Abstract
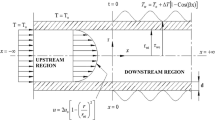
A fully implicit upwind finite difference numerical scheme has been proposed to investigate the characteristics of thermal entrance heat transfer in laminar pipe flows subject to a step change in ambient temperature. In order to demonstrate the results more clearly, a modified Nusselt number is introduced. The unsteady axial variations of modified Nusselt number, bulk fluid temperature, and wall temperature and the transient temperature profiles at certain axial locations are presented graphically for various outside heat transfer coefficients. The effects of the outside heat transfer coefficient on the heat transport processes in the flow are examined in detail. The results can be comprehensively explained by the interaction between the upstream convective heat transfer and the diffusion heat transfer in the radial direction. Steady state is reached when the axial convection balances the radial diffusion.
Zusammenfassung
Eine vollständig implizite Differenzen-Methode mit gegen den Strom gerichteten Schritten (upwind) wird angewandt, um die Zustandsänderung im thermischen Einlauf einer laminaren Rohrströmung als Folge eines Sprunges der Umgebungstemperatur zu berechnen.
Um die Ergebnisse klarer darzustellen, wird eine modifizierte Nusselt-Zahl eingeführt. Die instationäre axiale Änderung dieser Zahl, der mittleren Flüssigkeits- und der Wandtemperatur und der Temperaturprofile in der Strömung werden für verschiedene äußere Wärmeübergangszahlen graphisch dargestellt. Der Einfluß des äußeren Wärmeüberganges auf den in der Rohrströmung wird untersucht. Die Ergebnisse lassen sich durch das Zusammenwirken des im thermischen Einlauf beginnenden konvektiven Wärmetransportes und der radialen Wärmeleitung erklären. Der stationäre Zustand ist erreicht, wenn der axiale konvektive Transport gleich der radialen Wärmeleitung wird.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a ij :
-
coefficients defined in Eq. (6)
- h :
-
heat transfer coefficient inside the pipe
- h e :
-
modified local heat transfer coefficient; Eq. (9)
- i, j, m :
-
indices for finite difference discretization
- J :
-
total number of grid points in radial direction
- k :
-
thermal conductivity of the fluid in the pipe
- Nu :
-
local Nusselt number;h (2 R)/k
- Nu e :
-
modified local Nusselt number; Eq. (10)
- Nu o :
-
outside Nusselt number;UR/k
- Pe :
-
Peclet number;u m (2 R)/α
- q″ w :
-
wall heat flux
- r :
-
radial coordinate
- R :
-
pipe radius
- t :
-
time
- T :
-
temperature
- u :
-
axial velocity
- U :
-
outside heat transfer coefficient; Eq. (2)
- x :
-
axial coordinate
- α :
-
thermal diffusivity of the fluid in the pipe
- Δη :
-
dimensionless radial interval
- Δξ :
-
dimensionless axial interval
- Δτ :
-
dimensionless time step
- η :
-
dimensionless radial coordinate
- θ :
-
dimensionless temperature difference
- ξ :
-
dimensionless axial coordinate
- τ :
-
dimensionless time
- a :
-
ambient
- b :
-
bulk
- e :
-
entrance
- m :
-
mean
- o :
-
outside
- w :
-
wall
References
Rizika, J. M.: Thermal Lags in Flowing Systems Containing Heat Capacitors. Trans. ASME 76 (1954) 411
Rizika, J. M.: Thermal Lags in Flowing Incompressible Fluid Systems Containing Heat apacitors. Trans. ASME 78 (1956) 1407
Dusinberre, G. M.: Calculation of Transient Temperatures in Pipes and Heat Exchangers by Numerical Methods. Trans. ASME 76 (1954) 421
Clark, J. A.; Arpaci, V. S.; Treadwell, K. M.: Dynamic Response of Heat Exchangers. Having Internal Heat Sources. I. Trans. ASME 80 (1958) 612
Arpaci, V. S.; Clark, J. A.: Dynamic Response of Heat Exchangers Having Internal Heat Sources. II. Trans. ASME 80 (1958) 625
Arpaci, V. S.; Clark, J. A.: Dynamic Response of Heat Exchangers Having Internal Heat Sources. III. J. of Heat Transfer 81 (1959) 253
Siegel, R.; Sparrow, E. M.: Transient Heat Transfer for Laminar Forced Convection in the Thermal Entrance Region of Flat Ducts. J. Heat Transfer 81 (1959) 29
Siegel, R.: Transient Heat Transfer for Laminar Slug Flow in Ducts. J. Applied Mech. 81 (1959) 140
Siegel, R.: Heat Transfer for Laminar Flow in Ducts with Arbitrary Time Variations in Wall Temperature. J. Applied Mech. 82 (1960) 241
Siegel, R.; Perlmutter, M.: Laminar Heat Transfer in a Channel with Unsteady Flow and Wall Heating Varying with Position and Time. J. Heat Transfer 85 (1963) 358
Perlmutter, M.; Siegel, R.: Unsteady Laminar Flow in a Duct with Unsteady Heat Addition. J. Heat Transfer 83 (1961) 432
Perlmutter, M.; Siegel, R.: Two-Dimensional Unsteady Incompressible Laminar Duct Flow with a Step Change in Wall Temperature. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 3 (1961) 94
Sparrow, E. M.; Parias, F. N.: Unsteady Heat Transfer in Ducts with Time-Varying Inlet Temperature and Participating Walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 11 (1968) 837
Kakac, S.; Yener, Y.: Exact Solution of the Transient Forced Convection Energy Equation for Timewise Variation of Inlet Temperature. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 11 (1973) 2205
Kakac, S.: Transient Heat Transfer by Forced Convection in Channels. In: Turbulent Forced Convection in Channels and Bundles. Kakac, S. and Spalding, D. B. (Ed.), p. 853. Washington D.C.: Hemisphere Publ. 1979
Lin, H. T.; Shih, Y. P.: Unsteady Thermal Entrance Heat Transfer of Power-Law Fluids in Pipes and Plate Slits. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 24 (1981) 1531
Spalding, D. B.: A Novel Finite-Difference Formulation for Differential Expressions Involving Both First and Second Derivatives. Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng. 4 (1972) 551
Patankar, S. V.: Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. Washington D.C.: Hemisphere Publ. 1980
Lin, T. F.; Hawks, K. H.; Leidenfrost, W.: Analysis of Viscous Dissipation Effects on Thermal Entrance Heat Transfer in Laminar Pipe Flows with Convective Boundary Conditions. Wärme-Stoffübertrag. 17 (1983) 97–105
Hsu, C. J.: Exact Solution to Entry-Region Laminar Heat Transfer with Axial Conduction and the Bundary Condition of the Third Kind. Chem. Eng. Sci. 23 (1968) 457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, T.F., Hawks, K.H. & Leidenfrost, W. Unsteady thermal entrance heat transfer in laminar pipe flows with step change in ambient temperature. Warme- und Stoffubertragung 17, 125–132 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02570522
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02570522