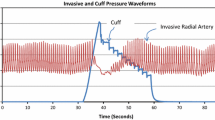
Abstract
Degraded catheter-manometer systems cause distortion of blood pressure waveforms, often leading to erroneously resonant or damped waveforms, requiring waveform quality control. We have tried multilayer perceptron back-propagation trained neural nets of varying architecture to detect damping on sets of normal and artificially damped brachial arterial pressure waves. A second-order digital simulation of a catheter-manometer system is used to cause waveform distortion. Each beat in the waveforms is represented by an 11 parameter input vector. From a group of normotensive or (borderline) hypertensive subjects, pressure waves are used to statistically test and train the neural nets. For each patient and category 5–10 waves are available. The best neural nets correctly classify about 75–85% of the individual beats as either adequate or damped. Using a single majority vote classification per subject per damped or adequate situation, the best neural nets correctly classify at least 16 of the 18 situations in nine test subjects (bionomial P=0.001). More importantly, these neural nets can always detect damping before clinically relevant parameters such as systolic pressure and computed stroke volume are reduced by more than 2%. Neural nets seem remarkably well adapted to solving such subtle problems as detecting a slight damping of arterial pressure waves before it affects waveforms to a clinically relevant degree.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Draper, N. R., andSmith, H. (1981): ‘Applied regression analysis, second edition’ (Wiley, Chichester, UK)
Fahlman, S. E. (1988): ‘An empirical study of learning speed in backpropagation networks’. Carnegie-Mellon University, Technical Report, June CMU-CS-88-162
Frank, O. (1903): ‘Kritik der elastischen Manometer,’Z. Biol.,44, pp. 455–613
Gardner, R. M. (1981): ‘Direct blood pressure measurement—dynamic response requirements,’Anaesthesiol.,54, pp. 227–236
Hamming, R. W. (1977): ‘Digital filters’ (Prentice Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey) p. 128
Hecht-Nielsen, R. (1987): ‘Kolmogorov’s mapping neural network existence theorem’. Proc. First IEEE Int. Joint Conf. on Neural Networks, San Diego, California, 21–24 June, Vol. 3, pp. 11–14
Idema, R. N., Van dem Meiracker, A. H., Imholz, B. P. M., Man Int Veld, A. J., Ritsema van Eck, A. D., Settels, J. J. andSchalekamp, A. H. (1989): ‘Comparison of Finapres non-invasive beat to beat finger blood pressures with intrabrachial artery pressures during and after bicycle ergometry,’J. Hypertens.,7 (suppl 6), pp. S58–59
Jain, A. K., andDubes, R. C. (1988): ‘Algorithms for clustering data’ (Prestice Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey)
Johnson, R. W., Scanlon, T. S., Smith, N. T., andMulier, J. P. (1991). A neural network for identification of damped and resonant blood pressure waveforms’. 13th Ann. Int. Conf. of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Orlando, Florida, USA, 31 October–3 November, Vol. 13, No. 3, pp. 1413–1414
Lippmann, R. P. (1987): ‘An introduction to computing with neural nets’,IEEE ASSP Mag., pp. 4–22
Maren, A. J., Harston, C. T., andPap, R. M. (1990): ‘Handbook of neural computing applications’ (Academic Press, London, UK)
McDonald, D. A. (1974): ‘Blood flow in arteries, second edition’ (Edward Arnold, London, UK)
Morrison, D. E. (1976): ‘Multivariate statistical methods, second edition’. (McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, USA)
Murtagh, F., andHeck, A. (1987): ‘Multivariate data analysis’. (Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands)
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., andWilliams, R. J. (1986): ‘Learning internal representations by error propagation’in Rumelhart, D. E. andMcClelland, J. L. (Eds.): ‘Parallel distributed processing: Explorations in the microstructure of cognition, Volume 1: Foundations’ (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts)
Siegel, S., andCastellan, N. J. (1988): ‘Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences’ (McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, USA)
Van Montfrans, G. A., Van der Hoeven, G. M. A., Karemaker, J. M., Wieling, W., andDunning, A. J. (1987): ‘Accuracy of auscultatory blood pressure measurement with a long cuff’,Br. Med. J.,295, pp. 354–355
Vrckovnik, G., Chung, T., andCarter, C. R. (1990): ‘Classifying impulse radar waveforms using principal components analysis and neural networks’. Proc. Int. Joint Conf. on Neural Networks, San Diego, California, 17–21 June, Vol. I, pp. 69–74
Wesseling, K. H. (1993a): ‘FAST-mf system User Manual’. TNO-Biomedical Instrumentation, Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Wesseling, K. H., Jansen, J. R. C., Settels, J. J., andSchreuder, J. J. (1993b): ‘Computation of aortic flow from pressure in humans using a nonlinear, three-element model’,J. Appl. Physiol.,74, (5) pp. 2566–2573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prentza, A., Wesseling, K.H. Catheter-manometer system damped blood pressures detected by neural nets. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 33, 589–595 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02522519
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02522519