Summary
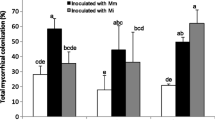
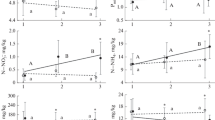
To explain the decline of Hippophaë scrub in the vegetation succession in the dunes of The Netherlands, the growth and nodulation of Hippophaë plants grown in pots, using soil from an early stage (site AH) and a post-optimum stage (site HP), were investigated. In HP-soil nodulation, yield, and the nitrogen and phosphorus content of test plants were always lower and the number of necrotic nodules and the dry matter content were always higher than in AH-soil, even after inoculation with crushed nodules and the addition of a nutrient solution. Plants in HP-soil also had darker roots, less root hairs, a higher number of short lateral roots and a higher percentage of dead roots than those in AH-soil. These characteristics of adverse growth conditions disappeared upon ignition or gamma-irradiation of HP-soil.
Possible explanations of these results are discussed. The degeneration of Hippophaë scrub cannot be ascribed to the age of the plants, the absence of sufficient infective endophyte particles or to abiotic factors such as unfavourable physical (particle size) or chemical soil conditions but is caused by biotic factors. No indications were obtained that plant-pathogenic fungi and bacteria are involved. HP-soil in contrast to AH-soil, however, contained large numbers of the nematodeLongidorus sp., a species known to cause root deformations. The conclusion was that this nematode is one of the biotic factors involved in the degeneration of the Hippophaë scrub. This degeneration is due to a restriction of the root system resulting in a low phosphate uptake, a low nodulation capacity and, as a consequence, a low nitrogen content. The results demonstrate that biotic soil factors are important in influencing succession in higher plant communities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adesiyan, S. O. 1977 Studies on the effects of gamma radiation (from Cobalt 60 source) on storage life of white yam (Dioscorea rotundata var. efon) infected withScutellonema bradys. Ann. Appl. Biol.86, 213–218.
Akkermans, A. D. L. 1978 Root nodule symbioses in non-leguminous N2-fixing plants.In Interactions between non-pathogenic Soil Microorganisms and Plants. Eds. Y. R. Dommergues and S. V. Krupa. Elsevier Scientific Publ. Comp., Amsterdam, pp 335–372.
Akkermans, A. D. L. and Van Dijk, C. 1981 Non-leguminous root-nodule symbioses with actinomycetes and rhizobiumIn Nitrogen Fixation: Vol 1 Ecology Ed. W. J. Broughton, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, pp 57–103.
Allen, M. B. and Arnon, D. I. 1955 Studies on nitrogen-fixing blue green algae. I. Growth and nitrogen fixation byAnabaena cylindrica Lemm. Plant Physiol Lancaster,30, 366–377.
Allen, S. E. (Ed.) 1974. Chemical analysis of ecological materials 565 p. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford.
Andrews, R. A. and Newman, I. N. 1970 Root density and competition. Oecol. Plant.5, 319–334.
Becking, J. H. 1970 Plant-endophyte symbiosis in non-leguminous plants. Plant and Soil32, 611–654.
Bhat, K. K. S., Nye, P. H. and Brereton, A. J. 1979 the possibility of predicting solute uptake and plant growth response from independently measured soil and plant characteristics. VI The growth and uptake of rape in solutions of constant nitrate concentration. Plant and Soil53, 137–167.
Bond, G., Fletcher, W. W. and Ferguson, T. P. 1954 The development and function of the root nodules of Alnus, Myrica and Hippophaë. Plant and Soil5, 309–323.
Bond, G., MacConnell, J. T. and McCallum, A. H. 1956 The nitrogen-nutrition ofHippophaë rhamnoides L. Ann. Bot.20, 501–512.
Bond, G. and MacKintosh, A. H. 1975 Effect of nitrate-nitrogen on the nodule symbioses of Coriaria and Hippophaë. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. B.190, 199–209.
