Abstract
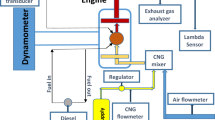
An experimental study is conducted to evaluate the use of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as a secondary fuel for a Ricardo E-6, naturally aspirated, four-stroke diesel engine having a turbulence combustion chamber (indirect injection). The gaseous LPG is introduced together with the aspirated air (fumigation) at various proportions with respect to the diesel fuel which constitutes the main part. The influence of fuel feed ratios (LPG/diesel), in a vast range of loads, on fuel consumption, pressure diagrams, exhaust smokiness and exhaust gas emissions (nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide) is investigated, the baseline being the single diesel fuel operation. The study for this type of engine, which has not being reported in the literature, shows a promise of the present method and reveals that above 60 per cent of maximum load the whole effect is beneficial concerning specific fuel consumption and smoke reduction. The examination of gaseous pollutant levels shows an involved relation with respect to load and fuel proportions. The best results (coupled to acceptable cylinder pressure levels) is obtained at a diesel fuel substitution value of 75% of maximum load, with an LPG mass fraction in the range 10 to 15%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patterson, D.J. andN.A. Henein: Emissions from combustion engines and their control. Ann Arbor Science Publ. Inc., Michigan 1972.
Löhner, K.: Die Brennkraftmaschine, 2. Aufl. VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf 1963.
Lyon, D., A.H. Howland andW.L. Lom: Controlling exhaust emissions from a diesel engine by LPG dual fuelling. Inst. Mech. Engrs (1971) pp. 42/56.
Antonucci, G., andL. Zandona: Heavy-duty dual-fuel diesel engine for smoke reduction in city bus service. SAE Paper No. 740121, 1974.
Derry, L.D., E.M. Dodds, E.B. Evans andD. Royle: The effect of auxiliary fuels on the smoke limited power output of diesel engines. Proc. Inst. Mech. Engrs, Vol. 168 (1954) pp. 280/86.
Alperstein, M., W.B. Swim andP.H. Schweitzer: Fumigation kills smoke and improves diesel performance. SAE Trans. Vol. 66 (1958) pp. 574/88.
Varde, K.S.: Propane fumigation in a direct injection type diesel engine. SAE Paper No. 831354, 1983.
Pishinger, F. andR. Menne: Dieselzweistoffbetrieb mit Flüssigeinspritzung von Propan/Butan ins Ansaugrohr. MTZ Vol. 40 (1979) No. 3, pp. 121/24.
Lowi, A. Jr.: Supplementary fuelling of four-stroke-cycle automotive diesel engines by propane fumigation. SAE Paper No. 841398, 1984.
Kouremenos, D.A., C.D. Rakopoulos, S. Christoyannis andG. Kedikoglou: An experimental investigation into the effect of propane feed to the intake air of a swirl chamber Diesel engine with emphasis on smoke reduction. 21st FISITA congress, Belgrade 1986, Paper No. 865018.
Ricardo, H.R.: Der schnellaufende Verbrennungsmotor, 3. Aufl. Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Göttingen/Heidelberg 1954.
Kouremenos, D.A., andC.D. Rakopoulos: Experimental investigation on using LPG in diesel engines. European Economic Community and PERPA REPORT DG XI (Project II.3). April 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kouremenos, D.A., Rakopoulos, C.D. The operation of a turbulence chamber diesel engine with LPG fumigation for exhaust emissions control. Forsch Ing-Wes 52, 185–190 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02560935
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02560935