Abstract
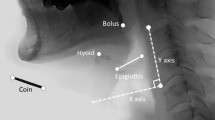
Preliminary results of an investigation that synchronizes the videotaped output of a ultrasound camera and the analog data from physiological measurements of swallowing and ventilation in normal and cerebral palsied (CP) children are presented. Four cerebral palsied children and three control children undertook a single sip-swallow of 5 ml of liquid and a solid mastication-swallow sequence on three occasions according to a defined protocol. The CP children exhibited much more variability and less control of the liquid bolus than did the controls. The ultrasound image clearly demonstrates the lack of control of the posterior of the tongue in many CP children. Some parts of the sequence of oral swallow and the time to achieve maximum anterior displacement of the hyoid bone appear to be slowed. The sequential events of swallowing show less variability as the sip-swallow proceeds from the oral voluntary to pharyngeal and lower involuntary phases. This study also identified a short-latency apnea that appears to accompany a saliva (protective) swallow and a long-latency apnea that accompanies semisolid or liquid bolus (alimentary) swallows. Further investigations of normal and CP children utilizing a combined diagnostic imaging-physiological measurement approach will follow this initial study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pape KE, Wigglesworth JS (eds): Patterns of intracranial haemorrhage and ischaemia in the newborn and their economic importance. In:Haemorrhage, Ischaemia and the Perinatal Brain. Suffolk: Spastics International Medical Publications, 1979, pp 1–10
Blumberg ML: Respiration and speech in the cerebral palsied child.Am J Dis Child 89:48–53, 1955
American Academy for Cerebral Palsy and Developmental Medicine. Statistical Information 1989. Richmond, Va.
Blair E, Stanley F: Interobserver agreement in the classification of cerebral palsy.Dev Med Child Neurol 27:615–622, 1985
Woods GE: The handicapped child. Assessment and management. In:Cerebral Palsy — Types of Movement Defect. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1975, pp 108–138
Miyasaka K, Hofman HJ, Froese AB: The influence of chronic cerebellar stimulation on respiratory muscle coordination in a patient with cerebral palsy.Neurosurgery 2(3):262–265, 1978
Wong PKH, Hoffman HJ, Froese AB, Platt LJ, Blacha S, Gear J: Cerebellar stimulation in the management of cerebral palsy: clinical and physiological studies.Neurosurgery 5(2):217–224, 1979
Storey AT: Interactions of alimentary and upper respiratory tract reflexes. In:Mastication and Swallowing, Biological and Clinical Correlates, Sessle BJ, Hannam AG (eds). Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1976, pp 22–31
McPherson KA:Clinical Evaluation and Statistical Analysis of Ventilation and Swallowing in Cerebral Palsy. Thesis, Toronto: University of Toronto, 1988
Kenny DJ, McPherson KA, Koheil R, Bablich K, Sochaniwskyj AE, Milner M: Ventilation/swallowing interactions in cerebral palsied and normal children.Dev Med Child Neurol accepted for publication, 1989
Coster ST, Schwarz WH: Rheology and the swallow-safe bolus.Dysphagia 1:113–118, 1987
Logemann JA: Evaluation of swallowing disorders. In:Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders. San Diego: College-Hill Press, 1983, pp 87–125
Shawker TH, Sonies B, Stone M, Baum BJ: Real-time ultrasound visualization of tongue movement during swallowing.J Clin Ultrasound 11:485–490, 1983
Shawker TH, Sonies B, Hall TE, Baum BJ: Ultrasound analysis of tongue, hyoid and larynx activity during swallowing.Invest Radiol 19:82–86, 1984
Stone M, Shawker TH: An ultrasound examination of tongue movement during swallowing.Dysphagia 1:78–83, 1986
Smith WL, Erenberg A, Nowak A, Franken EA: Physiology of sucking in the normal term infant using real-time US.Radiology 156:379–381, 1985
Shawker TH, Sonies BC: Tongue movement during speech: a real-time ultrasound evaluation.J Clin Ultrasound 12:125–133, 1984
Sonies BC, Baum BJ, Shawker TH: Tongue motion in elderly adults: initial in situ observations.J Gerontol 39:279–283, 1984
Skolnick WL, Zagzebski JA, Watkin KL: Two dimensional ultrasonic demonstration of lateral pharyngeal wall movement in real time-a preliminary report.Cleft Palate J 12:299–303, 1976
Sonies BC, Parent LJ, Morrish K, Baum BJ: Durational aspects of the oral-pharyngeal phase of swallow in normal adults.Dysphagia 3:1–10, 1988
Loveridge B, West P, Anthonisen NR, Kryger MH: Single-position calibration of the respiratory inductance plethysmograph.J Appl Physiol 55:1031–1034, 1983
Sochaniwskyj AE, Koheil RM, Bablich K, Milner M, Kenny DJ: Oral motor functioning, frequency of swallowing and drooling in normal children and in children with cerebral palsy.Arch Phys Med Rehab 67:866–874, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kenny, D.J., Casas, M.J. & McPherson, K.A. Correlation of ultrasound imaging of oral swallow with ventilatory alterations in cerebral palsied and normal children: Preliminary observations. Dysphagia 4, 112–117 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407155
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407155