Abstract
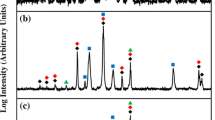
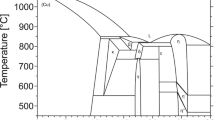
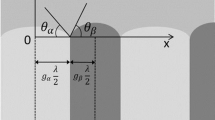
Electron beam solidification passes have been performed on a series of Ag-Cu alloys between 1 wt pct Cu and the eutectic composition (28.1 wt pct Cu) at speeds between 1.5 and 400 cm per second. At low growth rates conventional dendritic or eutectic structures are obtained. The maximum growth rate of eutectic structure is 2.5 cm per second. At high growth rates microsegregation-free single phase structures are obtained for all compositions. The velocity required to produce this structure increases with composition for dilute alloys and agrees with the theory of absolute stability of a planar liquid-solid interface with equilibrium partitioning. For alloys between 15 and 28 wt pct Cu, the velocity required to produce the microsegregation-free extended solid solution decreases with composition and is related to nonequilibrium trapping of solute at the liquid solid interface. At intermediate growth rates for alloys with 9 wt pct Cu or greater, a structure consisting of alternating bands of cellular and cell-free material is obtained. The bands form approximately parallel to the local interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Duwez, R. H. Willens, and W. Klement, Jr.:J. Appl. Phys., 1960, vol. 31, p. 1136.
P.G. Boswell and G.A. Chadwick:J. Mat. Sci., 1977, vol. 12, p. 1879.
R. Stoering and H. Conrad:Acta Metall., 1969, vol. 17, p. 933.
H. Jones:Aluminium, 1978, vol. 54, p. 274.
H. Jones:Matl. Sci. & Eng., 1969/70, vol. 5, p. 1.
P. Furrer and H. Warlimont:Z. Metallkunde, 1973, vol. 64, p. 236.
S. Kou, S.C. Hsu, and R. Mehrabian:Metall. Trans. B, 1981, vol. 12B, p. 33.
R. Kadalbal, J. Montoya-Cruz, and T. Z. Kattamis:Rapid Solidification Processing Principles and Technologies, II, R. Mehrabian, B. H. Kear, and M. Cohen, eds., Claitor’s, Baton Rouge, LA, 1980, p. 195.
B. G. Lewis, D. A. Gilbert, and P. R. Strutt:Rapid Solidification Processing Principles and Technologies, II, R.Mehrabian, B. H.Kear, and M.Cohen, eds., Claitor’s, Baton Rouge, LA, 1980, p. 221.
W. A. Elliott, F. P. Gagliano, and G. Krauss:Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, p. 2031.
M. Copley, M. Bass, E.W. Van Stryland, D.G. Beck, and O. Esquivel:Proc. III Int. Conf. Rapidly Quenched Metals, B. Cantor, ed., The Metals Society, London, 1978, vol. 1, p. 147.
D.G. Beck, S. M. Copley, and M. Bass:Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, p. 16.
D.G. Beck, S.M. Copley, and M. Bass:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, p. 1879.
W.W. Mullins and R. F. Sekerka:J. Appl. Phys., 1964, vol. 35, p. 444.
S.R. Coriell and R. F. Sekerka:Rapid Solidification Processing Principles and Technologies, II, R. Mehrabian, B.H. Kear, and M. Cohen, eds., Claitor’s, Baton Rouge, LA, 1980, pp. 35–49.
J. C. Baker and J. W. Cahn:Acta Metall., 1969, vol. 17, p. 575.
J. C. Baker and J. W. Cahn:Solidification, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1971, p. 23.
P. Baeri, G. Foti, D.M. Poate, S.V. Campisano, and A.G. Cullis:Appl. Phys. Lett., 1981, vol. 38, p. 800.
W. White, B.R. Appleton, B. Stritzker, D.M. Zehner, and S.R. Wilson:Laser and Electron Beam Solid Interactions and Materials Processing, North Holland, NY, 1981, p. 59.
J. C. Baker: Ph.D. Thesis, Chapter V, MIT, 1970. Also reported by J. W. Cahn, S. R. Coriell, and W. J. Boettinger:Laser and Electron Beam Processing of Materials, Academic Press, NY, 1980, p. 89.
M. J. Aziz:J. Appl. Phys., 1982, vol. 53, p. 1158.
K. A. Jackson, G. H. Gilmer, and H. J. Leamy:Laser and Electron Beam Processing of Materials, Academic Press, NY, 1980, p. 104.
R. F. Wood:Phys. Rev., 1982, vol. B25, p. 2786.
S.R. Coriell and R. F. Sekerka:J. Crystal Growth, 1983, vol. 61, p. 499.
see, for example, P. Löhberg and H. Müller:Z. Metallkunde, 1969, vol. 60, p. 231.
M. Hillert and B. Sundman:Acta Metall., 1977, vol. 25, p. 11.
W. J. Boettinger, S. R. Coriell, and R. F. Sekerka: Third Conference on Rapid Solidification Processing, held at NBS in December 1982, R. Mehrabian, Chairman.
J. L. Murray:Metall. Trans. A, 1984.
B. Giessen and R.H. Willens:The Use of Phase Diagrams in Ceramics, Glass, and Metal Technology, Academic Press, NY, 1970, vol. 3, p. 103.
R. J. Schaefer, W. J. Boettinger, F. S. Biancaniello, and S. R. Coriell:Lasers in Metallurgy, TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1981, p. 43.
R. K. Linde:J. Appl. Phys., 1966, vol. 37, p. 934.
B. Giessen:Bull. of Alloy Phase Dia., 1980, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 41.
. J.H. Perepezko: Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, unpublished research, 1983.
T. Yamamura and T. Ejima:J. Japanese Inst. Met., 1973, vol. 37, p. 901.
J.H. Holloman and D. Turnbull:Prog. Met. Phys., 1953, vol. 4, p. 333.
S. R. Coriell: National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC, unpublished research, 1983.
H. E. Cline and H. Lee:Acta Metall., 1970, vol. 18, p. 315.
W. J. Boettinger:Rapidly Solidified Amorphous and Crystalline Alloys, Elsevier, 1982, p. 15.
K.A. Jackson and J.D. Hunt:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 236, p. 1129.
R. Trivedi: Iowa State University, Ames, IA, unpublished research, 1983.
M.H. Burden and J.D. Hunt:J. Cryst. Growth, 1974, vol. 22, p. 109.
B.L. Jones, G. M. Weston, and R.T. Southin:J. Cryst. Growth, 1971, vol. 10, p. 313.
M.H. Burden and J.D. Hunt:J. Cryst. Growth, 1974, vol. 22, p. 328.
M. J. Aziz: Third Conference on Rapid Solidification Processing held at National Bureau of Standards in December 1982, R. Mehrabian, Chairman; alsoAppl. Phys. Lett., 1983, vol. 43, p. 552.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
On leave at the Center for Materials Research, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD 21218.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boettinger, W.J., Shechtman, D., Schaefer, R.J. et al. The Effect of Rapid Solidification Velocity on the Microstructure of Ag-Cu Alloys. Metall Trans A 15, 55–66 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02644387
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02644387