Abstract
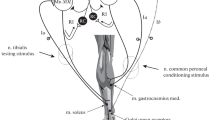
Various electrical stimuli with frequencies from 10 Hz to 1000 Hz and pulse widths from 10 μs to 1000 μs were applied to seven spinal-cord injured patients with spasticity of the knee muscle. Spasticity was assessed with the pendulum test and EMG activity in the quadriceps and hamstrings. No universal optimum combination of stimulation parameters could be established but stimuli of 100 Hz and 100 μs pulse width were more effective than other combinations. Subjective remarks of patients regarding the effects over 24 h did not always correlate with measured data obtained within one hour after stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajd, T. andVodovnik, L. (1984) Pendulum testing of spasticity.J. Biomed. Eng.,6, 9–16.
Bajd, T., Gregorič, M., Vodovnik, L. andBenko, H. (1985) Electrical stimulation in treating spasticity resulting from spinal cord injury.Arch. Phys. Med. & Rehab.,66, 515–517.
Burke, R. E. (1977) The effect of stimulation rate and pattern on synaptic transmission in the mammalian central nervous system. InFunctional electrical stimulation.Hambrecht, F. T. andReswick, J. B. (Eds.), Marcel Dekker, New York, 367–378.
Cheng, R. S. S. andPomeranz, B. (1979) Electroacupuncture analgesia could be mediated by at least two pain-relieving mechanisms: endorphin and non-endorphin systems.Life Sci.,25, 1957–1962.
Cook, A. W. andNidzgorski, F. (1984) Spinal cord stimulation in multiple sclerosis.IEEE Eng. in Med. & Biol. Mag.,3, 34–38.
Gersh, M. R., Wolf, S. L. andRao, V. R. (1980) Evaluation of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for pain relief in peripheral neuropathy.Physical Therapy,60, 48–52.
Gottlieb, G. L., Myklebust, B. M., Penn, R. D. andAgarwal, G. C. (1982) Reciprocal excitation of muscle antagonists by primary afferent pathway.Exp. Brain Res.,46, 454–456.
McNeal, D. (1977) 2000 years of electrical stimulation. InFunctional electrical stimulation.Hambrecht, F. T. andReswick, J. B. (Eds.), Marcel Dekker, New York, 3–25.
Pette, D. (1983) Transformation of skeletal muscle by chronic nerve stimulation. Proc. Int. Workshop on Functional Electrostimulation. Vienna, p 111.
Roland, M. O. (1986) A critical review of the evidence for a pain-spasm-pain cycle in spinal disorders.Clin. Biomech.,1, 102–108.
Rosenthal, J. (1969) Posttetanic potentiation at the neuromuscular junction of the frog.J. Physiol.,203, 121–133.
Vodovnik, L. (1981) Therapeutic effects of functional electrical stimulation of extremities.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,19, 470–478.
Vodovnik, L., Bajd, T., Kralj, A., Gračanin, F. andStrojnik, P. (1981) Functional electrical stimulation for control of locomotor systems.CRC Crit. Rev. in Bioeng.,6, 63–131.
Vodovnik, L., Bowman, B. R. andHufford, P. (1984a) Effects of electrical stimulation on spinal spasticity.Scand. J. Rehab. Med.,19, 29–34.
Vodovnik, L., Bowman, B. R. andBajd, T. (1984b) Dynamics of spastic knee joint.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,22, 63–69.
Vodovnik, L., Bajd, T., Reberšek, S. andStefanovska, A. (1984c) Therapy with electrical stimulation—a pharmacokinetic approach. InAdvances in external control of human extremities.Popović, D. (Ed.), ETAN, Belgrade, 127–136.
Wachtel, H. andKandel, E. R. (1971) Conversion of synaptic excitation to inhibition of a dual chemical synapse.J. Neurophysiol.,34, 56–68.
Walker, J. B. (1982) Modulation of spasticity: prolonged suppression of a spinal reflex by electrical stimulation.Science,216, 203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vodovnik, L., Stefanovska, A. & Bajd, T. Effects of stimulation parameters on modification of spinal spasticity. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 25, 439–442 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02443365
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02443365