Abstract
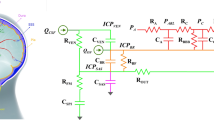
A lumped-parameter compartmental model for the cerebrovascular fluid system is constructed and solved for quasi-steady-state flow. The model predicts the pressure waves in the various compartments of the intracranial region in response to changes in the arterial pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, G. C. (1971) Fluid flow—a special case InBiomedical engineering.Brown, J. H. V., Jacobs, J. E. andStark, L. (Eds.), F. A. Davis Co., Philadelphia, 69–81.
Bruce, D. A. (1978)The pathophysiology of increased intracranial pressure. Upjohn Co., Philadelphia.
Chopp, M. andPortnoy, H. D. (1980) Systems analysis of intracranial pressure.J. Neurosurg. 53, 516–527.
Griffith, R. L., Sullivan, H. G. andMiller, J. D. (1978) Modeling of intracranial pressure dynamics. Proc. 2nd Ann. IEEE Symp. on Computer Applications in Medical Care, 244–253.
Guyton, A. C. (1969)Function of the human body, 3rd edn., W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia.
Hakim, S., Venegas, J. G. andBurton, J. D. (1976) The physics of the cranial cavity, hydrocephalus and normal pressure: mechanical interpretation and mathematical models.Surg. Neurol.,5, 187–210.
Hamit, H. F., Beal, A. C. Jr. andde Bakey, M. E. (1965) Hemodynamic influences upon brain and cerebrospinal fluid pulsations and pressures.J. Trauma,5, 174–184.
Kellie, G. (1824) An account ..., with some reflections on the pathology of the brain.Edinburgh Med. Chir. Soc. Trans.,1, 84–169.
Lewer Allen, K. andBunt, E. A. (1978) Dysfunction of the fluid mechanical craniospinal systems as revealed by stress/strain diagrams.S. Afr. Mech. Eng.,28, 159–166.
Livingston, R. B., Woodbury, D. M. andPatterson, J. L. Jr. (1965) Fluid compartments of the brain, cerebral circulation. InPhysiology and biophysics, (19th edn.).Ruch, T. C. andPatton, H. D. (Eds.), W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 935–958.
Lundberg, N., Kjällquist, A., Kullberg, G., Pontén, V. andSundbärg, G. (1974) Non-operative management of intracranial hypertension. InAdvances and technical standards in neurosurgery, vol. 1.Krayenbühl, H. (Managing Ed.), Springer-Verlag, Wien, 3–59.
Marmarou, A., Shulman, K. andLaMorgese, J. (1975) Compartmental analysis of compliance and outflow resistance of the cerebrospinal fluid system.J. Neurosurg.,43, 523–534.
Miller, J. D. (1975) Volume and pressure in the craniospinal axis.Clin. Neurosurg.,22, 76–105.
Miller, J. D. andGaribi, J. (1972) Intracranial volume/pressure relationships during continuous monitoring of ventricular fluid pressure. InIntracranial pressure: experimental and clinical aspects.Brock, M. andDietz, H. (Eds.), Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 270–274.
Monro, J. (1783)Observations on the structure and functions of the nervous system. Creech & Johnson, Edinburgh.
Pamidi, M. R. andAdvani, S. H. (1978) Nonlinear constitutive relations for human brain tissue.Trans. ASME,100, 44–48.
Ryder, H. W., Espey, F. F., Kimbell, F. D., Penka, E. J., Rosenauer, A., Podolsky, B. andEvans, J. P. (1953) The mechanism of the change in cerebrospinal fluid pressure following an induced change in the volume of the fluid space.J. Lab. Clin. Med.,41, 428–435.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Deceased
In the spring of 1983, a Visiting Scholar at the Bio-Medical Engineering Department, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, under the Henry Goldberg Chair
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karni, Z., Bear, J., Sorek, S. et al. Quasi-steady-state compartmental model of intracranial fluid dynamics. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 25, 167–172 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442846
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442846