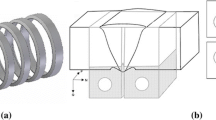
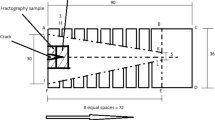
Abstract
The stress-corrosion cracking (SCC) behavior of high-strength steel weld metals, as indexed by KIscc, was examined with emphasis on the relative influences of yield strength, electrochemical potential, welding process, and weld metal composition. The weld metals were from weldments fabricated by the gas metal arc (GMA) or gas tungsten arc (GTA) process. Filler metals with four different compositions—designated 120S, 140S, AX140 and HY-130—were used. The multi-pass welding procedures and their associated thermal cycles produced very complex martensitic-bainitic type microstructures. The GTA weld metals were considerably more fine-grained and more highly tempered than the GMA weld metals. This enhanced the fracture toughness of all four of the higher strength GTA weld metals but improved the SCC properties of only two GTA weld metals—HY-130 and 140S. The effectiveness of microstructural influences on SCC behavior is correlated with the sulfur content of the weld metals assuming that hydrogen is the cause of SCC in these materials. The role of sulfur is presumed to be that of catalytic poison for the hydrogen recombination reaction which increases opportunities for nascent hydrogen absorption. The results show that the weld metals with improved SCC properties contain the lower concentrations of sulfur.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. G. Gooch:Welding J., 1974, vol. 53, no. 7, pp. 287s 98-s.
Kenichiro Yoshino and C. J. McMahon, Jr.:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 363–70.
C. L. Briant and S. K. Banerji:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 1151–55.
Robert O. Ritchie:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1131–40.
R. Viswanathan and S, J. Hudak, Jr.:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1633–3.
S. R. Novak, A. W. Loginow, H. M. Reichold, J. G. Bassett, and G. C. McKelvey: Report No. AFML-TR-78-89, U.S. Steel Corp. Research Laboratory, Monroeville, PA, July 1978.
C. A. Zanis: Private communication, David W. Taylor Naval Ship Research and Development Center, Annapolis, MD, 1979.
B. F. Brown:Materials Research and Standards, 1966, vol. 6, pp. 129–33.
J. A. Kies, H. L. Smith, H. E. Romine, and H. Bernstein: ASTM STP 381, pp. 328-56, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1965.
R. W. Judy, Jr., and R. J. Goode: NRL Report 7865, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC, Mar. 17, 1975.
Frances W. Fraser and Edward A. Metzbower: NRL Report 8370, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC, Jan. 10, 1980.
Alexander R. Troiano:Trans. ASM, 1960, vol. 52, pp. 54–80.
Anthony W. Thompson:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1980, vol. 43, pp. 41–46.
1975 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, part 10, pp. 561-58, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1975.
C. T. Fujii: NRL Report 8236, Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC, May 31, 1978.
R. M. Latanision, O. H. Gastine, and C. R. Compeau:Environment-Sensitive Fracture of Engineering Materials, pp. 48–70, TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1979.
R. M. Latanision and H. Opperhauser, Jr.:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 483–92.
Makio Iino:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 1691–98.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujii, C.T. Factors Influencing Stress-Corrosion Cracking of High-Strength Steel Weld Metals. Metall Trans A 12, 1099–1105 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02643491
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02643491