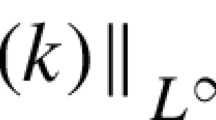Summary
The oscillatory motion of a liquid-liquid interface induced by the Marangoni effect,i.e. the variation of surface tension with the concentration of a surfactant, is described as the harmonic oscillation of the surfactant concentration at the interface. Then, at vanishing damping, threshold values and parameter regions for sustainedlongitudinal (Marangoni-Lucassen) waves are given in terms of the transport coefficients of the two liquids.
Riassunto
Si descrive il moto oscillatorio di un interfaccia tra liquido e liquido indotto dall'effetto di Marangoni, cioè la variazione della tensione di superficie con la concentrazione di un tensioattivo nell'interfaccia. Poi si danno, quanto lo smorzamento si attenua, valori di soglia e regioni di parametri per onde longitudinali sostenute (Marangoni-Lucassen) in termini dei coefficienti di trasporto dei due liquidi.
Резюме
Осцилляторное движение границы раздела двух жидкостей, индуцированное эффектом Марангони, т.е. изменением поверхностного натяжения с концентрацией поверхностно-активного вещества, описывается, как гармоническое колебание концентрации поверхностно-активного вещества на границе раздела. Затем при исчезающе малом затухании в терминах транспортных коэффициентов двух жидкостей определяются пороговые значения и область параметров для незатухающих продольных волн (Марангони-Лукасена).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. A. Miller andP. Neogi:Interfacial Phenomena (Marcel Dekker, New York, N. Y., 1985).
B. G. Levich:Physicochemical Hydrodynamics (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1962).
P. L. Garcia-Ybarra andM. G. Velarde:Phys. Fluids,30, 1649 (1987).
M. G. Velarde, P. L. Garcia-Ybarra andJ. L. Castillo:Physicochem. Hydrodyn. 9, 387 (1987).
J. Lucassen:Trans. Faraday Soc.,64, 2221 (1968).
E. H. Lucassen-Reynders andJ. Lucassen:Adv. Colloid Interface Sci.,2, 347 (1969).
R. S. Hansen andJ. Ahmad:Prog. Surface Membrane Sci.,4, 1 (1971).
C. V. Sternling andL. E. Scriven:A.I.Ch.E.J.,5, 514 (1959).
M. Hennenberg, P. M. Bisch, M. Vignes-Adler andA. Sanfeld:J. Colloid Interface Sci.,69, 128 (1979).
H. Linde, P. Schwartz andH. Wilke: inDynamics and Instability of Fluid Interfaces, edited byT. S. Sorensen (Springer-Verlag, New York, N.Y.), p. 75.
J. T. Davies andE. K. Rideal:Interfacial Phenomena, 2nd edition (Academic Press, New York, N. Y.), p. 183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
To speed up publication, the authors of this paper have agreed to not receive the proofs for correction.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velarde, M.G., Chu, X.L. Dissipative hydrodynamic oscillators. Il Nuovo Cimento D 11, 709–716 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02451557
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02451557