Summary
-
1.
The isolated, saline-perfused head of the freshwater rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) was used to investigate adrenergic control of branchial chloride transport.
-
2.
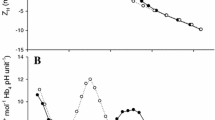
Perfusing only with physiological saline (no catecholamines present) resulted in extremely low values of chloride influx (J iCl−) which approached zero with time.
-
3.
By perfusing with a range of sympathetomimetics and adrenergic antagonists, it was demonstrated that branchial chloride influx was enhanced by alpha receptor stimulation and inhibited by beta receptor stimulation.
-
4.
It is proposed that the effects of catecholamines onJ iCl− are specific in nature and not due to accompanying haemodynamic alterations.
-
5.
From the results of these experiments, together with previous knowledge of adrenergic effects on branchial Na+/H+ (NH +4 ) exchange, it is possible to postulate a scheme for piscine acid-base regulation involving altered rates of Cl−/HCO −3 and Na+/H+ (NH +4 ) exchanges, both a result of adrenergic stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergman HL, Olson KR, Fromm PO (1974) The effects of vasoactive agents on the functional surface area of isolated perfused gills of rainbow trout. J Comp Physiol 94: 267–286
Booth JH (1980) The effects of oxygen supply, epinephrine and acetylcholine on the distribution of blood flow in trout gills. J Exp Biol 83: 31–39
Bornancin M, de Renzis G, Girard JP, Maetz J (1977) Branchial chloride transport, anion stimulated ATPase and acid-base balance inAnguilla adapted to freshwater: effects of hyperoxia. J Comp Physiol 117: 313–322
Cameron JN (1976) Branchial ion uptake in the Arctic grayling: resting values and effects of acid-base disturbance. J Exp Biol 65: 511–515
Cameron JN (1978) Regulation of blood pH in teleost fish. Respir Physiol 33: 129–144
Claiborne JB, Evans DH (1980) The isolated perfused head of the marine teleost fish,Myoxocephalus octodecimspinosus: hemodynamic effects of epinephrine. J Comp Physiol 138: 79–85
Degnan KJ, Karnaky J, Zadunaisky JA (1977) Active chloride transport in thein vitro opercular skin of a teleost (Fundulus heteroclitus), a gill-like epithelium rich in chloride cells. J Physiol (Lond) 271: 155–191
de Renzis G, Maetz J (1973) Studies on the mechanism of chloride absorption by the goldfish gill: relation with acid-base regulation. J Exp Biol 59: 339–358
de Renzis G (1975) The branchial chloride pump in the goldfish,Carassius auratus: relationship between Cl−/HCO −3 exchange and Cl−/Cl− exchange and the effect of thiocyanate. J Exp Biol 63: 587–602
Girard JP (1976) Salt excretion by the perfused head of trout adapted to seawater and its inhibition by adrenaline. J Comp Physiol 111: 77–91
Girard JP, Payan P (1976) Effect of epinephrine on vascular space of gills and head of rainbow trout. Am J Physiol 230: 1555–1560
Girard JP, Payan P (1977) Kinetic analysis of sodium and chloride influxes across the gills of trout in freshwater. J Physiol (Lond) 273: 195–209
Girard JP, Payan P (1980) Ion exchange through respiratory and chloride cells in freshwater and seawater adapted teleosteans. Am J Physiol 238: 260–268
Heisler N (1980) Regulation of the acid-base status in fishes. In: Ali MA (ed) Environmental physiology of fishes. Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York, pp 123–162
Isaia J, Payan P, Girard JP (1979) A study of the water permeability of the gills of freshwater and seawater adapted trout (Salmo gairdneri): mode of action of epinephrine. Physiol Zool 52: 269–279
Kerstetter TH, Kirschner LB (1972) Active chloride transport by the gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Exp Biol 56: 263–272
Kerstetter TH, Kirschner L, Rafuse DD (1970) On the mechanisms of sodium transport by the irrigated gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Exp Biol 56: 342–359
Keys A, Bateman JB (1932) Branchial responses to adrenaline and pitressin in the eel. Biol Bull 63: 327–336
Krogh A (1938) The active absorption of ions in some freshwater animals. Z Vergl Physiol 25: 335–350
Maetz J (1973) Na+/NH +4 , Na+/H+ and NH3 movements across the gills ofCarassius auratus. J Exp Biol 58: 255–275
