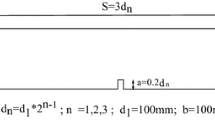
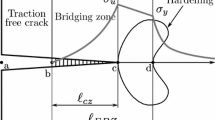
Abstract
In this paper, we examine the correlation between the width of the fracture process zone, the parameters entering in the description of size effect (related to the dimension of the specimen especially), and the internal length in non local constitutive relations for a model mortar material with a controlled macro-porosity. Experimental investigations on this material in compression, bending, acoustic emission measurements and their analysis are detailed. The experiments show a good agreement between the evolution of Bažant's size effect parameterd 0 and the evolution of the width of the FPZ. The internal length obtained with the help of inverse finite element analysis is also proportional to these quantities. This correlation provides a reasonable approximation of the internal length, from an experimental test on specimens of a single size directly, equipped with acoustic emission localization devices.
Résumé
Dans cet article, nous examinons les corrélations entre la largeur de la zone de microfissuration (FPZ), les paramètres entrant dans la description de l'effet d'échelle et la longueur interne du modèle d'endommagement non local pour un mortier à macro-porosité contrôlée. Des résultats expérimentaux sur ce matériau en comparession, en flexion ainsi que des mesures d'émission acoustiques et leur analyse sont présentés. Les résultats d'essais montrent une bonne corrélation, entre l'évolution du paramètre d0, paramètre de la loi d'effet d'échelle de Bažant, et la largeur de la PFZ. La longueur interne obtenue numériquement par analyse inverse est aussi proportionnelle à ces paramètres. Une bonne approximation de la longueur interne à partir d'essais sur une seule taille d'éprouvette équipée d'un système d'émission, acoustique est aussi obtenue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bažant, Z.P. and Planas, J., ‘Fracture and size effect in concrete and other quasibrittle materials’,CRC Press (1998).
Hillerborg, A., Modéer, M., and Petersson, P.E., ‘Analysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements’,Cem. Concr. Res. 6 (1976) 773–781.
Bažant, Z.P. and Pijaudier-Cabot, G., ‘Measurement of the characteristic length of non local continuum’,J. Engrg Mech. ASCE 115 (1989) 755–767
Mazars, J. and Pijaudier-Cabot, G., ‘From damage to fracture mechanics and conversely: a combined approach’Int. J. Solids. Struct. 33 (1996) 3327–3342.
Sluys, L.J., ‘Wave propagation, localization and dispersion in softening solids’ PhD thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands (1992).
Peerlings, R.H., de Borst, R., Brekelmans W.A.M. and de Vree, J.H.P., ‘Gradient enhanced damage for quasi-brittle materials’,Int. J. Num. Meth. Engrg.,39 (1996) 3391–3403.
Carmeliet, J., ‘Optimal estimation of gradient damage parameters from localization phenomena in quasi-brittle materials’,Int. J. Mech. Cohesive Frict. Mats. 4 (1999) 1–16.
Le Bellégo, C., Dubé, J.F., Pijaudier-Cabot, G. and Gérard, B., ‘Calibration of non local damage from size effect tests’,European J. of Mech. 22 (2003) 33–46.
Hild, F., Berthaud, Y. and Roux, S., ‘Measurement of displacement field using a correlation method in white light’ OASIS 1999—1er Congrès européen de l'Organisation pour l'Application des Sciences de l'Ingénieur au Sport, Palaiseau, France (1999).
Geers, M.G.D., de Borst, R., Brekelmans, W.A.M. and Peerlings, R.H.J., ‘On the use of local strain fields for the determination of the intrinsic length scale’,Journal de Physique IV 8 (1998) 167–174.
Otsuka, K., ‘Detection of fracture process zone in concrete by means of x-ray with contrast medium’ Fracture mechanics of concrete structures, Proc. FRAMCOS 1, Z.P. Bažant editor, Elsevier applied science (1992) 485–490.
Berthaud, Y., ‘Damage measurements in concrete via an ultrasonic technique. Part 1 Experiments’,Cem. Concr. Res. 21 (1991) 73–82.
Selleck, S.F., Landis, E.N., Peterson, M.L., Shah, S.P. and Achenbach, J.D., ‘Ultrasonic investigation of concrete with distributed damage’,ACI Materials Journal 95 (1998)m 27–36.
Maji, A.K. and Shah, S.P., ‘Process zone and acoustic emission in concrete’,Experimental mechanics 28 (1988) 27–33.
Berthelot, J.M. and Robert, J.L., ‘Modelling concrete damage by acoustic emission’,Journal of Acoustic Emission 7 (1987) 43–60.
Mihashi, H., Nomura, N. and Niiseki, S., ‘Influence of Aggregate size on fracture process zone of concrete detected with three dimensional acoustic emission technique’,Cem. Concr. Res. 21 (1991) 737–744.
Otsuka, K., Date, H. and Kurita, T., ‘Fracture process zone in concrete tension specimens by X-ray and AE techniques’. Fracture Mechanics of Concrete Structures; Proceedings of FRAMCOS-3 (1998) 3–16.
Haidar, K., ‘Damage modelling of concrete structures— Numerical approaches and microstructure effects on the rupture properties’, Ph.D thesis, Ecole Centrale de Nantes and Université de Nantes, France (2002) [in French].
Sussman, V., ‘Lightweight plastic-aggregate concrete’,Journal American. Concr. Inst. 72 (1975) 321–323.
Yamura, K. and Yamauchi, M., ‘Use of polystyrene pieces for aggregate of concrete’, Proc. Annual Conf. of Chugoku-Shikoku branch of JSCE (1982) 346–347 [in Japanese].
Perry, S.H., Biscoff, P.H. and Yamura, K., ‘Mix details behaviour of polystyrene aggregate concrete’,Magazine of Concrete Research 43 (1991) 71–76.
Kendall, J., Howard, A.J. and Birchall, J.D., ‘The relation between porosity, microstructure and strength, and the approach to advanced cement-based materials’, Phil. Trans. R. Soc., London, A 310 (1983) 139–153.
zimmerman, W., ‘Elastic moduli of solid containing spherical inclusions’,Mechanics of Materials 12 (1991) 17–24.
RILEM Draft Recommendations, ‘Size effect method for determining fracture energy and process zone size of concrete’,Mater. Struct. 23 (1990) 461–465.
Tada, H., Paris, P.C. and Irwin, G.R., ‘The stress analysis of cracks handbook’, 2nd Edition (Paris production, St. Louis, 1985).
Pijaudier-Cabot, G. and Bažant, Z.P., ‘Non local damage theory’,J. of Engrg. Mech. ASCE 113 (1987) 1512–1533.
Mazars, J., ‘Application de la mécanique de l'endommagement au comportement non linéaire et à la rupture du béton de structure’, Thèse de Doctorat ès Sciences, Université Paris 6, France (1984) [in French].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Editorial Note Prof. Gilles Pijaudier-Cabot and Dr. Ahmed Loukili are RILEM Senior Members. Dr. Loukili participates in RILEM TC 195-DTD ‘Recommendation for test methods for autogeneous deformation and thermal dilation of early age concrete’.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haidar, K., Pijaudier-Cabot, G., Dubé, J.F. et al. Correlation between the internal length, the fracture process zone and size effect in model materials. Mat. Struct. 38, 201–210 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02479345
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02479345