Abstract
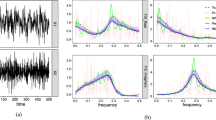
The techniques used and the results obtained in a spectral analysis of two specific responses in the human electroencephalogram are presented in this paper. The purposes are to show how the techniques may be applied to the necessarily short lengths of EEG data and to illustrate these techniques and the useful results obtained by relevant examples. The necessary data-processing procedures and precautions for transforming from the time to frequency domain are presented in a tutorial fashion. The importance of augmenting zeros, choice of the most appropriate data window and pretransformation of the data to avoid the combined effects of energy loss and low frequency content biasing caused by windowing is explained. The pros and cons of the tapered-cosine (Tukey) and Kaiser-Bessel windows are illustrated. The usefulness of applying certain statistical tests, which are based on a physical model of the responses, to the harmonic components of the responses is demonstrated. Thus a comparison is made between the features of auditory evoked responses and of the contingent negative variation, and the usefulness of predictive statistical diagnosis in differentiating between subject groups is illustrated by application to normal subjects and Huntington's chorea patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitchison, J. andDunsmore, I. R. (1975)Statistical prediction analysis. Cambridge Press.
Aitchison, J. andKay, J. W. (1975) Principles, practice, and performance in decision making in clinical medicine. Proc. 1973 NATO Conf. on the Role and Effectiveness of Decision in Practice.White, D. J. andBrown, K. C. (Eds.), Hodder & Stoughton, London.
Aitchison, J., Habbema, J. D. F. andKay, J. W. (1977) A critical comparison of two methods of statistical discrimination.Appl. Statist.,26, (1), 15–25.
Beagley, H. A., Sayers, B. McA. andRoss, A. J. (1979) Fully objective ERA by phase spectral analysis.Acta Otolaryngol.,87, 270–278.
Bergland, G. D. (1969) A guided tour of the fast fourier transform.IEEE Spectrum, July, 41–52.
Bloomfield, P. (1976) Fourier analysis of time series: a introduction. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York.
Chatfield, C. (1984)The analysis of time series: an introduction, 3rd edn. Chapman & Hall.
Cochran, W. T., Cooley, J. W., Favin, D. L., Helms, H. D., Kaenel, R. A., Lane, W. W., Maling, G. C., Nelson, D. E., Rader, C. M. andWelch, P. D. (1967) What is the fast fourier transform?Proc. IEEE,55, 1664–1674.
Cohen, J. (1974) Cerebral psychophysiology: the contingent negative variation. InBioelectric recording techniques, part B: electroencephalography and human brain potentials.Thompson, R. F. andPatterson, M. M. (Eds.), Academic Press, New York and London.
Cooley, J. W. andTukey, J. W. (1965) An algorithm for the machine calculation of complex Fourier series.Math. Comput.,19, 297–301.
Cooper, R. Osselton, J. W. andShaw, J. C. (1980)EEG technology, 3rd edn. Butterworths.
Glazer, E. M. andRuchkin, D. S. (1976)Principles of neurobiological signal analysis. Academic Press, New York, 470.
Harris, F. J. (1978) On the use of windows for harmonic analysis with the discrete Fourier transform.Proc. IEEE,66, 51–83.
Jenkins, G. M. andWatts, D. G., (1968)Spectral analysis and its applications. Holden-Day.
Jervis, B. W., Nichols, M. J., Johnson, T. E., Allen, E. M. andHudson, N. R. (1983) A fundamental investigation of the composition of auditory evoked potentials.IEEE Trans.,BME-30, 43–50.
Jervis, B. W., Allen, E. M., Johnson, T. E., Nichols, M. J. andHudson, N. R. (1984) The application of pattern recognition techniques to the contingent negative variation for the differentiation of subject categories. -31, 342–349.
Jervis, B. W., Morgan, G., Allen, E. M. andHudson, N. R. (1985) Diagnosis of CNV data quantifies subjects classification. 7th Ann. Conf. on Frontiers of Eng. and Comput. in Health Care, IEEE Eng. in Med. & Biol. Soc., Chicago, USA, 27th–30th Sept., Vol. 2, 905–909.
Jervis, B. W., Ifeachor, E. C. andAllen, E. M. (1988) The removal of ocular artefacts from the electroencephalogram: a review.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,26, 2–12.
Loveless, N. E. andSanford, A. J. (1975) The impact of warning signal intensity on reaction time and components of the contingent negative variation.Biol. Psychol.,2, 217–226.
Majumder, K. L. andBhattacharjee, G. P. (1973) Incomplete beta integral.Appl. Statist.,22, 409–411.
Remond, A. (Ed.) (1976a)Handbook of electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology. Elsevier/North Holland, Vol. 4, Part B, 4B-14.
Remond, A. (Ed.) (1976b)Handbook of electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology. Elsevier/North Holland, Vol. 4, Part A, Section VI, 4A–50.
Remond, A. (Ed.) (1976c)Handbook of electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology. Elsevier/North Holland, Vol. 5, Part A, 5A–33.
Remond, A. (Ed.) (1976d)Handbook of electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology. Elsevier/North Holland, Vol. 5, Part A, 5A–62.
Remond, A. (Ed.) (1977)EEG informatics: a didactic review of methods and applications of EEG data processing. Elsevier/North Holland.
Robinson, E. A. (1978)Multichannel time series analysis with digital computer programs. Holden Day, San Francisco, revised edn.
Rohrbaugh, J. W., Syndulko, K. andLindsley, D. B. (1976) Brain wave components of the contingent negative variation in humans.Science,191, 1055–1057.
SAS (1982) SAS user's guide: basics, 1982 edition. SAS Institute Inc.
Sayers, B. McA., Beagley, H. A. andRiha, J. (1979) Pattern analysis of auditory evoked EEG potentials.Audiol.,18, 1–16.
Shapiro, S. S. andWilk, M. B. (1965) An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples).Biometrika,52, (3 and 4), 591–611.
Tecce, J. J. (1972) Contingent negative variation (CNV) and psychological process in man.Psychol. Bull.,77, 73–108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jervis, B.W., Coelho, M. & Morgan, G.W. Spectral analysis of EEG responses. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 27, 230–238 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441479
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441479