Clement, C. R., Jones, L. H. P. and Hopper, M. J. 1979 Uptake of nitrogen from flowing nutrient solution: effect of terminated and intermittent nitrate supplies.In Nitrogen Assimilation of Plants. Eds. E. J. Hewitt and C. V. Cutting, pp 123–133. Acad. Press Inc., New York.
Dijk, C. van, 1978 Spore formation and endophyte diversity in root nodules ofAlnus glutinosa (L) Vill. New Phytol.81, 601–615.
Dijk, C. van, 1979 Endophyte distribution in the soil.In Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in the Management of temperate Forests. Eds. J. C. Gordon, C. T. Wheeler and D. A. Perry, pp 84–94, Forest Research Laboratory, Oregon, State University, Corvallis.
Fisher, C. 1971 The new Quantimet 720. Microscope19, 1–20.
Hague, N. G. M. 1980 Nematodes of Legume Crops.In Advances in Legume Science Eds. R. J. Summerfield and A. H. Bunting, pp 199–205, Royal Bot. Garden, Kew.
Heringa, J. W., Groenewold, J. and Schoonderbeek, D. 1980 An unproved method for the isolation and the quantitative measurement of crop roots. Neth. J. Agric. Sci.28, 127–134.
Ingestad, T. and Lund, A. B. 1979 Nitrogen stress in birch seedlings. I. Growth technique and growth. Physiol. Plant.45, 137–148.
Ledwood, J. S. and Shimwell, D. W. 1971 Growth rates ofHippophaë rhamnoides L. Ann. Bot.35, 1053–1058.
Maas, P. W. Th. and Brinkman, H. 1980 Sampling of soil for nematode vectors of plant viruses in The Netherlands. Meded. Fac. Landbouw. Rijks Univ. Gent45, 769–773.
Oostenbrink, M. 1960 Estimating nematode nodulations by some selected methods.In Nematology. Eds. J. N. Sasser and W. R. Jenkins, pp 85–102, N. Car. Press, Chapel Hill.
Oremus, P. A. I. 1979 A quantitative study of nodulation inHippophaë rhamnoides L. ssp.rhamnoides in a coastal dune area. Plant and Soil52, 59–68.
Oremus, P. A. I. 1980 Occurrence and infective potential of the endophyte ofHippophaë rhamnoides L. ssp.rhamnoides in coastal sand-dune areas. Plant and Soil56, 123–139.
Quispel, A. 1954 Symbiotic nitrogen fixation in non-leguminous plants. II. The influence of the inoculation density and external factors on the nodulation ofAlnus glutinosa and its importance to our understanding of the mechanism of the infection. Acta Bot. Neerl.3, 512–532.
Salisbury, E. 1952 Downs and Dunes. Their plant life and its environment. G. Bell and Sons Ltd., London, 328 p.
Schouwenburg, J. Ch. van and Walinga, I. 1973 Methods of analysis for plant material. M. Sc. Course, Wageningen.
Seinhorst, J. W. 1966Longidorus elongatus onFragaria vesca. Nematologica12, 275–279.
Seinhorst, J. W. and Kozlowska, I. 1979Longidorus elongatus andTylenchorhynchus dubius onLolium perenne. Nematologica25, 314–321.
Tsao, P. H. 1970 Selective media for the isolation of pathogenic fungi. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol.8, 157–186.
Westhoff, V., Bakker, P. A., Van Leeuwen, C. G. and Van der Voo, E. E. 1970 Wilde planten, part 1. Ver. Beh. Natuurmonumenten Ned., 320 p.
Wollum, A. G., Youngberg, C. T. and Chichester, F. W. 1968 Relation of previous timber stand age to nodulation ofCeanothus velutinus. For. Sci.14, 114–118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oremus, P.A.I., Otten, H. Factors affecting growth and nodulation ofHippophaë rhamnoides L. ssp.Rhamnoides in soils from two successional stages of dune formation. Plant Soil 63, 317–331 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370033
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370033