Abstract
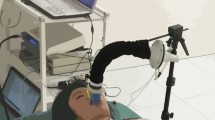
A new method, which uses a fibre-optic probe to monitor respiratory and heart rates simultaneously has been developed and evaluated. The results provide evidence that it is possible to monitor respiratory and heart rates using the reflection mode of photoplethysmography (PPG). The fibre-optic probe makes it possible to monitor from different sites on the patient, and the method is convenient to use. In addition, the probe is X-ray transparent, insensitive to electromagnetic interference (e.g. during MRI investigation) and may be made very light and small. Therefore the method is suitable for the observation of both adults and neonates, in hospitals as well as in other environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, A. K., Harness, J. B. andMearns, A. J. (1982) Respiratory control of heart rate.Eur. J. Appl. Physiol.,50, 95–104.
Allison, R. D., Holmes, E. L. andNyboer, J. (1964) Volumetric dynamics of respiration as measured by electrical impedance plethysmography.J. Appl. Physiol.,19, 166–173.
Almond, N. E. andCooke, E. D. (1989) Observations on photoplethysmograph pulse derived from a laser Doppler flowmeter.Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas.,10, 137–145.
Anderson, R. R. andParrish, J. A. (1981) The optics of the human skin.J. Invest. Dermatol.,77, 13–19.
Ashutosh, K., Gilbert, R., Auchincloss, J. H., Erlebacher, J. andPeppi, D. (1974) Impedance pneumograph and magnetometer methods for monitoring tidal volume.J. Appl. Physiol.,37, 964–966.
Blake, A. M., Collins, L. M., Langham, J. andReynolds, E. O. R. (1970) Clinical assessment of apnoea-alarm mattress for newborn infants.The Lancet, 25th July, 183–185.
Brown, B. H. (1966) Some new instruments for the continuous monitoring of body temperature, respiration-rate and pulserate.Phys. Med. Biol.,11, 135–137.
Challoner, A. V. J. (1979) Photoelectric plethysmography for estimating cutaneous blood flow.In Non-invasive physiological measurements, vol. 1.Rolfe, P. (Ed.), Academic Press, London, 125–151.
Cohn, M. A., Watson, H., Weisshaut, R., Stott, F. andSackner, M. A. (1975) A transducer for noninvasive monitoring of respiration.In IFAM Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. on Ambulatory Monitoring.Scott, F. F., Raftery, E. B., Goulding, L. andSleight, P. (Eds.), Academic Press, London, 119–128.
Colantuoni, A., Bertuglia, S. andIntaglietta, M. (1984) Quantitation of rhythmic diameter changes in arterial microcirculation.Am. J. Physiol.,246, H508-H517.
Cui, W., Ostrander, L. E. andLee, B. Y. (1990)In vivo reflectance of blood and tissue as a function of light wavelength.IEEE Trans.,BME-37, 632–639.
Cyna, A. M., Kulkarni, V., Tunstall, M. E., Hutchison, J. M. S. andMallard, J. R. (1991) Aura: a new respiratory monitor and apnoea alarm for spontaneously breathing patients.Br. J. Anaesth.,67, 341–345.
Dorlas, J. C. andNijboer, J. A. (1985) Photo-electric plethysmography as a monitoring device in anaesthesia. —Ibid.,,57, 524–530.
Fleisch, A. (1925) Der Pneumotachograph; ein Apparat zur Geschwindigkeitsregistrierung der Atemluft.Arch. Ges. Physiol.,209, 713–722.
Hamilton, L. H., Beard, J. D., Carmean, R. E. andKory, R. C. (1967) An electrical impedance ventilometer to quantitate tidal volume and ventilation.Med. Res. Eng.,6, 11–16.
Henneberg, S., Hök, B., Wiklund, L. andSjōdin, G. (1992) Remote auscultatory patient monitoring during magnetic resonance imaging.J. Clin. Monit.,8, 37–43.
Kamal, A. A. R., Harness, J. B., Irving, G. andMearns, A. J. (1989) Skin photoplethysmography—a reviewComp. Meth. & Progr. in Biomed.,28, 257–269.
Konno, K. andMead, J. (1967) Measurement of the separate volume changes of rib cage and abdomen during breathing.J. Appl. Physiol.,22, 407–422.
Lewin, J. E. (1969) An apnoea alarm mattress.The Lancet, 27th Sept., 667–668.
Lindberg, L.-G. andÖberg, P. Å. (1991) Photoplethysmography. Part 2. Influence of light source wavelength.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,29, 48–54.
Mead, J., Peterson, N., Grimby, M. andMead, J. (1967) Pulmonary ventilation as measured from body surface movement.Science 156, 1383–1384.
Penaz, J. (1978) Mayor waves: history and methodology.Automedica,2, 135–141.
Rolfe, P. (1971) A magnetometer respiration monitor for use with premature babies.Biomed. Eng.,6, 402–404.
Sackner, J. D., Nixon, A. J., Davis, B., Atkins, N. andSackner, M. A. (1980) Non-invasive measurement of ventilation during exercise using a respiratory inductive plethysmograph.Am. Rev. Respirat. Disease,122, 867–871.
Salerud, E. G., Tenland, T., Nilsson, G. E. andÖberg, P. Å. (1983) Rhythmical variations in human skin blood flow.Int. J. Microcirc.: Clin. Exp.,2, 91–102.
Sullivan, W. T., Peters, G. M. andEnright, P. L. (1984) Pneumotachographs: theory and clinical application.Respirat. Care,29, 736–749.
Werthammer, J., Krasner, J., Dibenedetto, J. andStark, A. R. (1983) Apnea monitoring by acoustic detection of airflow.Pediatrics,71, 53–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindberg, L.G., Ugnell, H. & Öberg, P.Å. Monitoring of respiratory and heart rates using a fibre-optic sensor. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 30, 533–537 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02457833
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02457833