic vesicles in optic nerve terminals induced by intraocular injection of colchicine. Brain Res.39, 285–296 (1972)
Devine, C. E., Robertson, A. A., Simpson, F. O.: Effect of sympatholytic drugs on sympathetic axonal fine structure and tissue catecholine levels. NZ med. J.66, 390–391 (1967)
Devine, C. E., Simpson, F. O.: The effect of noradrenaline-depleting drugs on the granular vesicles of the axons around rat intestinal blood vessels. Proc. Univ. Otago med. Sch.44, 54–56 (1966)
Evans, B., Iwayama, T., Burnstock, G.: Long lasting supersensitivity of the rat vas deferens to norepinephrine after chronic guanethidine administration. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.185, 60–69 (1973)
Falck, B., Owman, Ch.: A detailed methodological description of the fluorescence method for the cellular demonstration of biogenic amines. Acta Univ. Lund. Sec. II. No. 7, 1–23 (1965)
Fillenz, M.: Fine structure of noradrenaline storage vesicles in nerve terminals of the rat vas deferens. Phil. Trans. B,261, 319–323 (1971)
Fine, R. E., Bray, D.: Actin in growing nerve cells. Nature (Lond.) New Biol.234, 115–118 (1971)
Furness, J. B., Campbell, G. R., Gillard, S. M., Malmfors, T., Cobb, J.L.S., Burnstock, G.: Cellular studies of sympathetic denervation produced by 6-hydroxydopamine in the vas deferens. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.174, 111–122 (1970)
Furness, J. B., Iwayama, T.: The arrangement and identification of axons innervating the vas deferens of the guinea-pig. J. Anat. (Lond.)113, 179–196 (1972)
Heath, J. W., Evans, B. K., Gannon, B. J., Burnstock, G., James, V. B.: Degeneration of adrenergic neurons following guanethidine treatment: an ultrastructural study. Virchows Arch. Abt. B,11, 182–197 (1972)
Heath, J. W., Hill, C. E., Burnstock, G.: Axon retraction following guanethidine treatment. Studies of sympathetic neurons in tissue culture. J. Neurocytol. (submitted for publication)
Hill, C. E., Mark, G. E., Eränkö, O., Eränkö, L., Burnstock, G.: Use of tissue culture to examine the actions of guanethidine and 6-hydroxydopamine. Europ. J. Pharmacol.23, 162–174 (1973)
Huxley, H. E.: Muscular contraction and cell motility. Nature (Lond.)244, 445–449 (1973)
Jensen-Holm, J., Juul, P.: Ultrastructural changes in the rat superior cervical ganglion following prolonged guanethidine administration. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.)30, 308–320 (1971)
Juul, P.: Accumulation of guanethidine by sympathetic ganglia of reserpinized rats. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.)33, 79–80 (1973)
Juul, P., Sand, O.: Determination of guanethidine in sympathetic ganglia. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.)32, 487–499 (1973)
Kawana, E., Akert, K., Bruppacher, H.: Enlargement of synaptic vesicles as an early sign of terminal degeneration in the rat caudate nucleus. J. comp. Neurol.142, 297–308 (1971)
King, E.S.J., Willis, A. G.: Nerves in tumours. Aust. N.Z.J. Surg.27, 35–48 (1957)
Malmquist, J., Oates, J. A.: Effect of adrenergic neuron-blocking guanidine derivatives on mitochondrial metabolism. Biochem. Pharmacol.17, 1845–1854 (1968)
Reger, J. F.: Studies on the fine structure of normal and denervated neuromuscular junctions from mouse gastrocnemius. J. Ultrastruct. Res.2, 269–282 (1959)
Richardson, K. C.: The fine structure of autonomic nerve endings in smooth muscle of the rat vas deferens. J. Anat. (Lond.)96, 427–442 (1963)
Roth, C. D., Richardson, K. C.: Electron microscopical studies on axonal degeneration in the rat iris following ganglionectomy. Amer. J. Anat.124, 341–360 (1969)
Sjöstrand, N. O.: The adrenergic innervation of the vas deferens and the accessory male genital glands. Acta physiol. scand.65, Suppl. 257 (1965)
Spiedel, C. C.: Studies of living nerves. VII. Growth adjustments of cutaneous terminal arborisations. J. comp. Neurol.76, 57–73 (1942)
Spiedel, C. C.:In vivo studies of myelinated nerve fibres. Int. Rev. Cytol.16, 173–231 (1964)
Spooner, B. S., Ash, J. F., Wrenn, J. T., Frater, R. B., Wessells, N. K.: Heavy meromyosin binding to microfilaments involved in cell and morphogenetic movements. Tissue and Cell.5, 37–46 (1973)
Sumner, B.E.H., Watson, N. E.: Retraction and expansion of the dendritic tree of motor neurons of adult rats inducedin vivo. Nature (Lond.)233, 273–275 (1971)
Tamura, T.: Electron microscopical study concerning the effects of guanethidine on the nerve terminals and preterminals of the dilator muscle in rabbit iris. Acta Sec. ophthalmol. jap.73, 130–139 (1969)
Taxi, J.: Contribution à l'étude des connexions des neurones moteurs du système nerveux autonome. Ann. Sol. nat. Zool.7, 413–674 (1965)
Yamada, K. M., Spooner, B. S., Wessells, N. K.: Axon growth: role of microfilaments and microtubules. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)66, 1206–1212 (1970)
Yamada, K. M., Spooner, B. S., Wessells, N. K.: Ultrastructure and function of growth cones and axons of cultured nerve cells. J. Cell Biol.49, 614–635 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council, the National Heart Foundation and the Australian Research Grants Committee. We are grateful to Mr. A.G. Willis and Dr. D.G. Satchell of the Zoology Department and to Prof. E.G. Williams, Statistics Department, University of Melbourne for valuable discussion, and to Caryl Hill for thorough criticism of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heath, J.W., Evans, B.K. & Burnstock, G. Axon retraction following guanethidine treatment. Z.Zellforsch 146, 439–451 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347174
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347174