Abstract
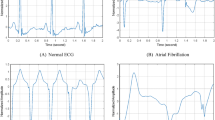
A method is presented for automatic analysis of the P-wave, based on lead II of a 12-lead standard ECG, in resting conditions during a routine examination for the detection of patients prone to atrial fibrillation (AF), one of the most prevalent arrhythmias. First, the P-wave was delineated, and this was achieved in two steps: the detection of the QRS complexes for ECG segmentation, using a wavelet analysis method, and a hidden Markov model to represent one beat of the signal for P-wave isolation. Then, a set of parameters to detect patients prone to AF was calculated from the P-wave. The detection efficiency was validated on an ECG database of 145 patients, including a control group of 63 people and a study group of 82 patients with documented AF. A discriminant analysis was applied, and the results obtained showed a specificity and a sensitivity between 65% and 70%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeysekera, R. M. (1994): ‘Detection and classification of ECG signals in the time frequency domain’,Appl. Signal Process.,1, pp. 35–51
Clavier, L., Boucher, J. M., andBlanc, J. J. (1996): ‘P-wave parameters for atrial fibrillation risk detection’. 18th Annual International Conference of IEEE Engineering in Medicine Biology Society (IV), pp. 1367–1368
Clavier, L., Maheu, B., Provost, K., Mansourati, J., Boucher, J. M., andBlanc, J. J. (1997): ‘Shape and time and frequency domain analysis in addition to P-wave duration markedly improves detection of patients prone to atrial fibrillation’,PACE. NASPE Abstr.,20, p. 1116
Clavier, L., Boucher, J. M., andPollard, e. (1998): ‘Hidden Markov models compared to the wavelet transform for P-wave segmentation in ECG signals’ IX European Signal Processing Conference, Rhodes, (IV), pp. 2453–2456
Coast, D. A., Stern, R. M., Cano, G. G., andBriller, S. A. (1990): ‘An approach to cardiac arrhythmia analysis using hidden Markov models’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,37, pp. 826–836
Czys, Z., Petelenz, T., Flak, Z., Sosnowski, M., andLeski, J. (1993): ‘A time frequency domain analysis of atrial late potentials for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and assessment’,Comput. Cardiol., pp. 45–48
Fukunami, M., Yamada, T., Ohmori, M., Kumagai, K., andUmemoto, K. (1991): ‘Detection of patients at risk of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm by P wave-triggered signalaveraged electrocardiogram’,Circulation,83, pp. 162–169
Kanel, W. B., Abbott, R. D., Savage, D. D., andMcNamara, P. M. (1982): ‘Epidemiologic features of chronic atrial fibrillation: the Framingham Study’,N. Engl. J. Med.,306, pp. 1018–1022
Lemire, D., Pharand, C., Rajaonah, J. C., Dube, B., andLeblanc, A. R. (2000): ‘Wavelet time entropy, T-wave morphology and myocardial ischemia’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,47, pp. 967–970
Li, C., Zheng, C., andTai, C. (1995): ‘Detection of ECG characteristic points using wavelet transform’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,42(1), pp. 21–28
Niranjan, U. C., andMurthy, I. S. N. (1993): ‘ECG component delineation by Prony's method’,Signal Process.,31, pp. 191–202
Pan, J., andTompkins, W. J. (1985): ‘A real-time QRS detector’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,32, pp. 230–236
Rabiner, L. R. (1989): ‘A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition’,Proc. IEEE,77, pp. 257–286
Raitt, M. H., Ingram, K. D., andShinnamon, A. F. (1997): ‘Frequency analysis of the signal averaged P-wave differentiates patients with history of atrial fibrillation from controls independent to P-wave duration’,RACE, NASPE abstracts,20, p. 1220
Raudys, S. J., andJain, A. N. (1991): ‘Small sample size effects in statistical pattern recognition: recommendations for practitioners’,IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.,13, pp. 252–264
Rix, H., andMalenge, J. P. (1980): ‘Detecting small variations in shape’,IEEE Trans. Syst Man Cybern.,10, pp. 90–96
Saoudi, S., Ghorbel, F., andHillion, A. (1997): ‘Some statistical properties of the Kernel diffeomorphism estimator’,Appl. Stochast. model Data Anal.,13, pp. 39–58
Stafford, P. J., Turner, I., Phil, D., andVincent, R. (1991): ‘Quantitative analysis of signal-averaged P-wave in idiopathic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation’,Am. J. Cardiol.,68, pp. 751–755
Thakor, N. V., andZhu, Y. S. (1991): ‘Applications of adaptive filtering to ECG analysis: noise cancellation and arrhythmia detection’,IEEE Trans. Biomed Eng.,38, pp. 785–794
Villani, G. O., Piepoli, M., Cripps, T., Rosi, A., andGazzola, U. (1994): ‘Atral late potentials in patient with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation detected using a high gain, signal averaged oesophageal lead’,Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol.,17, pp. 1118–1123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clavier, L., Boucher, J.M., Lepage, R. et al. Automatic P-wave analysis of patients prone to atrial fibrillation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 40, 63–71 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347697
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347697