Abstract
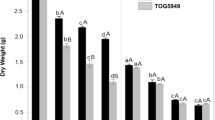
The response of the rice cultivars ‘M9’ and ‘M-201’ to nutrient cultures salinated at −0.4 MPa with varying ratios of Na and Ca was studied. Although the dry matter production of both cultivars was sensitive to the Na/Ca ratio, this correlation was significant only for M-201. Calcium nutrition was severely affected by the composition of the external solution, and the laminae exhibited Ca-deficiency symptoms at Na/Ca molar ratios of 78 and 198. Sodium concentration in the shoot decreased as the Na/Ca ratio in the external solution decreased. Patterns of Na and Cl distribution in the shoot tissues were similar; both ions were accumulated preferentially in the tillers and older leaves. The Na-induced inhibition of Ca uptake and transport appears to be more limiting to shoot growth of M9 and M-201 than Na toxicity per se.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carnahan H L, Johnson C W, Tseng S T and Mastenbroek J J 1978 Registration of ‘M9’ rice. Crop Sci. 18, 357–358.
Carnahan H L, Johnson C W, Tseng S T, Oster J J and Hill J E 1982 Registration of M-201 rice. Crop Sci. 22, 1087–1088.
Cotlove E 1963 Determination of true chloride content of biological fluids and tissues. II. Analysis by simple, nonisotopic methods. Anal. Chem. 35, 101–105.
Cramer G R, Läuchli A and Polito V S 1985 Displacement of Ca2+ by Na+ from the plasmalemma of root cells. Plant Physiol. 79, 207–211.
Flowers T J, Duque E, Hajibagheri M A, McGonigle T P and Yeo A R 1985 The effect of salinity on leaf ultrastructure and net photosynthesis of two varieties of rice: further evidence for a cellular component of salt-resistance. New Phytol. 100, 37–43.
Flowers T J and Yeo A R 1981 Variability in the resistance of sodium chloridesalinity within rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. New Phytol 88, 363–373.
Grattan S R, Maas E V and Ogata G 1981 Foliar uptake and injury from saline aerosol. J. Environ. Qual 10, 406–409.
Hanson J B 1983 The roles of calcium in plant growth. In Current Topics in Plant Biochemistry and Physiology. Eds. D D Randall, D G Blevins and R Larson. pp 1–24. University of Missouri, Columbia.
Kawasaki T and Moritsugu M 1973 Calcium effect on the absorption of monovalent cations by plant roots. VII. The effect of calcium on the absorption of monovalent cations by plant—especially in relation to salt injury. (2. Barley and paddy rice plants). J. Sci. Soil Manure, Japan 44, 133–137.
Kawasaki T and Moritsugu M 1979 A characteristic symptom of calcium deficiency in maize and sorghum. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 10, 41–56.
Kitson R E and Mellon M G 1944 Colorimetric determination of phosphorus as molybdovanado phosphoric acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 16, 379–383.
Lynch J and Läuchli A 1985 Salt stress disturbs the calcium nutrition of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) New Phytol. 99, 345–354.
Maas E V and Grieve C M 1987 Sodium-induced calcium deficiency in salt stressed corn. Plant, Cell Environ. (In press)
Pearson G A and Ayres A D 1960 Rice as a crop for salt-affected soil in process of reclamation. Production Research Report No. 43. Agric. Res. Ser. USDA, 13 pp.
Ponnamperuma F N 1976 Screening rice for tolerance to mineral stresses.In Plant Adaption to Mineral Stress in Problem Soils. Eds. M J Wright and S A Ferrari. pp 341–353 Cornell University, Ithaca, New York.
Ponnamperuma F N 1984 Role of cultivar tolerance in increasing rice production on saline lands.In Salinity Tolerance in Plants: Strategies for Crop Improvement. Eds. R C Staples and G A Toenniessen pp 255–271 Wiley International, New York.
Tanaka A 1961 Studies on the nutrio-physiology of leaves of rice plant. J. Fac. Agric. Hokkaido Univ. 51, 449–550.
Yamanouchi M, Shimada Y and Yoshida S 1983 The effects of calcium ion to reduce the toxicity of sodium chloride for rice plant. Jap. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 54, 499–504.
Yeo A R, Caporn S J M and Flowers T J 1985 The effect of salinity upon photosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Gas exchange by individual leaves in relation to their salt content J. Exp. Bot. 36, 1240–1248.
Yeo A R and Flowers T J 1982 Accumulation and localisation of sodium ions within the shoots of rice (Oryza sativa) varieties differing in salinity resistance. Physiol. Plant. 56, 343–348.
Yeo A R and Flowers T J 1983 Varietal differences in the toxicity of sodium ions in rice leaves. Physiol. Plant. 59, 189–195.
Yeo A R and Flowers T J 1984 Mechanisms of salinity resistance in rice and their role as physiological criteria in plant breeding.In Salinity Tolerance in Plants: Strategies for Crop Improvement. Eds. R C Staples and G A Toenniessen. pp. 151–170. Wiley International, New York.
Yeo A R and Flowers T J 1985 The absence of an effect of the Na/Ca ratio on sodium chloride uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.). New Phytol. 99, 81–90.
Yoshida S, Forna D A, Cock J H and Gomez K A 1972 Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila.
Yoshida S 1981 Fundamentals of Rice Crop Science. International Rice Research Institute, Manila.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grieve, C.M., Fujiyama, H. The response of two rice cultivars to external Na/Ca ratio. Plant Soil 103, 245–250 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370396
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370396