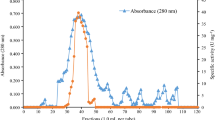
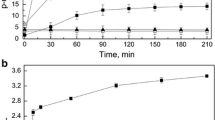
Abstract
The starch-degrading yeastCandida tsukubaensis CBS 6389 secreted amylase at high activity when grown in a medium containing soluble starch. The extracellular α-amylase activity was very low. The major amylase component was purified by DEAE-Sephadex A-50 chromatography and Ultrogel AcA 44 gel filtration and characterized as a glucoamylase. The enzyme proved to be a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 56000. The glucoamylase had a temperature optimum at 55°C and displayed highest activity in a pH range of 2.4–4.8. Acarbose strongly inhibited the purified glucoamylase. Debranching activity was present as demonstrated by the release of glucose from pullulan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous. 1980. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Laboratory Techniques. —Pharmacia Fine Chemicals, Uppsala, Sweden.
Bergmeyer, H. U. andBernt, E. 1974. D-Glucose. Determination with glucose oxidase and peroxidase. p. 1205–1215. In H. U. Bergmeyer (ed.), Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, Second edition, Vol. 3. —Verlag Chemie, Weinheim.
Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. —Anal. Biochem.72: 248–254.
De Mot, R., Andries, K. andVerachtert, H. 1984a. Comparative study of starch degradation and amylase production by ascomycetous yeast species. —Syst. Appl. Microbiol.5: 106–118.
De Mot, R., Demeersman, M. andVerachtert, H. 1984b. Comparative study of starch degradation and amylase production by non-ascomycetous yeast species. —Syst. Appl. Microbiol.5: 421–432.
De Mot, R., Van Oudenduck, E., Hougaerts, S. andVerachtert, H. 1984c. Effect of medium composition on amylase production by some starch-degrading yeasts. —FEMS Microbiol. Lett.25:169–173.
De Mot, R., Van Oudendijck, E. andVerachtert, H. 1984d. Production of extracellular debranching activity by amylolytic yeasts. —Biotechnol. Lett.6: 581–586.
Ebertová, H. 1966. Amylolytic enzymes ofEndomycopsis capsularis II. A study of the properties of isolated α-amylase, amyloglucosidase and maltase-transglucosidase. —Folia Microbiol. (Prague)11: 422–438.
Erratt, J. A. 1980. Genetic, biochemical and technological studies of yeast strains capable of fermenting dextrin. —Ph. D. Thesis, University of Western Ontario, London, Canada.
Frelot, D., Moulin, G. andGalzy, P. 1982. Strain selection for the purpose of alcohol production from starch substrates. —Biotechnol. Lett.4: 705–708.
Hansen, S. A. 1975. Thin-layer chromatographic method for identification of oligosaccharides in starch hydrolyzates. —J. Chromatogr.105: 388–390.
Kelly, C. T. andFogarty, W. M. 1983. Microbial α-glucosidases. —Process Biochem.18(3): 6–12.
Manjunath, P., Shenoy, B. C. andRaghavendra Rao, M. R. 1983. Fungal glucoamylases. —J. Appl. Biochem.5: 235–260.
Marciniak, G. P. andKula, M. R. 1982. Vergleichende Untersuchung der Methoden zur Bestimmung der Aktivität bakterieller alpha-Amylasen. —Staerke34: 422–430.
Onishi, H. 1972.Candida tsukubaensis sp.n. —Anionic van Leeuwenhoek38: 365–367.
Oteng-Gyang, K., Moulin, G. andGalzy, P. 1980. Influence of amylase excretion on biomass production by amylolytic yeasts. —Acta Microbiol. Acad. Sci. Hung.27: 155–159.
Oteng-Gyang, K., Moulin, G. andGauzy, P. 1981. A study of the amylolytic system ofSchwanniomyces castellii. —Z. Allg. Mikrobiol.21: 537–544.
Pringle, J. R. andMor, J. R. 1975. Methods for monitoring the growth of yeast cultures and for dealing with the clumping problem. p. 131–168. In D. M. Prescott (ed.), Methods in Cell Biology, Vol. 11, Yeast Cells. —Academic Press, New York.
Ruttloff, H., Friese, R., Kupke, G. andTäufel, A. 1969. Differenzierung und Charakterisierung von Glucoamylase-Isoenzymen ausEndomycopsis bispora. —Z. Allg. Mikrobiol.9: 39–47.
Sills, A. M., Russell, I. andStewart, G. G. 1983. The production and use of yeast amylase in the brewing of low carbohydrate beer. p. 377–384. In Proc. 19th EBC Congr., London. —IRL Press, Oxford.
Sills, A. M., Sadder, M. E. andStewart, G. G. 1984. Isolation and characterization of the amylolytic system ofSchwanniomyces castellii. —J. Inst. Brew., London90: 311–314.
Skogman, H. 1976. The Symba process. —Staerke28: 278–282.
Spencer-Martins, I. andVan Uden, N. 1977. Yields of yeast growth on starch. —Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol.4:29–35.
Spencer-Martins, I. andVan Uden, N. 1979. Extracellular amylolytic system of the yeastLipomyces kononenkoae. —Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.6: 241–250.
Sukhumavasi, J., Kato, K. andHarada, T. 1975. Glucoamylase of a strain ofEndomycopsis fibuligera isolated from mould bran (Look Pang) of Thailand. —J. Ferment. Technol.53: 559–565.
Touzi, A., Prebois, J. P., Moulin, G., Deschamps, F. andGauzy, P. 1982. Production of food yeast from starchy substrates. —Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.15: 232–236.
Truscheit, E., Frommer, W., Junge, B., Müller, L., Schmidt, D. D. andWingender, W. 1981. Chemie und Biochemie mikrobieller α-Glucosidasen-Inhibitoren. —Angew. Chem.93: 738–755.
Weber, K. andOsborn, M. 1969. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. —J. Biol. Chem.244: 4406–4412.
Wilson, J. J. andIngledew, W. M. 1982. Isolation and characterization ofSchwanniomyces alluvius amylolytic enzymes. —Appl. Environ. Microbiol.44: 301–307.
Wilson, J. J., Khachatourians, G. G. andIngledew, W. M. 1982.Schwanniomyces: SCP and ethanol from starch. —Biotechnol. Lett.4: 333–338.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Mot, R., Van Oudenduck, E. & Verachtert, H. Purification and characterization of an extracellular glucoamylase from the yeastCandida tsukubaensis CBS 6389. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 51, 275–287 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02439937
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02439937