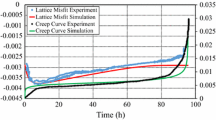
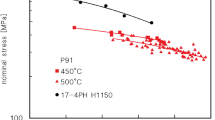
Abstract
The high-temperature creep behavior of the oxide-dispersion-strengthened (ODS) nickel-base superalloys MA 754 and MA 6000 has been investigated at temperatures up to 1273 K and lifetimes of approximately 4000 hours using monotonic creep tests at constant true stressσ, as well as true constant extension rate tests (CERTs) at\(\dot \varepsilon \). The derivation of creep rupture-lifetime diagrams is usually performed with conventional engineering parametric methods, according to Sherby and Dorn or Larson and Miller. In contrast, an alternative method is presented that is based on a more microstructural approach. In order to describe creep, the effective stress model takes into account the hardening contributionσ p caused by the presence of second-phase particles, as well as the classical Taylor back-stressσ p caused by dislocations. The modeled strain rate-stress dependence can be transferred directly into creep-rupture stress-lifetime diagrams using a modified Monkman-Grant (MG) relationship, which adequately describes the interrelation between\(\dot \varepsilon \) representing dislocation motion, and lifetimet f representing creep failure. The comparison with measured creep-rupture data proves the validity of the proposed micromechanical concept.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Heilmaier, K. Wetzel, and B. Reppich:Proc. 10th Int. Conf. on the Strength of Materials, H. Oikawa, K. Maruyama, S. Takeuchi, and M. Yamaguchi, ed., The Japan Institute of Metals, Sendai, 1994, pp. 563–66.
M. Heilmaier, K. Wetzel, J. Wunder, and B. Reppich:Proc. 10th Int. Conf. on the Strength of Materials, H. Oikawa, K. Maruyama, S. Takeuchi, and M. Yamaguchi, eds., The Japan Institute of Metals, Sendai, 1994, pp. 567–70.
H. Alexander and P. Haasen:Solid State Phys., 1968, vol. 22, p. 27.
B. Ilschner:Hochtemperaturplastizität, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1973.
B. Reppich: inMaterials Science and Technology, R.W. Cahn, P. Haasen, and E.J. Kramer eds., vol. 6,Plastic Deformation and Fracture of Materials, (H. Mughrabi), ed., VCH-Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim, 1992, pp. 312–57.
B. Reppich:Z. Metallkd., 1982, vol. 73, pp. 697–705.
B. Reppich, H. Bügler, R. Leistner, and M. Schütze:Proc. 2nd. Int. Conf. on Creep and Fracture of Engineering Materials and Structures, B. Wilshire and D.R.J. Owen, eds., Pineridge Press, Swansea, 1984, pp. 279–97 and 299–305.
B. Reppich, M. Heilmaier, H. Schmidt, and C. Schossig:Proc. 9th Int. Conf. on the Strength of Metals and Alloys, (D.G. Brandon, R. Chaim, and A. Rosen), eds., Freund Publishing House, London, 1991, pp. 405–12.
G. Taylor:Proc. R. Soc., 1934, vol. A145, pp. 362–404.
W. Blum, S. Straub, and S. Vogler:Proc. 9th Int. Conf. on the Strength of Metals and Alloys, D.G. Brandon, R. Chaim, and A. Rosen, eds., Freund Publishing House, London, 1991, pp. 111–26.
B. Reppich, M. Heilmaier, K. Liebig, G. Schumann, K.D. Stein, and T. Woller:Steel Res., 1990, vol. 61, pp. 251–57.
F.C. Monkman and N.J. Grant:Proc. ASTM, 1956, vol. 56, pp. 593–97.
F. Dobes and K. Milička:Met. Sci., (1976), vol. 10, pp. 382–84.
J.S. Benjamin:Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, pp. 2943–51.
R.F. Singer and E. Arzt:Proc. Conf. High Temperature Alloys for Gas Turbines and other Applications, W. Betz, R. Brunetaud, D. Coutsouradis, H. Fischmeister, T.W. Gibbons, I. Kvernes, Y. Lindblom, J.B. Marriott, and D.B. Meadowcroft, eds., Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht, 1986, pp. 97–125.
M.V. Heimendahl:Einführung in die Elektronenmikroskopie, Vieweg-Verlag, Braunschweig, 1970.
M. Heilmaier and B. Reppich:Proc. 5th Int. Conf. on Creep and Fracture of Engineering Materials and Structures, B. Wilshire and R.W. Evans, eds., The Institute of Materials, London, 1993, pp. 231–44.
B. Reppich and G. Schumann:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1988, vol. A101, pp. 171–82.
J. Hammer and H. Mughrabi:Proc. 1st Eur. Conf. on Advanced Materials and Processes, H.E. Exner and V. Schumacher, eds., vol. 1,Advanced Processing and High Temperature Materials, D. Driver and H. Mughrabi, eds. DGM-Informationsgesellschaft, Oberurselials, 1990, pp. 445–50.
M. Schlegl: Diploma Thesis, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, 1991.
H. Stiele: Diploma Thesis, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, 1991.
J. Weertman:Rate Processes in Plastic Deformation of Materials, J.C.M. Li and A.K. Mukherjee, eds., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1975, pp. 315–36.
J. Rösler and E. Arzt:Acta Metall., 1990, vol. 38, pp. 671–83.
R.L. Orr, O.D. Sherby, and J.E. Dom:Trans. ASM, 1954, vol. 46, pp. 113–28.
F.R. Larson and J. Miller:Trans. ASME, 1952, vol. 74, pp. 765–75.
R.F. Singer, R.C. Benn, and S.K. Kang:Proc. Conf. Frontiers of High Temperature Materials II, IncoMAP, London, 1983, pp. 336–57.
E. Arzt:Z. Metallkd., 1984, vol. 75, pp. 206–12.
J.J. Stephens and W.D. Nix:Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 281–93.
H. Zeizinger and E. Arzt:Z. Metallkd. 1988, vol. 79, pp. 774–81.
P. Cosse, D. Coutsouradis, L. Habraken, and A. Piccinin:Z. Metallkd., 1980, vol. 71, pp. 138–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heilmaier, M., Reppich, B. Creep lifetime prediction of oxide-dispersion-strengthened nickel-base superalloys: A micromechanically based approach. Metall Mater Trans A 27, 3861–3870 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02595635
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02595635