Maetz J, Garcia-Romeu F (1964) The mechanism of sodium and chloride uptake by the gills of a freshwater fish,Carassius auratus. II. Evidence for Na+/NH +4 and Cl−/HCO −3 exchange. J Gen Physiol 47: 1209–1226
Maetz J, Payan P, de Renzis G (1976) Controversial aspects of ionic uptake in freshwater animals. In: Davies S (ed) Perspectives in experimental biology. Zoology, vol I Pergamon Press, New York, pp 77–92
Mazeaud MM, Mazeaud F, Donaldson EM (1977) Primary and secondary effects of stress in fish: some new data with a general review. Trans Am Fish Soc 106: 201–211
Nakano T, Tomlinson N (1967) Catecholamine and carbohydrate concentrations in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) in relation to physical disturbance. J Fish Res Bd Canada 24: 1701–1714
Östlund E, Fänge R (1962) Vasodilation by adrenaline and noradrenaline, and the effects of some other substances on perfused fish gills. Comp Biochem Physiol 5: 307–309
Part P, Kiessling A, Ring O (1982) Adrenaline increases vascular resistance in perfused rainbow trout gills. Comp Biochem Physiol 72: 107–108
Payan P (1978) Utilization d'un technique de perfusion de la tète isolée à l'etude de contrôle adrénergique de l'hémodynamique et de l'échange Na+/NH +4 au niveau de la branchie de la truite,Salmo gairdneri. PhD thèse, Université de Nice
Payan P, Girard JP (1977) Adrenergic receptors regulating patterns of blood flow through the gills of trout. Am J Physiol 232: 18–23
Payan P, Girard JP (1978) Mise en évidence d'un échange Na+/NH +4 dans la branchie de la truite adaptée à l'eau de mer: contrôle adrénergique. CR Acad Sci Paris Ser D 286: 335–338
Payan P, Maetz J (1973) Branchial sodium transport mechanisms inScyliorhinus canicula: evidence for Na+/NH +4 exchange and a role for carbonic anhydrase. J Exp Biol 58: 487–503
Payan P, Matty AJ (1975) The characteristics of ammonia excretion by a perfused isolated head of trout (Salmo gairdneri): effect of temperature and CO2-free Ringer. J Comp Physiol 96: 167–184
Payan P, Matty AJ, Maetz J (1975) A study of the sodium pump in the perfused head preparation of the trout,Salmo gairdneri, in freshwater. J Comp Physiol 104: 33–48
Perry SF, Haswell MS, Randall DJ, Farrell AP (1981) Branchial ionic uptake and acid-base regulation in the rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri. J Exp Biol 92: 289–303
Pettersson K (1983) Adrenergic control of oxygen transfer in perfused gills of the cod,Gadus morhua. J Exp Biol 102: 327–335
Pettersson K, Johansen K (1982) Hypoxic vasoconstriction and the effects of adrenaline on gas exchange efficiency in fish gills. J Exp Biol 97: 263–272
Peyraud-Waitzenegger M (1979) Simultaneous modifications of ventilation and arterial\(P_{O_2 }\) by catecholamines in the eel,Anguilla anguilla: participation of alpha and beta effects. J Comp Physiol 129: 343–354
Pic P, Mayer-Gostan N, Maetz J (1975) Branchial effects of epinephrine in the seawater adapted mullet. II. Na+ and Cl− extrusion. Am J Physiol 228: 441–447
Richards BD, Fromm PO (1969) Patterns of blood flow through filaments and lamellae of isolated perfused trout gills. Am Zool 8: 766–771
Shuttleworth TJ (1978) The effect of adrenaline on potentials in the gills of the flounder (Platichthys flesus L.). J Comp Physiol 124: 129–136
Wahlqvist I, Nilsson S (1980) Adrenergic control of the cardiovascular system of the Atlantic Cod,Gadus morhua, during ‘stress’. J Comp Physiol 137: 145–150
Wood CM (1974) A critical examination of the physical and adrenergic factors affecting blood flow through the gills of rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 60: 241–265
Wood CM (1975) A pharmacological analysis of the adrenergic and cholinergic mechanisms regulating branchial vascular resistance in the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Can J Zool 53: 1569–1577
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perry, S.F., Payan, P. & Girard, J.P. Adrenergic control of branchial chloride transport in the isolated perfused head of the freshwater trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Comp Physiol B 154, 269–274 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02464406
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02464406